At 5:10 in this video, Trudeau says that Canada will be giving 50% of the doses of vaccine it pays for to the 3rd World. Motion M-132 really was about financing drugs for the entire world.
1. Canadian Politicians Connected To WEF
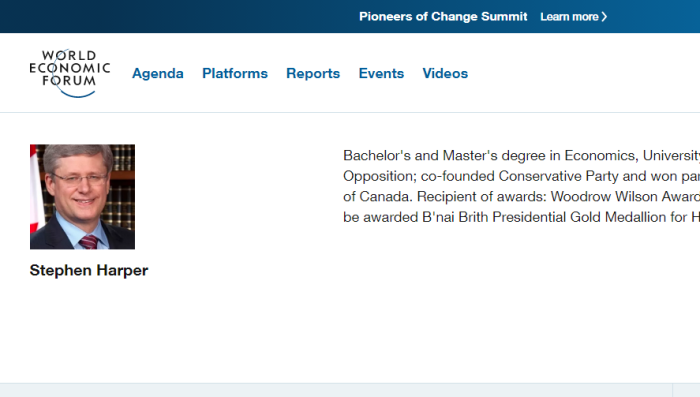
Bachelor’s and Master’s degree in Economics, University of Calgary. 2002, Leader of the Opposition; co-founded Conservative Party and won party leadership; 2006, Prime Minister of Canada. Recipient of awards: Woodrow Wilson Award for Public Service; first Canadian to be awarded B’nai Brith Presidential Gold Medallion for Humanitarianism (2008).
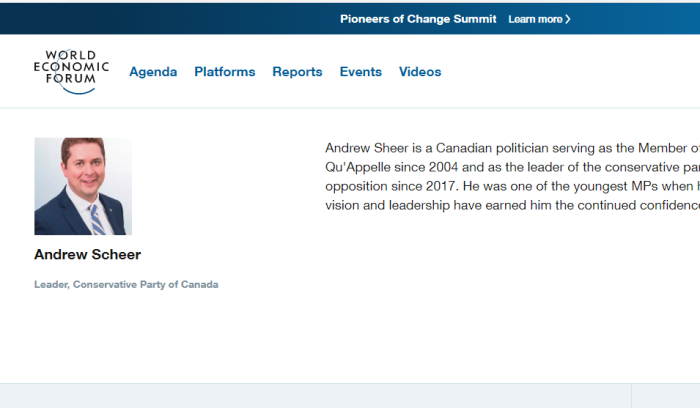
Andrew Sheer is a Canadian politician serving as the Member of Parliament for Regina-Qu’Appelle since 2004 and as the leader of the conservative party and leader of the official opposition since 2017. He was one of the youngest MPs when he was first elected and his vision and leadership have earned him the continued confidence to be re-elected.

Build Back Stronger
The Liberals want to “build back better.” Conservatives will “build back stronger.”
We are facing the greatest economic crisis of our lifetime.
Canada’s Conservatives led by Erin O’Toole will bring back certainty and stability.
The Liberal agenda is to launch a risky experiment with Canada’s economy.
Justin Trudeau says, “We are all in this together.” But, under the Liberals, Canada is more divided than ever before.
With the Liberals, it’s the haves over the have-nots.
It’s Bay Street over Main Street.
It’s those with a salary, benefits, and a pension over those without.
It’s those with Liberal connections over the outsiders who have to play by the rules.
Instead, Erin O’Toole’s Conservatives will fight for you and your family, and the countless Canadians left behind by the Trudeau Liberal government.
.
Sign below if you want to build back stronger!
Canadian Member of Parliament. Has served in Cabinet as a Minister of State in the government of Stephen Harper. Has also managed the sponsored research portfolio for one of Canada’s top research intensive universities. Has over a decade of experience in managing and commercializing intellectual property, and in management consulting. Named one of Canada’s Top 100 Most Powerful Women, Women’s Executive Network. Twice named as Parliamentarian of the Year – Rising Star, Maclean’s Magazine.
