With the end of this so-called “pandemic” in Canada, expect the agenda to move ahead. There were increases in every category in 2021 (compared to 2020). Expect this to get worse.
1. Mass LEGAL Immigration In Canada
Despite what many think, LEGAL immigration into Canada is actually a much larger threat than illegal aliens, given the true scale of the replacement that is happening. What was founded as a European (British) colony is becoming unrecognizable due to forced demographic changes. There are also social, economic, environmental and voting changes to consider. See this Canadian series, and the UN programs for more detail. Politicians, the media, and so-called “experts” have no interest in coming clean on this.
CLICK HERE, for UN Genocide Prevention/Punishment Convention.
CLICK HERE, for Barcelona Declaration & Kalergi Plan.
CLICK HERE, for UN Kalergi Plan (population replacement).
CLICK HERE, for UN replacement efforts since 1974.
CLICK HERE, for tracing steps of UN replacement agenda.
Note: If there are errors in calculating the totals, please speak up. Information is of no use to the public if it isn’t accurate.
2. Annual Immigration Reports To Parliament
2004 Annual Immigration Report To Parliament
2005 Annual Immigration Report To Parliament
2006 Annual Immigration Report To Parliament
2007 Annual Immigration Report To Parliament
2008 Annual Immigration Report To Parliament
2009 Annual Immigration Report To Parliament
2010 Annual Immigration Report To Parliament
2011 Annual Immigration Report To Parliament
2012 Annual Immigration Report To Parliament
2013 Annual Immigration Report To Parliament
2014 Annual Immigration Report To Parliament
2015 Annual Immigration Report To Parliament
2016 Annual Immigration Report To Parliament
2017 Annual Immigration Report To Parliament
2018 Annual Immigration Report To Parliament
2019 Annual Immigration Report To Parliament
2020 Annual Immigration Report To Parliament
2021 Annual Immigration Report To Parliament
2022 Annual Immigration Report To Parliament
The information in this article, and similar ones, comes directly from information provided by the Government of Canada in their annual reports. These numbers, while likely not truly accurate, are at least a good starting point.
3. Immigration Largely Controlled By Provinces
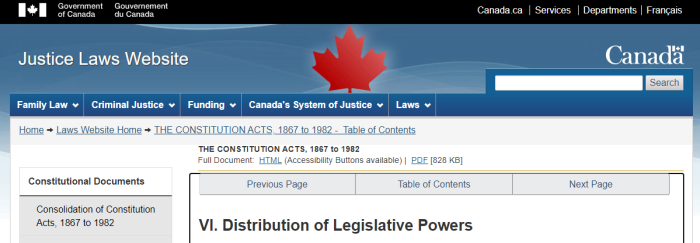
Concurrent Powers of Legislation respecting Agriculture, etc.
.
95 In each Province the Legislature may make Laws in relation to Agriculture in the Province, and to Immigration into the Province; and it is hereby declared that the Parliament of Canada may from Time to Time make Laws in relation to Agriculture in all or any of the Provinces, and to Immigration into all or any of the Provinces; and any Law of the Legislature of a Province relative to Agriculture or to Immigration shall have effect in and for the Province as long and as far only as it is not repugnant to any Act of the Parliament of Canada.
Contrary to popular belief, immigration is largely set by the Provinces. This is laid out in Section 95 of the Constitution. While Ottawa may impose laws from time to time, the understanding seems to be that the Premiers will be mostly the decision makers. While it’s understandable to get angry at Trudeau, he’s far from the only deserving target.
Additionally, there are talks underway to launch a Municipal Nominee Program, which will allow cities to directly bring people in, and to sponsor their bids to become permanent residents. It’s unclear at this point how large it will ultimately be.
4. Key Highlights From The Year 2021

AS stated before, it’s not entirely clear how many people are staying after some kind of temporary visa, v.s. how many leave. We also don’t have hard data on the “inadmissibles” who don’t leave, and on the visitors who overstay. Consequently, take this as a rough estimate:
405,999 new permanent residents
-191,338 temps transitioning to PR
= 214,661 new permanent residents brought into Canada
Temporaries Brought Into Canada
445,776 (Student Visas Issued)
+103,552 (Temporary Foreign Worker Program)
+313,294 (International Mobility Program)
= 862,622 (in the temporary classes)
6,687 “inadmissibles” allowed under Rule 24(1) of IRPA
95 “inadmissibles” allowed under Rule 25.2(1) of IRPA
813,306 eTAs (electronic travel authorizations)
+654,027 TRV (temporary resident visas)
1,467,333 combined eTAs and TRV
221,919 permanent residents became citizens in 2021. That’s interesting, considering it’s far lower than the number of people who got their PR. Perhaps the population of Canada is much larger than we think, with a huge number who remain as PR, and don’t officially become citizens.
How many people remained in Canada? Who knows?
Other immigration (PR pathway) plans to take note of:
- 2 pathways for Hong Kong residents (June 1, 2021 to August 31, 2026)
- PR for TRP holders and their families (May 6, 2021 to November 5, 2021)
- Families of air crashes PS 752 and EA302 can get PR
- 500 people (+families) amnesty for illegals to work in construction
- “Refugees” willing to work in health care settings can get PR
The Government brags about expediting work permits for “essential workers”, even as Canada experienced record high unemployment. They even created a program for “refugees” to get accelerated permanent residence if they work in health care settings. This comes at a time when Canadian workers are being let go for refusing the experimental shots.
