LEAF comes across as such a well intentioned and benevolent group. However, dig a little deeper, and the problems start to show through.
1. Trafficking, Smuggling, Child Exploitation
While abortion is trumpeted as a “human right” in Western societies, the obvious questions have to be asked: Why is it a human right? Who are these groups benefiting financially, and why are so they so fiercely against free speech? Will the organs be trafficked afterwards?
2. Important Links
(1) https://www.ic.gc.ca/app/scr/cc/CorporationsCanada/fdrlCrpSrch.html
(2) https://www.canada.ca/en/status-women/news/2019/07/government-of-canada-invests-in-projects-to-improve-gender-equality-in-the-justice-system.html
(3) https://www.leaf.ca/legal/reproductive-justice/
(4) https://www.leaf.ca/leaf-calls-on-government-of-canada-to-fund-abortion-services-abroad/
(5) https://www.parl.ca/Content/Bills/421/Private/C-225/C-225_1/C-225_1.PDF
(6) https://www.leaf.ca/leaf-urges-toronto-public-library-to-reconsider-event-featuring-meghan-murphy/
(6) https://www.leaf.ca/leaf-and-the-asper-centre-welcome-the-ontario-court-of-appeals-decision-in-r-v-sharma/
(7) https://ca.news.yahoo.com/ontario-sex-ed-curriculum-consent-003452043.html
(8) https://www.rcmp-grc.gc.ca/en/gazette/illegal-organ-trade
(9) https://parl.ca/DocumentViewer/en/43-1/bill/S-204/first-reading
unodc.organ.and.human.trafficking
Smuggling_of_Migrants_A_Global_Review
3. Two Federal Non-Profit Corporations
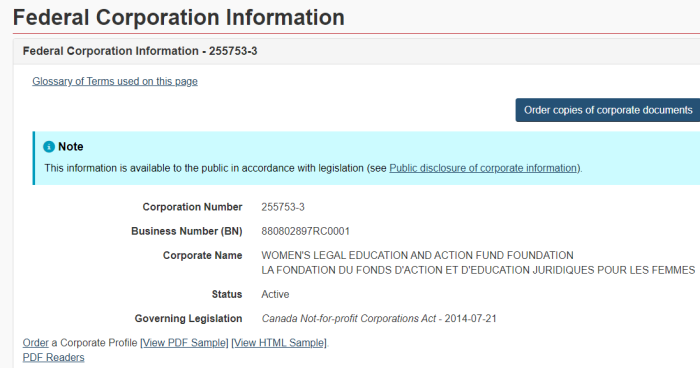
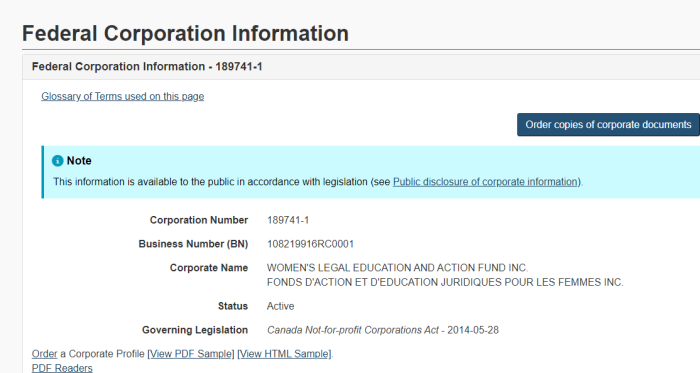
[1] WOMEN’S LEGAL EDUCATION AND ACTION FUND FOUNDATION
Corporation Number: 255753-3
Business Number (BN): 880802897RC0001
[2] WOMEN’S LEGAL EDUCATION AND ACTION FUND INC.
Corporation Number: 189741-1
Business Number (BN): 108219916RC0001
A point of clarification: there are actually 2 separate Federal corporations registered with the Government. They have different (though similar) names, and different corporate and business numbers. They also have different addresses in Toronto.
It’s worth pointing out that LEAF has branches across Canada and the United States. They operate with the same basic philosophy.
4. Mental Gymnastics In LEAF Agenda
The Women’s Legal Education and Action Fund (LEAF) works to advance the substantive equality rights of women and girls through litigation, law reform, and public education. Since 1985, we have intervened in landmark cases that have advanced equality in Canada—helping to prevent violence, eliminate discrimination in the workplace, provide better maternity benefits, ensure a right to pay equity, and allow access to reproductive freedoms. For more information, please visit www.leaf.ca.