Journalist and author. Began career as a Ukraine-based stringer; went on to hold senior positions at the Globe and Mail, the Financial Times and Thomson Reuters. First elected as a Member of Parliament in November 2013, was appointed International Trade Minister in November 2015, Minister of Foreign Affairs in January 2017 and Deputy Prime Minister and Minister for Intergovernmental Affairs in November 2019. Has written two books: “Sale of the Century” (2000) and “Plutocrats” (2012). In 2018, recognised as Foreign Policy’s Diplomat of the Year and awarded the Eric M. Warburg Award by Atlantik-Brücke. Speaks Russian, Ukrainian, Italian, French and English. Member of the Board of Trustees of the World Economic Forum.
Bachelor’s in Administrative Studies, York University, MBA, University of Windsor. Certified Management Accountant. Formerly: several years with the Ford Motor Company of Canada; Privy Councillor and Parliamentary Secretary to Prime Minister Paul Martin; Critic for Public Works and Government Services, the Treasury Board, International Trade, Natural Resources, and Small Business and Tourism. Member of Parliament for Mississauga-Malton; November 2015, appointed Minister of Innovation, Science and Economic Development. Former: Adjunct Lecturer, Master of Public Service programme, University of Waterloo; Distinguished Visiting Professor, Ted Rogers School of Management, Ryerson University. Former director of social and cultural organizations within the non-profit sector. Recipient of numerous awards recognizing work in promoting diversity in communities.

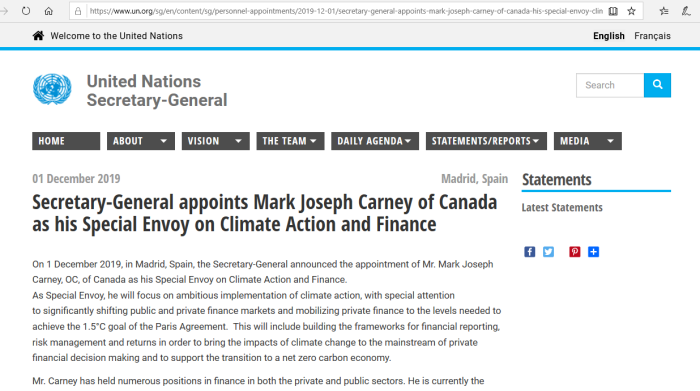
1988, Bachelor’s in Economics, Harvard University; 1993, Master’s in Economics and 1995, Doctorate in Economics, Oxford University. Thirteen years with Goldman Sachs in London, Tokyo, New York, Toronto. 2003-04, Deputy Governor, Bank of Canada. 2004-08, Senior Associate Deputy Minister of Finance. 2008-13, Governor of the Bank of Canada. Since July 2013, Governor of the Bank of England. Chairman, Financial Stability Board (FSB); Member: Board, Bank for International Settlements and Chairman; Group of Thirty; Board of Trustees, World Economic Forum.
Carney isn’t officially a politician, but he may as well be, considering the many roles he plays.
https://www.weforum.org/people/stephen-harper
https://www.weforum.org/people/andrew-scheer
https://www.conservative.ca/cpc/build-back-stronger/
https://www.weforum.org/people/michelle-rempel
https://www.weforum.org/people/chrystia-freeland
https://weforum.org/people/navdeep-bains
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/authors/mark-carney
https://www.weforum.org/people/jagmeet-singh
2. More On The International Banking Cartel
For more on the banking cartel, check this page. The Canadian Government, like so many others, has sold out the independence and sovereignty of its monetary system to foreign interests. BIS, like its central banks, exceed their agenda and try to influence other social agendas. See who is really controlling things, and the common lies that politicians and media figures tell. Now, the bankers work with the climate mafia and pandemic pushers to promote their mutual goals of control and debt slavery.
3. Debunking The Climate Change Scam
The entire climate change industry, (and yes, it is an industry) is a hoax perpetrated by the people in power, run by international bankers. Plenty has also been covered on the climate scam, the propaganda machine in action, and some of the court documents in Canada. Carbon taxes are just a small part of the picture, and conservatives are intentionally sabotaging their court cases.
4. Other Articles On CV “Planned-emic”
The rest of the series is here. Many lies, lobbying, conflicts of interest, and various globalist agendas operating behind the scenes, obscuring the “Great Reset“. The Gates Foundation finances: the WHO, the US CDC, GAVI, ID2020, John Hopkins University, Imperial College London, the Pirbright Institute, the BBC, and individual pharmaceutical companies. Also: there is little to no science behind what our officials are doing; they promote degenerate behaviour; the Australian Department of Health admits the PCR tests don’t work; the US CDC admits testing is heavily flawed; and The International Health Regulations are legally binding. See here, here, and here. The media is paid off, and our democracy is thoroughly compromised, as shown: here, here, here, and here.