Foreign students (under a rule change) became exempt from the 20 hour/week work limit that their visas typically imposed. Supposedly, this was to enable them to provide essential services. Again, this seems screwed up given how many Canadians were forced out of work.
Foreign students also received emergency benefits designed for Canadians, although the full extent of this is not yet published.
In January 2020, the G.T.A./IIRC started their program to give out permanent residencies to 500 people — and their families — who had overstayed their initial visas. This could be interpreted as an amnesty-for-illegals program, and we’ll have to see how much it expands.
IIRC also extended the Interim Federal Health Program, or IFHP, which is a plan that also covers so-called asylum claimants. This applies also to people who’ve illegally entered from the United States. Some 14% of claimants in 2020 had entered the country illegally, primarily via Roxham Road.
There’s also an initiative underway to bring in large numbers of people from Hong Kong, who claim to be fleeing persecution. Interesting, as Canada doesn’t seem to be run much better these days.
The Rainbow Refugee Assistance Program is supposed to grow. This is to resettle people alleging they are persecuted because of their questionable behaviours.
Canada also will allow people (women primarily) fleeing domestic violence to get a temporary permit, with a the possibility of becoming a permanent resident. There isn’t any information given about whether the abuser will be deported.
New initiatives have been announced to fast-track Afghans, Ukranians and Iranians into Canada. Expect details (and numbers) in the next annual report.
There is, of course, the usual GBA+ nonsense in the document.
5. Continued Population Replacement
(Page 18 of the 2004 Annual Report to Parliament)
(Page 24 of the 2005 Annual Report to Parliament)
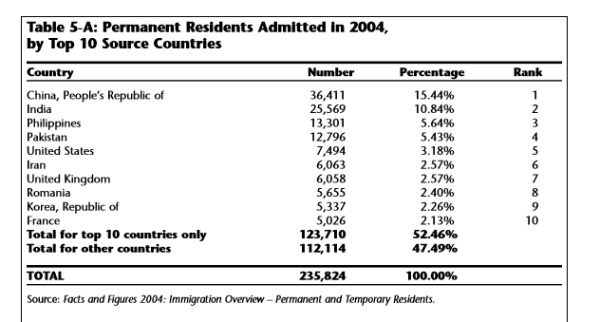
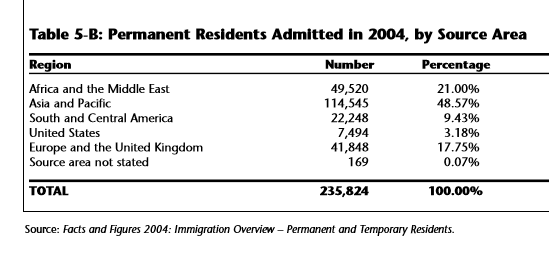
(Page 18, 19 of the 2006 Annual Report to Parliament)
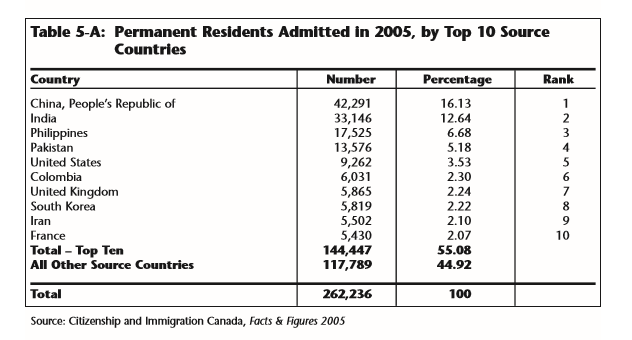
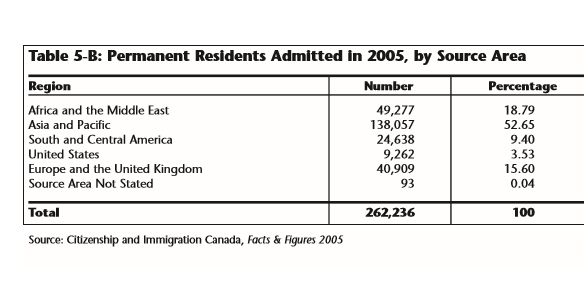
(Page 19, 20 of the 2007 Annual Report to Parliament)
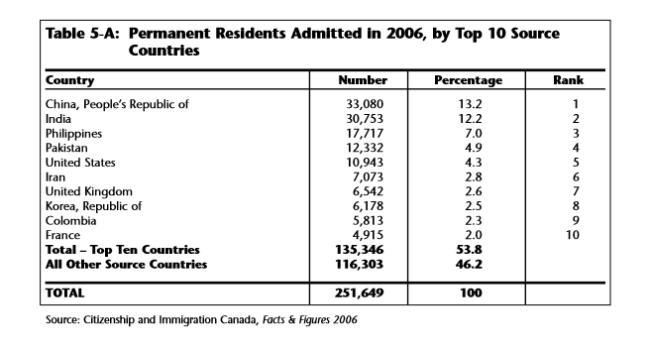
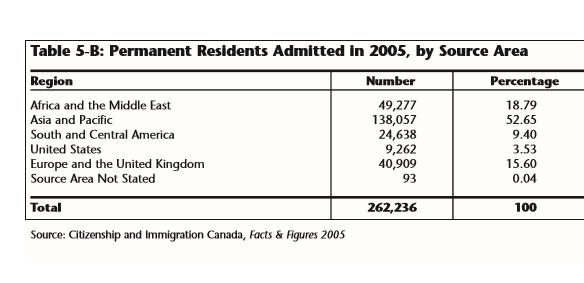
(Page 21, 22 of the 2008 Annual Report to Parliament)
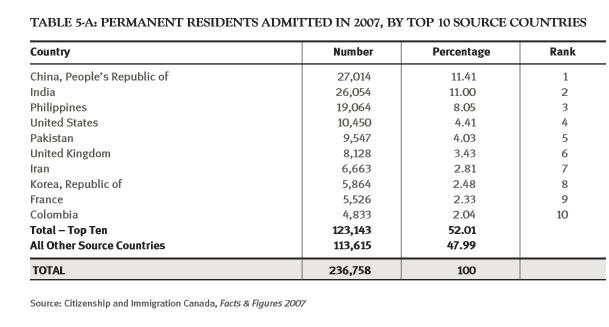
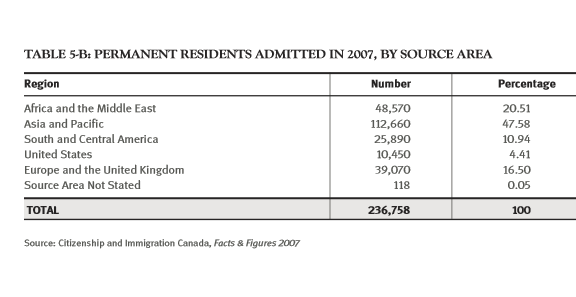
(Page 16 of the 2009 Annual Report to Parliament)
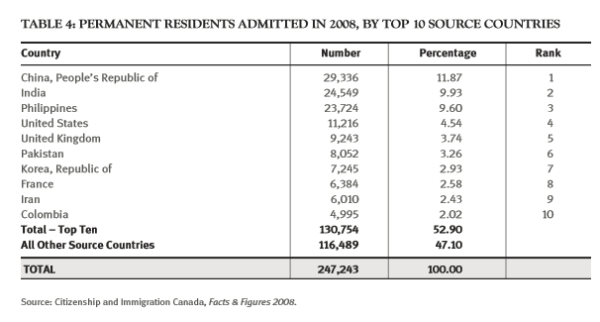
(Page 14 of the 2010 Annual Report to Parliament)
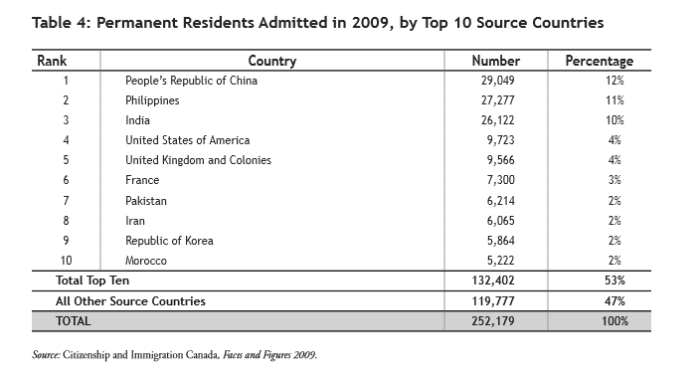
(Page 18 of the 2011 Annual Report to Parliament)
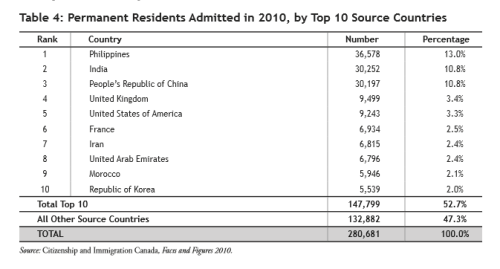
(Page 15 of the 2012 Annual Report to Parliament)
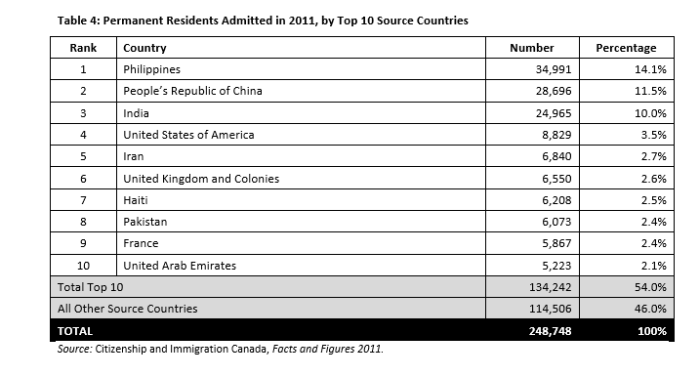