LEAF claims to be committed to a variety of good causes. However, their logic seems messed up. While they want better childcare benefits, it’s okay to kill the child up to the point of birth. And even when the mother DOES kill the child after birth, the penalties should be reduced.
And by what stretch of logic is murdering children compatible with preventing violence?
5. Canadian Taxpayers Are Financing This

Women’s Legal Education and Action Fund (LEAF) is receiving $880,000 to develop a modern, intersectional, and feminist strategic litigation plan that will enable feminists and gender equality advocates to address systemic barriers to gender equality and eliminate gender discrimination.
Canadian taxpayers will be footing the bill for some $880,000, for this 2019 grant. This is to develop a litigation plan to for what they refer to as fighting for gender equality. It’s unclear from the announcement how much (if any) will end up being diverted into actual court challenges.
6. LEAF’s Take On “Reproductive Justice”
1987 Baby R.
LEAF argued that children not yet born shouldn’t be allowed to be taken by government officials. Custody should be for people already alive.
leaf.intervenor.factum.1988-baby-r
1989 Borowski v. Canada (Attorney General)
LEAF argued that the right to life should apply to the mother (and not to the child). The criminal code and charter shouldn’t apply to the unborn baby.
leaf.intervenor.factum.1989-borowski
1989 Daigle v. Tremblay
LEAF argued that biological fathers should have no say over whether the child lives or dies, and that otherwise, it is an attempt to control the mother using the child as a proxy.
leaf.intervenor.factum.1989-daigle
1991 R. v. Sullivan
LEAF argued that 2 midwives convicted of criminal negligence causing death (for the death of the baby) should have that charge thrown out, since the baby isn’t actually a person.
leaf.intervenor.factum.1991-sullivan
1996 R v. Lewis
LEAF argued in favour maintaining “bubble zones”. These effectively were areas where abortion protesting would be banned. Free speech is fine, just not in certain areas.
leaf.intervenor.factum.1996-lewis
1997 Winnipeg Child and Family Services v. G. (D.F.)
LEAF argued against the the state’s ability to detain a pregnant women, who was harming her own child. In this case, the mother was sniffing glue.
leaf.intervenor.factum.1997-winnipeg-child-family
2003 R. v. Demers
LEAF argued again against the rights of people who were protesting abortion, although the arguments differed somewhat.
leaf.intervenor.factum.2003-demers
2006 Watson v. R; Spratt v. R
LEAF once again arguing that “bubble zones” need to be maintained, and that freedom of speech needs to be curtailed in order to ensure smooth access to abortion.
leaf.intervenor.factum.2008-R-V-WATSON-SPRATT-Factum
2016 R v. MB
LEAF argued that a woman who killed her newborn child should not face the wrath of the criminal justice system, and should be cut a break
leaf.intervenor.factum.2016.r.v.mb.infanticide
LEAF is Pro-Life?
Yeah, not really seeing that here.
LEAF is Anti-Life
- 1987 Baby R
- 1989 Borowski v. Canada (Attorney General)
- 1989 Daigle v. Tremblay
- 1991 R. v. Sullivan
- 1996 R v. Lewis
- 1997 Winnipeg Child and Family Services v. G. (D.F.)
- 2003 R. v. Demers
- 2006 Watson v. R; Spratt v. R
- 2016 R v. MB
Keep in mind, these are not cases that impact LEAF directly. Instead, they go searching for cases to act as an intervenor (or interested party). In short, they insert themselves into OTHER cases in order to get the outcomes they want.
An astute person will realize that LEAF is fundamentally anti-free speech. Among the challenges they brag about is getting free speech restricted in order to facilitate abortion access.
This list is hardly exhaustive, but should give a pretty good idea of the things they stand against: rights for unborn children.
7. LEAF Wants Foreign Abortions Funded Too
As organizations who are deeply committed to the rights of women and girls, we are very concerned by recent statements regarding the Government of Canada’s refusal to fund safe abortion services abroad, including in cases of rape and for young women and girls in forced marriages. This approach represents a serious setback on women’s human rights and the health and wellbeing of survivors of sexual violence and girls in early and forced marriages.