5. Great Reset To Abolish Private Property
A large part of the Great Reset is abolishing real private property rights, at least for the average person. The Reset has been openly discussed for a long time, and they aren’t even bothering to hide their agenda anymore.
Beyond physical property, this refers to money as well. Overhauling the monetary system, and removing physical cash means much less (or none), control for people over their own wealth.
The World Economic Forum (and its participants), want people to view property not as theirs, but as the community’s. This is Marxism.
6. “Stakeholder Capitalism” Being Pushed
The concept of stakeholder capitalism has been gaining traction against the prevailing shareholder-primacy model of profit maximization. As the World Economic Forum’s founder, Klaus Schwab, asked in a recent editorial: “What kind of capitalism do we want”?
Profits are not the sole purpose of a business. Let us remind ourselves that corporations exist to solve problems and provide services. If they are successful at doing this, shareholder long-term returns can increase, as society in general is better served.
The debate regarding the role of stakeholders within a firm is, primarily, a governance debate. As in most challenges that require robust leadership to change the way we live, work and interact, transformation starts from the top. Corporate governance sits at the heart of this – and for this reason, the World Economic Forum has recently published a framework structured around seven pillars:
These people are communists, but want to make it less obvious. Consequently, they refer to property owners as “shareholders”, and the public at large as “stakeholders”. The focus is on converting from a shareholder economy to a stakeholder one.
7. Great Reset & Digital Cooperation
A lot of what is talked about is access to the internet for more and more of the population. While this sounds fine, there are areas that are quite alarming. These include the ever ambiguous “trust and safety” provisions, laid out in the Digital Cooperation Roadmap.
Terrorist groups and violent extremists have exploited the Internet and social media to cause harm in both the digital and physical worlds. Cyberattacks and disinformation campaigns targeting election infrastructure, political parties and politicians are undermining political participation, as well as the legitimacy of essential institutions, while sowing discontent and mistrust. States and non-State actors are rapidly increasing their cyber capabilities and developing increasingly sophisticated cyber arsenals. Nevertheless, close to half of all countries in the world do not have a Computer Emergency Response Team, which would give them the organizational and technological capacity to respond to cyberthreats.
Over the past few years, important efforts have been under way to address the rising threats to the online world. Encouraging voluntary efforts have been seen, including the Paris Call for Trust and Security in Cyberspace, the Global Forum on Cyber Expertise, the Global Commission on the Stability of Cyberspace and the Contract for the Web, many of which are multi-stakeholder, as well as initiatives on specific issues, such as the Christchurch Call to Action to address terrorist and violent extremist narratives. The initiatives have helped to bring about important progress for multi-stakeholder engagement. However, these efforts are not yet universal, and their reach, though broad in some cases, does not yet cover large swathes of the world.
Of course, everyone supports free speech. However, there needs to be some global regulations, such as digital cooperation, to manage it all.
Along with the dilution of free speech, one can expect privacy to be eroded as well. After all, you can’t hunt down people to cut off their freedom if you don’t know who they are.
8. WEF Great Reset & Digital Identity
At the World Economic Forum’s Annual Meeting 2018 in Davos, a diverse group of public and private stakeholders committed to shared cooperation on advancing good, user-centric digital identities. The Platform for Good Digital Identity seeks to advance global activities towards digital identities that are collaborative and put the user interest at the center: e.g. they are fit for purpose, inclusive, useful, secure, and offers choice to individuals. It will do so by advancing the Identity Coalitions Network: the learning and action network of organizations that implement Good ID solutions that are human centric and collaborative, by:
.
– Mapping digital identity coalitions advancing digital identity
.
– Encouraging shared learnings and new coalitions through a global action network
.
– Focusing on practitioners implementing user-centric use cases collaboratively: e.g. e-KYC, payments, health credentials, safe work, safe mobility, etc.
.
– Creating a digital identity implementation guidance for current and future coalitions
Well, the digital ID system will make it easier to eliminate cash, since everyone will be hooked into the financial system electronically. No word on people being microchipped, but that will probably come up later.