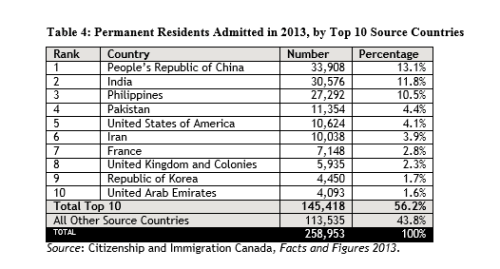
(Page 19 of the 2013 Annual Report to Parliament)
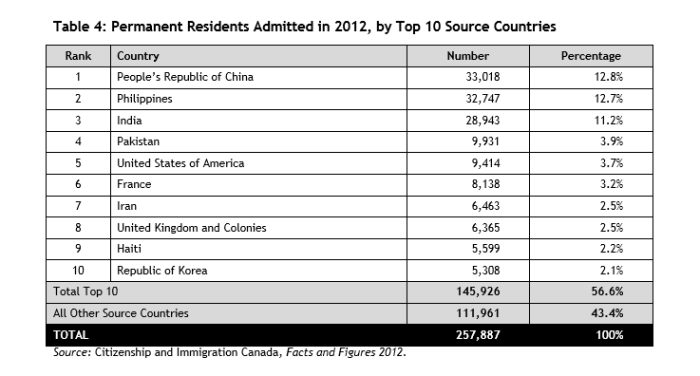
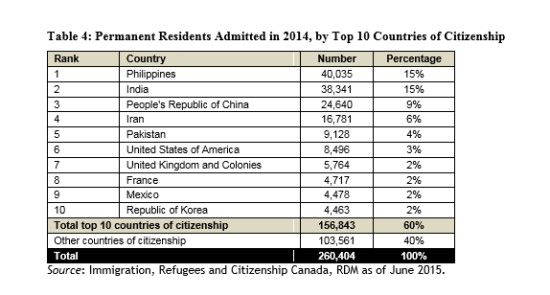
(Page 16 of the 2014 Annual Report to Parliament)
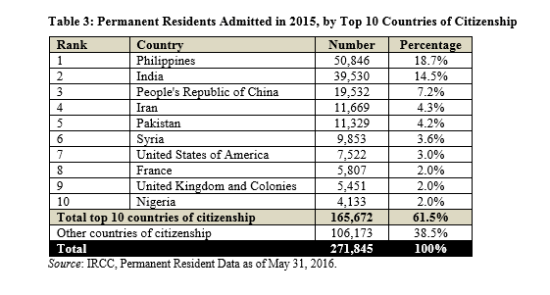
(Page 16 of the 2015 Annual Report to Parliament)
(Page 10 of the 2016 Annual Report to Parliament)
(Page 14 of the 2017 Annual Report to Parliament)
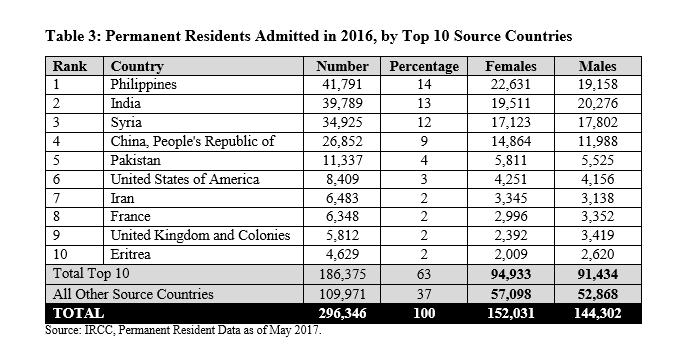
(Page 28 of the 2018 Annual Report to Parliament)
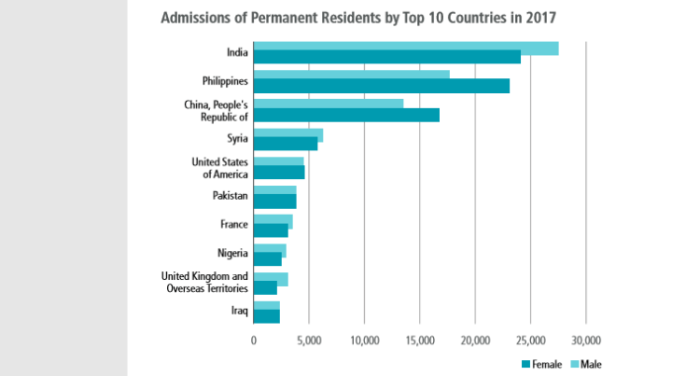
(Page 36 of the 2019 Annual Report to Parliament)
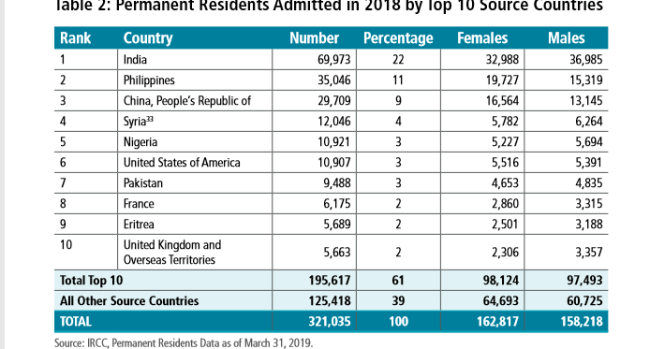
(Page 33 of the 2020 Annual Report to Parliament)
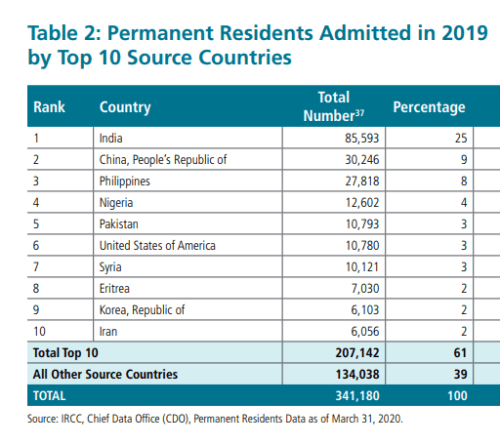
(Page 36 of the 2021 Annual Report to Parliament)
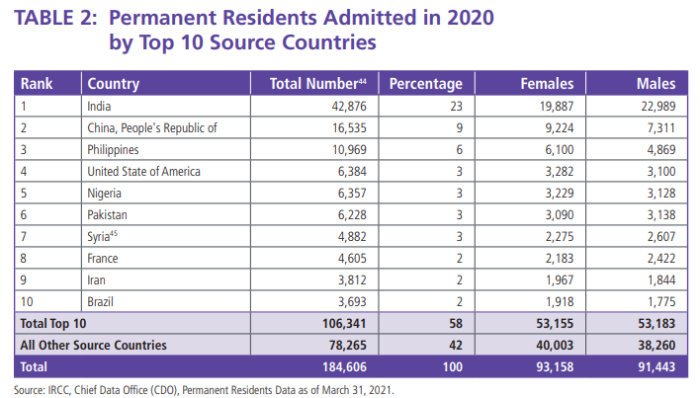
(Page 50 of the 2022 Annual Report to Parliament)
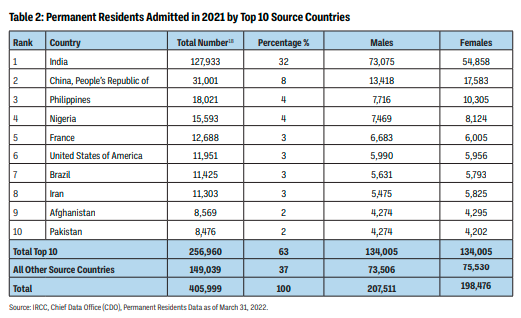
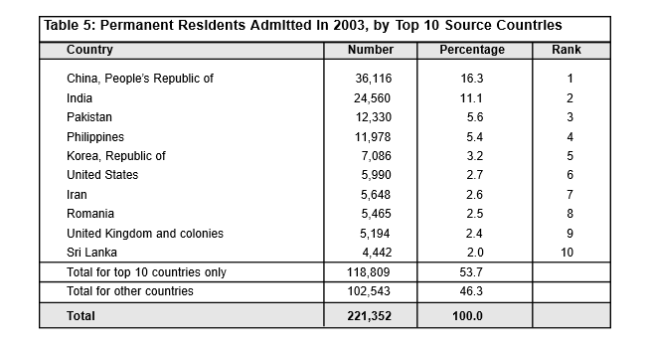
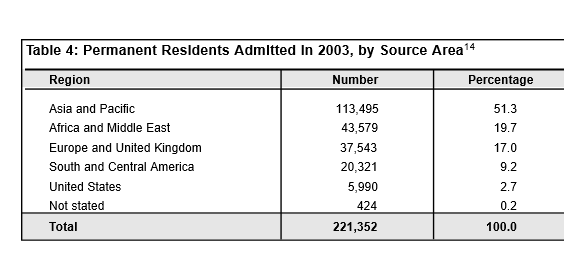
Ever get the sense that people are European descent are being replaced? It’s no coincidence. The plan for decades has been to bring in large numbers of people from the 3rd World (mostly Asia and Africa), to remake society.
As usual, the top 3 are: (a) India; (b) China; and (c) The Philippines. No surprise that the enclaves in Canada are growing. More data from the recent census will be released later this year, and the results shouldn’t be a shock to anyone. India itself comprises nearly 1/3 of the total.