We call on the Canadian government to:
1. Include access to safe abortion services as part of the package of sexual and reproductive health services funded by Canadian international cooperation initiatives;
2. Support effective strategies to ensure that survivors of sexual violence and young women and girls in early and forced marriage have access to a comprehensive package of sexual and reproductive health services, including safe abortion; and
3. Produce clear policy for Canada’s international initiatives that adopts a human rights-based approach to sexual and reproductive health.
What about the babies being killed? Don’t their human rights matter? Oh, that’s right, these groups don’t consider babies to be people.
Sincerely,
The undersigned organizations:
.
-Abortion Rights Coalition of Canada (ARCC) / Coalition pour le droit à l’avortement au Canada (CDAC)
-Action Canada for Population and Development / Action Canada pour la population et le développement
-Amnesty International Canada (English)
-Amnistie International Canada (Francophone)
-Canadian Council of Muslim Women
-Canadian Federation for Sexual Health
-Canadian Federation of University Women
-Canadian Women’s Foundation
-Choice in Health Clinic
-Clinique des femmes de l’Outaouais
-Fédération du Québec pour le planning des naissances (FQPN)
-Kensington Clinic
-Institute for International Women’s Rights – Manitoba
-Inter Pares
-MATCH International Women’s Fund
-Oxfam Canada
-Oxfam Quebec
–Planned Parenthood Ottawa
-West Coast LEAF
-Women’s Health Clinic, Winnipeg
-Women’s Legal Education and Action Fund / Fonds d’action et d’education juridiques pour les femmes
-YWCA Canada
(also addressed to)
-CC The Right Honourable Stephen Harper, P.C.
Prime Minister of Canada
.
-CC Hélène Laverdière, NPD, MP
NDP International Development Critic
.
-CC Kirsty Duncan, Liberal, MP
Liberal International Development and Status of Women Critic
.
-CC Paul Dewar, NDP, MP
NDP Foreign Affairs Critic
.
-CC Marc Garneau, Liberal, MP
Liberal Foreign Affairs Critic
.
-CC Niki Ashton, NDP, MP
NDP Status of Women Critic
Not content with killing Canadian children, this coalition demands that the Canadian Government finance foreign abortions as well. That is correct. Use taxpayer money to pay to kill children in other countries.
It’s not at all a surprise to see a Planned Parenthood Ottawa has joined this group in making the call. After all, Planned Parenthood is involved in trafficking organs.
It never seems to dawn on these people that in many parts of the world, girls and women are viewed as far less than boys and men. This leads often to SEX SELECTIVE abortions. Is it really a feminist idea to deliberately target female babies?
8. No protection For Unborn Victims Of Crime

Considering the 1989 Boroski intervention (see list of cases above), it’s no surprise that LEAF, and other feminist groups oppose Bill C-225. This would have made it an additional crime to injury or kill a fetus while in the commission of another offense.
9. LEAF Forcing Abortion/Euth On Doctors
There was a 2019 decision from the Ontario Court of Appeals. It mandated that doctors either had to perform abortions and/or euthanasia, or provide a referral to someone who would. LEAF was one of the groups pushing it. They had no standing, other than to push their own pro-death views on others.
10. LEAF Wants Gender Ideology Critic Banned
The Women’s Legal Education and Action Fund (LEAF) is troubled by the decision of the Toronto Public Library (the “TPL”) to rent one of its branch spaces to a group hosting an event with Meghan Murphy, who has a track record for denying the existence and rights of trans women. We are particularly concerned with Murphy’s history of publicly opposing efforts to codify the rights of trans people, specifically trans women, including her vocal opposition to federal human rights legislation prohibiting discrimination on the basis of gender identity and gender expression.
LEAF was founded in 1985 with a mandate to advance substantive equality for women and girls in Canada. LEAF has long been committed to a vision of feminism that is inclusive of all, regardless of sex, gender identity or gender expression. LEAF’s advocacy is and remains focused on challenging sex and gender discrimination that results in inequality for self-identified women and girls. The long-term success of this mission demands that LEAF work towards challenging and dismantling patriarchy, in all its forms.
LEAF believes freedom of speech plays an important role in strengthening and upholding substantive equality. Holding space for respectful dialogue among diverse viewpoints is essential to this work. However, LEAF has long maintained that freedom of speech is not absolute. Like all rights enjoyed by Canadians, freedom of speech must be balanced with other fundamental rights and freedoms, especially equality. Speech that perpetuates harmful stereotypes only serves to further marginalize and exclude an already vulnerable population and does not merit protection.