The other benefit (from their perspective), is that it becomes much easier to erase and financially cripple dissidents if they are completely dependent on the electronic systems.
9. Central Bankers Support Great Reset
Taking place from 16-20 Nov, the Pioneers of Change Summit is happening as the news is full of optimistic reports about vaccines for COVID-19. If there is light at the end of the tunnel, what needs to happen next to get economies back on their feet and make the transformations needed to cope with future pandemics and climate change – and to make the benefits of scientific advances available to all?
Christine Lagarde, head of the ECB, (European Central Bank), appeared on the Pioneers of Change podcast.
10. Central Banks Pushing Digital Currency
The decline of cash use in western economies has accelerated due to COVID-19. Meanwhile, central bank digital currencies are emerging, potentially upending the existing global economic hierarchy.
Lockdowns limit physical interactions and naturally reduce physical cash use. But there also credible concerns that paper money can transmit the virus. Research has shown that the average European banknote plays host to around 26,000 colonies of bacteria. The human influenza virus can survive on a banknote for up to 17 days; with one-dollar and five-dollar bills changing hands more than 100 times per year on average, the risk during a global pandemic is considerable.
Who then can blame the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) when it announced in February that it would be destroying cash collected in high-risk environments, such as public transport, markets or in hospitals?
China is not alone. Deutsche Bank Research has tracked almost 20 digital currency projects led by central banks across all regions globally. Meanwhile, the private banking sector has also launched multiple initiatives, such as the R3 consortium, or in India, the Blockchain Infrastructure Company.
Using the “pandemic” to convert to cashless system had been decried for a long time as a conspiracy theory. Now, it is quite openly admitted, but advocates just put a different spin on it.
11. Central Banks Support Climate Hoax
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2020/02/fossil-fuel-monetary-policy-economics-reassessment/
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2015/01/financial-policymakers-climate-change/
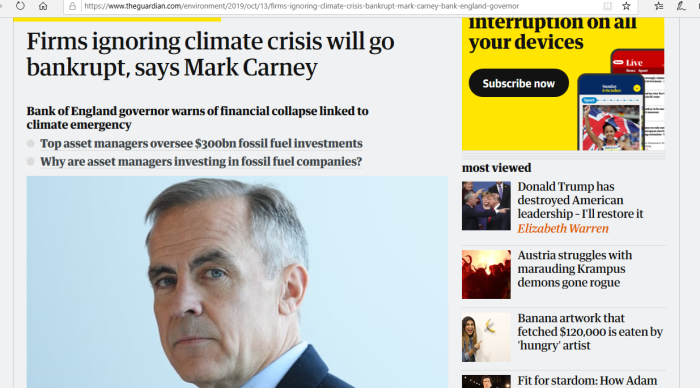
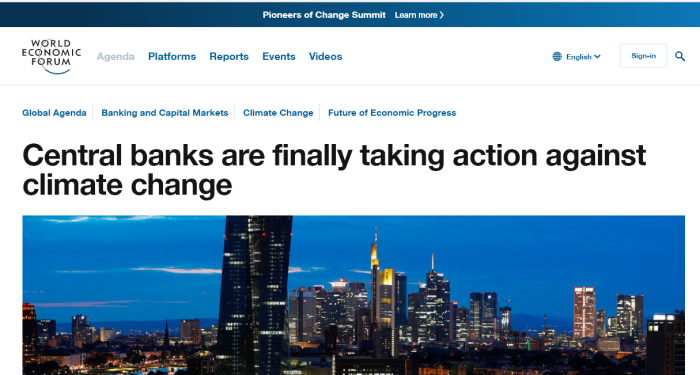
In a 2015 speech, Mark Carney, the outgoing governor of the Bank of England, sparked a debate about whether monetary policymakers should look beyond the horizon of the business and credit cycles to ensure financial stability in light of the risks posed by climate change. More recently, European Central Bank President Christine Lagarde has said that she wants the ECB to tackle climate change, in addition to its traditional price-stability remit.
The climate threats to financial stability that central bankers worry about could arise not only from increasingly frequent and severe natural disasters, but also from the shift away from fossil fuels as a source of energy. That transition ultimately would turn reserves of oil, natural gas, and coal into stranded assets, jeopardizing the financial health of corporations, insurers, and other financial institutions that are exposed to fossil fuels.