And keep in mind, these are just official statistics for Permanent Residents. This is by no means everyone who is coming into the country.
6. Temporary Visitors To Canada
TRV = Temporary Resident Visa
eTA = Electronic Travel Authorization
| YEAR | TRV Issued | eTA Issued | Totals |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 1,347,898 | 2,605,077 | 3,952,975 |
| 2017 | 1,617,222 | 4,109,918 | 5,570,197 |
| 2018 | 1,898,324 | 4,125,909 | 6,024,233 |
| 2019 | 1,696,871 | 4,077,471 | 5,774,342 |
| 2020 | 257,330 | 648,789 | 906,119 |
| 2021 | 654,027 | 813,306 | 1,467,333 |
813,306 eTAs (electronic Travel Authorizations)
654,027 TRV (Temporary Resident Visa)
Travelers entering Canada increased by 62%, compared to 2020, according to the Government’s data. Expect the numbers in 2022 to come pretty close to 2018/2019 levels.
7. More “Inadmissibles” Let Into Canada
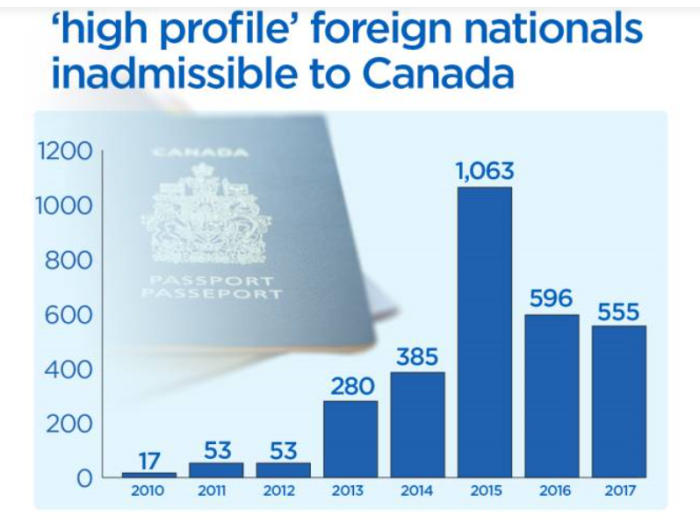
Broadly speaking, there are two provisions within IRPA, the Immigrant and Refugee Protection Act, that allow people who were previously deemed inadmissible to Canada to be given Temporary Resident Permits anyway. Here are the totals from the Annual Reports to Parliament on Immigration. Note: the first one listed only started in 2010.