In a case of “eating your own“, LEAF tried to get Meghan Murphy dis-invited from a Toronto talk on trans-activism. And Murphy is about as hardcore feminist as they come. According to her biography:
- Bachelor’s degree in women’s studies
- Master’s degree in women’s studies
- Wrote for feminist publications
- Believes in the wage-gap nonsense
- Believes women are oppressed
- Pro-abortion
- Pro-gay agenda
Still, that wasn’t enough to prevent feminist and “women’s rights” groups life LEAF from turning against her.
For a group that “claims” to support women, one has to ask why LEAF is trying to take away the rights of a woman (Murphy), specifically her free speech.
Murphy does address legitimate issues that trans-activists are involved with, (such as sports, pronounc, etc…), and how they are conflicting head on with the rights of women. It seems that the committment to women’s rights can be tossed aside in favour of this extremely small group.
11. LEAF: Reduce Sentence For Drug Mule
Somehow, LEAF believes that arguing against a mandatory minimum sentence for a person convicted of smuggling 2kg of cocaine (worth some $200,000), is a woman’s rights issue. What about the women who are harmed as a result of the drug trade? Don’t they matter?
While not directly related to the abortion/organs issue, it’s still bizarre to see how this group feels entitled to meddle in other people’s cases.
12. LEAF Supports ON Sex-Ed Agenda
This week’s move is getting a thumbs-up from a national women’s legal organization that teaches older students about consent.
“It’s extremely important for everyone to understand what their rights and responsibilities are under the law,” said Kim Stanton, legal director of the Women’s Legal Education and Action Fund, which runs workshops for high school and university students. “Students need to know what’s OK and what’s not.
LEAF supports Ontario’s largely inappropriate sex-ed ciricculum.
13. Honourable Mention: Tanya Granic Allen
Candid honesty is extremely rare in political circles. However, this critique of LEAF and Leslyn Lewis, is a true gem. Also see the video. Well worth the 10 minutes or so.
Now, what is the result of anti-life laws becoming normal?
14. RCMP & Illegal Organ Trade
There are far more people in the world in need of a new organ than there are organs available. Like in any market where a dollar can be made because demand far outweighs supply, people can turn to the black market to find what they need. When a person’s life is on the line, the will to survive may override morals. The following facts depict the seedy underbelly of organ trafficking.
- The United Nations Global Initiative to Fight Human Trafficking (UN GIFT) says the organ trade occurs in three broad categories: traffickers who force or deceive victims to give up an organ, those who sell their organs out of financial desperation, often only receiving a fraction of the profit or are cheated out of the money altogether and victims who are duped into believing they need an operation and the organ is removed without the victim’s knowledge.
- Organ trafficking is considered an organized crime with a host of offenders, including the recruiters who identify the vulnerable person, the transporter, the staff of the hospital or clinic and other medical centres, the medical professionals themselves who perform the surgery, the middleman and contractors, the buyers and the banks that store the organs.
- And according to the UN GIFT, it’s a fact that the entire ring is rarely exposed.
- A World Health Assembly resolution adopted in 2004 urges Member States to “take measures to protect the poorest and vulnerable groups from ‘transplant tourism’ and the sale of tissues’ and organs.
- “Transplant tourism” is the most common way to trade organs across national borders. These recipients travel abroad to undergo organ transplants (WHO Bulletin). There are websites that offer all-inclusive transplant packages, like a kidney transplant that ranges from US$70,000 to US$160,000.
- There’s no law in Canada banning Canadians from taking part in transplant tourism — travelling abroad and purchasing organs for transplantation and returning home to Canada.
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), one out of 10 organ transplants involves a trafficked human organ, which amounts to about 10,000 a year.
- While kidneys are the most commonly traded organ, hearts, livers, lungs, pancreases, corneas and human tissue are also illegally traded.
- In a recent report, Global Financial Integrity says that illegal organ trade is on the rise, and it estimates that it generates profits between $600 million and $1.2 billion per year with a span over many countries.
- In Iran, the only country where organ trade is legal, organ sales are closely monitored and the practice has eliminated the wait list for kidney transplants and has provided an increase in post-mortem organ donations, which aren’t remunerated in Iran.
- A Harvard College study says donors come from impoverished nations, like countries in South America, Asia and Africa, while recipients are from countries like Canada, the United States, Australia, the United Kingdom, Israel and Japan.