The overall exposure of advanced economies such as the United Kingdom or those of the European Union to fossil fuels may appear to be relatively small. Nonetheless, we should not underestimate the systemic risk posed by stranded assets – after all, the 2008 global financial crisis was triggered by developments in the relatively small subprime mortgage market in the United States. And, for fossil-fuel exporters, stranded-asset risks are undeniably larger. The collapse in oil prices that started in June 2014 provided a recent stark reminder of the risks posed by excessive dependence on fossil fuels.
In addition, central banks’ response to the risk of stranded assets may influence how fossil-fuel exporters invest their wealth. Many oil exporters have accumulated vast financial assets. These countries’ strategic allocation of such assets is all the more important given the mounting risks to their main source of wealth. By looking beyond the business-cycle horizon, central banks can play a critical role in facilitating these countries’ investments in non-fossil-fuel assets.
In the face of the challenge posed by climate change, the focus of monetary policy often seems very short term. Central bankers must break this “curse of horizons” and take decisive steps to address fossil-fuel-related risks. They need to reflect on and communicate the existential threat of stranded reserves and capital, advocate the adoption of appropriate structural policies, pursue a suitable interest-rate policy, and provide supportive financial policies to encourage both economic diversification and changes in strategic asset allocation. Combating climate change while maintaining global financial stability requires nothing less.
A question has to be asked here: have the bankers simply infiltrated and hijacked the environment movement? Or have they always played a role, even if behind the scenes?
Instead of simply ripping off the public under the guise of fiscal policy, now it’s done under the pretense of stopping climate change.
12. WEF Interested In Gun Control
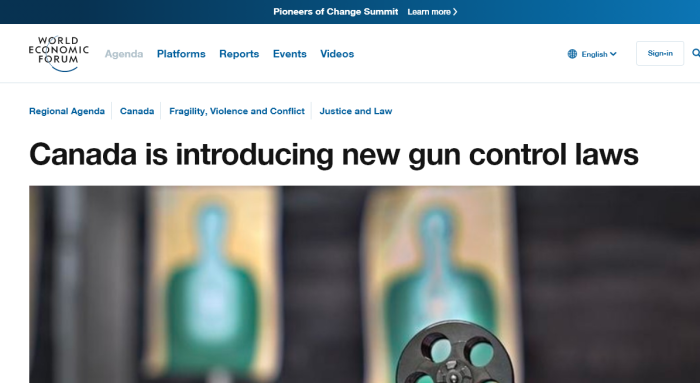
Canada’s Liberal government unveiled proposals on Tuesday to tighten already tough gun control laws to address a spike in crimes involving firearms, including a deadly attack on a mosque last year.
The measures include enhanced background checks on people seeking to buy firearms, especially those with a history of violence. They also would oblige retailers to maintain adequate records of inventories and sales.
The World Economic Forum took notice of Bill C-71, introduced in 2018 to create a backdoor long gun registry, and to make it harder to own guns. In fact, WEF publishes many articles on the topic of guns, and gun control.
13. WEF’s Predicted Dystopian Paradise
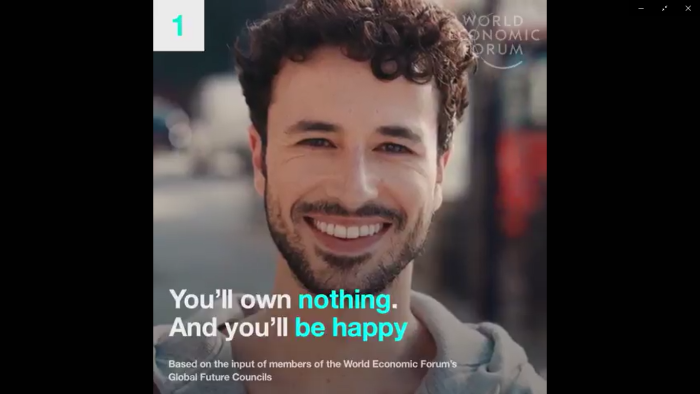
You’ll own nothing, and you’ll be happy.
Can’t really top that.
This has nothing to do with a virus. It is, and has always been, about implementing much larger social changes. Everything in the mainstream media is a lie.
Like this:
Like Loading...