Those allowed in under Rule 25.1(2) of IRPA
| YEAR | TRP Issued | Cumulative |
|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 17 | 17 |
| 2011 | 53 | 70 |
| 2012 | 53 | 123 |
| 2013 | 280 | 403 |
| 2014 | 385 | 788 |
| 2015 | 1,063 | 1,851 |
| 2016 | 596 | 2,447 |
| 2017 | 555 | 3002 |
| 2018 | 669 | 3,671 |
| 2019 | 527 | 4,198 |
| 2020 | 115 | 4,313 |
| 2021 | 95 | 4,408 |
From 2010 to 2021, a total of 4,408 people who were otherwise inadmissible to Canada were allowed in anyway under Rule 25.1(2) of IRPA. This is the category that Global News previously reported on. As for the other one, under Rule 24(1) of IRPA, Global News leaves that out:
| Year | Permits | Cumulative |
|---|---|---|
| 2002 | 12,630 | 12,630 |
| 2003 | 12,069 | 24,699 |
| 2004 | 13,598 | 38,297 |
| 2005 | 13,970 | 52,267 |
| 2006 | 13,412 | 65,679 |
| 2007 | 13,244 | 78,923 |
| 2008 | 12,821 | 91,744 |
| 2009 | 15,640 | 107,384 |
| 2010 | 12,452 | 119,836 |
| 2011 | 11,526 | 131,362 |
| 2012 | 13,564 | 144,926 |
| 2013 | 13,115 | 158,041 |
| 2014 | 10,624 | 168,665 |
| 2015 | 10,333 | 178,998 |
| 2016 | 10,568 | 189,566 |
| 2017 | 9,221 | 198,787 |
| 2018 | 7,132 | 205,919 |
| 2019 | 6,080 | 211,999 |
| 2020 | 2,044 | 214,043 |
| 2021 | 6,687 | 220,730 |
From 2002 to 2020 (inclusive), a total of 220,730 people previously deemed inadmissible to Canada were given Temporary Resident Permits anyway. This has almost certainly been going on for a lot longer, but is as far back as the reports go. Now let’s consider the reasons these people are initially refused entry.
SEC = Security (espionage, subversion, terrorism)
HRV = Human or International Rights Violations
CRIM = Criminal
S.CRIM = Serious Criminal
NC = Non Compliance
MR = Misrepresentation
| YEAR | Total | SEC | HRV | Crim | S.Crim | NC | MR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2002 | 12,630 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| 2003 | 12,069 | 17 | 25 | 5,530 | 869 | 4,855 | 39 |
| 2004 | 13,598 | 12 | 12 | 7,096 | 953 | 4,981 | 20 |
| 2005 | 13,970 | 27 | 15 | 7,917 | 981 | 4,635 | 21 |
| 2006 | 13,412 | 29 | 20 | 7,421 | 982 | 4,387 | 18 |
| 2007 | 13,244 | 25 | 8 | 7,539 | 977 | 4,109 | 14 |
| 2008 | 12,821 | 73 | 18 | 7,108 | 898 | 4,170 | 17 |
| 2009 | 15,640 | 32 | 23 | 6,619 | 880 | 7,512 | 10 |
| 2010 | 12,452 | 86 | 24 | 6,451 | 907 | 4,423 | 36 |
| 2011 | 11,526 | 37 | 14 | 6,227 | 899 | 3,932 | 11 |
| 2012 | 13,564 | 20 | 15 | 7,014 | 888 | 5,206 | 18 |
| 2013 | 13,115 | 17 | 10 | 6,816 | 843 | 5,135 | 8 |
| 2014 | 10,624 | 12 | 2 | 5,807 | 716 | 3,895 | 14 |
| 2015 | 10,333 | 3 | 3 | 5,305 | 578 | 4,315 | 28 |
| 2016 | 10,568 | 8 | 4 | 4,509 | 534 | 2,788 | 20 |
| 2017 | 9,221 | 10 | 5 | 5,035 | 591 | 3,412 | 121 |
| 2018 | 7,132 | 5 | 3 | 4,132 | 559 | 2,299 | 131 |
| 2019 | 6,080 | 2 | 0 | 3,202 | 546 | 2,139 | 175 |
| 2020 | 2,044 | 2 | 1 | 666 | 131 | 1,000 | 37 |
| 2021 | 6,687 | 1 | 2 | 602 | 134 | 1,552 | 48 |
In 2021, there 6,687 people barred were allowed in under Rule 24(1) of IRPA. That is triple what it was in 2020. Nevertheless, none of these people should be coming in.
Interestingly, even though the Government has wide discretion to let people into the country under 24(1) and 25.1(2) of IRPA, it chose not to use its discretion to prohibit anyone from entering.
Even if people are excluded from Canada — for a variety of valid reasons — often they will still be given temporary entrance into Canada. Will they ever leave? Who knows?