- According to research out of Michigan State University that looked at the black market for human organs in Bangladesh, the average quoted rate for a kidney was US$1,400 but has dropped because of the abundant supply.
- In Bangladesh, the trade is propelled by poverty, where 78 per cent of residents live on less than $2 a day. They give their organs to pay off loans and take care of their families. If they received the money at all, it disappears quickly and they are often left sick and unable to work after the operations.
- The Voluntary Health Association of India estimates about 2,000 Indians sell a kidney every year.
- Given that the organ trade is often a transnational crime, international law enforcers must co-operate across borders to address the crimes.
This comes from a 2014 post on the RCMP’s website. Despite being several years old, it has a lot of useful information.
Now, it’s true that there are only so many people dying with usable organs. It’s also true that abducting and/or murdering people for their organs is risky, and can only be done so often. However, that isn’t really the case with aborted babies, as they typically have healthy organs. Sure, they are smaller, but still usable at some point.
Ever wonder why the recent push to have later and later abortions? It’s because the organs of a 35 week fetus are much more developed than those of a 20 week fetus.
15. UNODC On Organ, Human Trafficking

III. Guidance for response
.
A. Definitions
6. Article 3 (a) defines trafficking in persons:
“Trafficking in persons” shall mean the recruitment, transportation, transfer, harbouring or receipt of persons, by means of the threat or use of force or other forms of coercion, of abduction, of fraud, of deception, of the abuse of power or of a position of vulnerability or of the giving or receiving of payments or benefits to achieve the consent of a person having control over another person, for the purpose of exploitation. Exploitation shall include, at a minimum, the exploitation of the prostitution of others or other forms of sexual exploitation, forced labour or services, slavery or practices similar to slavery, servitude or the removal of organs.”
unodc.organ.and.human.trafficking
It’s illegal to kidnap, force, or otherwise coerce people into giving up organs. However, aborted babies (even very late term) are just considered property with no legal rights of their own. At least, this is the case in Canada.
This UNODC paper is from 2011. However, its information is still very relevant today.
Whether this is intentional or not, it is one of the consequences of the actions of groups like LEAF. Removing any sort of legal protection from the unborn creates legal carte blanche to harvest and sell their organs at will.
16. UNODC: Illegal Entry Facilitates T&S

Smuggling_of_Migrants_A_Global_Review
This was addressed in Part 9, the connection between illegal immigration, and the trafficking and smuggling of migrants. However, in the context of organ harvesting, it does put the issue in a whole new light.
17. Bill S-204, Criminal Code Change
Senate Bill S-204 would make it criminal offence to go abroad for the purposes of obtaining organs where consent was not given. While promising, however, it hasn’t gone anywhere since being introduced. Now, would these penalties apply to the trafficked organs of aborted fetuses, or only to trafficked organs of people living for some period of time?
18. Abortion Fuels Organ Trafficking
Now, to tie all of this together: the abortion industry helps fuel the organ trafficking industry.
It’s a straightforward idea: in order to traffic organs in a large scale, there has to be a large, constant supply available.
The abortion industry (and their advocates) ensure this by waging lawfare. They fight in court to keep stripping away any protections unborn children may have. They also change the law to allow for later and later abortions, and thus, more developed organs. Advocates will gaslight others who make attempts to limit this, or enshrine rights for the children. Child rights must be removed in favour of women’s rights.
Is LEAF involved with trafficking organs? They don’t appear to be, but their frequent court efforts ensure that this will continue. Whether intentional of not, groups like LEAF are part of the problem.
And to be clear, LEAF openly supports restricting free speech, under the guise of protecting abortion and gender rights. Of course, open discourse on these subjects would immediately weaken their arguments.
19. Defending Non-Disclosure Of HIV
Note: this was added after the article was originally published. LEAF argued in a Parliamentary hearing that failure to disclose HIV status should be removed from sexual assault laws, and in some cases, decriminalized altogether. Way to protect women.
Hear the audio clip starting at 8:59:30.
https://www.ourcommons.ca/Committees/en/WitnessMeetings?witnessId=248439
20. LEAF Is Anti-Free Speech
Free Speech Submission womens LEAF
https://www.ourcommons.ca/Committees/en/JUST/StudyActivity?studyActivityId=10543157
In 2019, LEAF actually made submissions in the “online hate” study, and took the position AGAINST free speech. Again, this was added after the original article was released.
Like this:
Like Loading...