8. Students & Temporary Workers
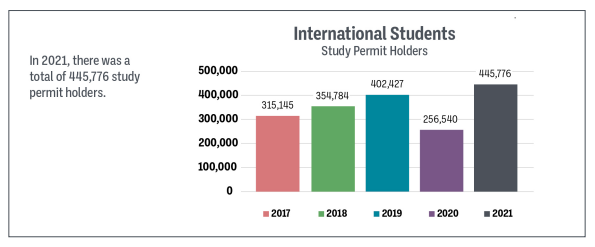
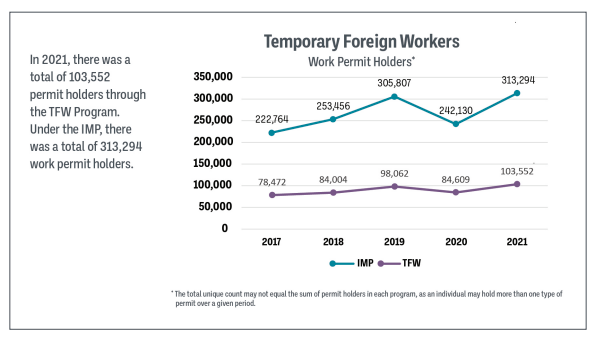
After a steep decline in 2020, the number of student visas being issued has shot back up in 2021. Expect this to get worse in the coming years.
As for the “temporary” workers, the image here seems to imply that these are the total numbers of people with permits. However, it elsewhere states that these are the number issued in 2021. Of course, the International Mobility Visas (a.k.a. “working holiday”) are only 1-2 years in length.
| Year | Stu | TFWP | IMP | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | 61,293 | 82,151 | – | 143,444 | |
| 2004 | 56,536 | 90,668 | – | 147,204 | |
| 2005 | 57,476 | 99,146 | – | 156,622 | |
| 2006 | 61,703 | 112,658 | – | 174,361 | |
| 2007 | 64,636 | 165,198 | – | 229,834 | |
| 2008 | 79,509 | 192,519 | – | 272,028 | |
| 2009 | 85,140 | 178,478 | – | 263,618 | |
| 2010 | 96,157 | 182,276 | – | 278,433 | |
| 2011 | 98,383 | 190,842 | – | 289,225 | |
| 2012 | 104,810 | 213,573 | – | 318,383 | |
| 2013 | 111,865 | 221,310 | – | 333,175 | |
| 2014 | 127,698 | 95,086 | 197,924 | 420,078 | |
| 2015 | 219,143 | 73,016 | 175,967 | 468,126 | |
| 2016 | 265,111 | 78,402 | 207,829 | 551,342 | |
| 2017 | 317,328 | 78,788 | 224,033 | 620,149 | |
| 2018 | 356,876 | 84,229 | 255,034 | 696,139 | |
| 2019 | 402,427 | 98,310 | 306,797 | 807,534 | |
| 2020 | 256,740 | 84,609 | 242,130 | 583,452 | |
| 2021 | 445,776 | 103,552 | 313,294 | 862,622 |
Stu = Student Visa
TFWP = Temporary Foreign Worker Program
IMP = International Mobility Program
Even during a “global pandemic” there were still 862,452 international student and temporary worker visas issued. This does represent an increase of about 48% from the 583,452 that came in 2020. Still, this is a staggering large number. As long as they were willing to take the shots, it seems anyone is welcome.
There are, of course, a number of pathways to remain in Canada longer and/or transition in permanent residence. Let’s not pretend that they’re all leaving afterwards. In fact, recent changes have allowed students to remain in their home countries while collecting time towards a PR designation here.
It would be nice to have more of a breakdown on the number of people who use more than 1 type of visa, but it doesn’t seem to be included here.
9. Refugee And Asylum Programs In Canada
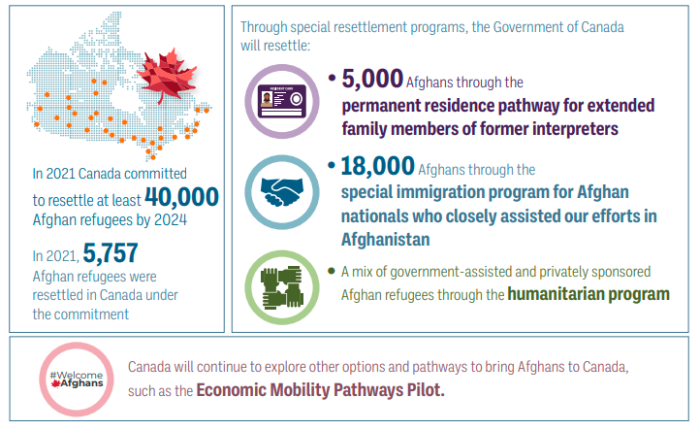
The report claims to have resettled some 20,428 refugees in 2021. There isn’t a full breakdown. As far as the top 5 source countries, they are listed as:
(a) Afghanistan (6,105)
(b) Syria (4,195)
(c) Eritrea (3,674)
(d) Iraq (1,520)
(e) Democratic Republic of Somalia (1,297)
Expect far more Afghans, Ukranians and Iranians in the next few years.
10. “Anti-Racism” Initiatives To Be Advanced In Canada
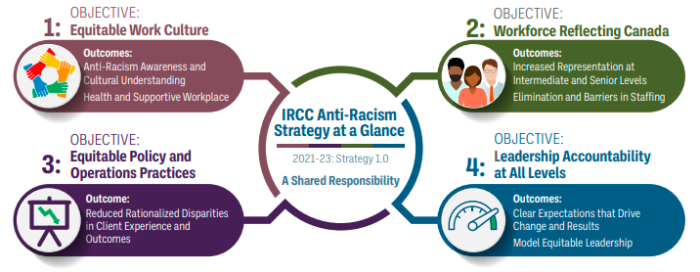
The agenda endorsed by the Federal Government is to be implemented into immigration policy as well. It’s quite openly anti-white, and gaslights objections as racism and oppressions.
- That racism against Indigenous Peoples, Black people and racialized groups has persisted over time; it exists to support, reinforce and build upon supremacy of one group over many. In our society, this is the elevation of (the) white people (or settler groups) above everyone else in many areas of Canadian life. The inertia continues to be upheld by access, privilege and indifference.
- That colonialism, through our immigration system, has had an impact on Indigenous Peoples.
- That global events, such as the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on Asian communities, fuel the rise of hate crimes in Canada. This has a profound effect on the safety and mental health of our racialized clients and employees.
- That the experiences of many Indigenous Peoples, Black people and racialized groups intersect with sexism, ethnocentrism, classism, homophobia, Islamophobia, anti-Semitism, xenophobia and other forms of discrimination, such as those experienced by persons with visible and non-visible disabilities. These intersections exacerbate an already difficult and in some cases precarious existence.
- That, despite efforts and some progress made, IRCC has not yet achieved a fully diverse, equitable and inclusive workplace. Black employees remain in entry-level positions, and Indigenous employees, as well as employees from racialized groups, are not sufficiently represented at the executive level.
- That many of our staff, as expressed in town halls, focus groups, trust circles and surveys, experience racism in the workplace, feel it impacts their career advancement and lack trust in senior management to address this.
- That our fight against racism happens in solidarity with our fight against all forms of inequity.
- That our renewed focus on Anti-Racism today builds on the tireless efforts of many unsung heroes who have long contributed to the fight against racism and all forms of inequity.
- That racism spans beyond hate; it includes unconscious and unintended actions.
Interestingly, the idea of colonialism via immigration is mentioned. Of course, it’s primarily non-whites who are coming these days, which should throw the narrative for a loop.
When they speak of making workplaces more diverse and equitable, they really mean that the goal is to make them less white.
Pretty strange that people continue to come to Canada in record numbers, if this place really is the racist hellhole that’s being displayed.
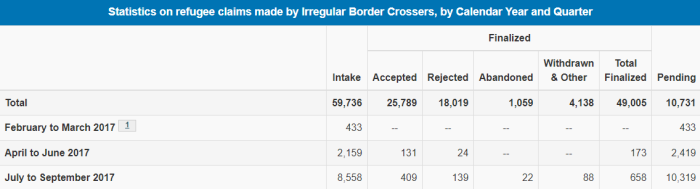
11. Illegals Entering Via U.S./Canada Border
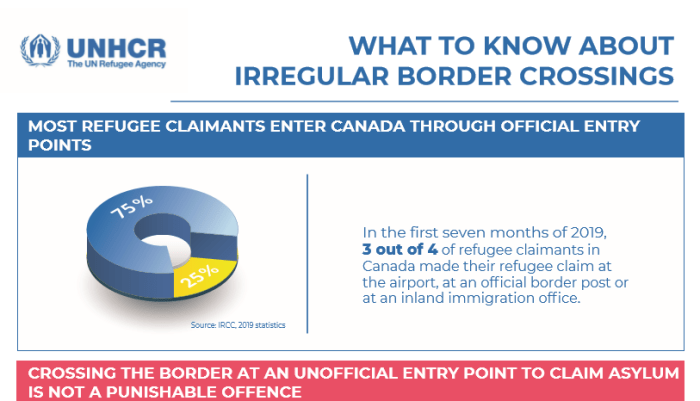
Although the report focused primarily on LEGAL immigration into Canada, the illegal brand is still worth talking about, since so few actually do. The United Nations gives detailed instructions and guidance on how to go about circumventing the border. The result, quite predictably, is that people keep trying to cross over.
| YEAR: 2019 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MONTH | QUEBEC | MANITOBA | British Columbia | OTHERS | TOTAL |
| January | 871 | 1 | 16 | 1 | 888 |
| February | 800 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 808 |
| March | 967 | 13 | 22 | 0 | 1,002 |
| April | 1,206 | 15 | 25 | 0 | 1,246 |
| May | 1,149 | 27 | 20 | 0 | 1,196 |
| June | 1,536 | 26 | 5 | 0 | 1,567 |
| July | 1,835 | 23 | 15 | 1 | 1,874 |
| August | 1,712 | 26 | 22 | 2 | 1,762 |
| September | 1,706 | 19 | 17 | 0 | 1,737 |
| October | 1,595 | 18 | 8 | 1 | 1,622 |
| November | 1,118 | 9 | 21 | 0 | 1,148 |
| December | 1,646 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 1,653 |
| TOTAL | 16,136 | 180 | 182 | 9 | 16,503 |
| YEAR: 2020 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MONTH | QUEBEC | MANITOBA | British Columbia | OTHERS | TOTAL |
| January | 1,086 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 1,100 |
| February | 976 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 980 |
| March | 930 | 7 | 18 | 0 | 955 |
| April | 1 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 6 |
| May | 17 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 21 |
| June | 28 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 33 |
| July | 29 | 2 | 17 | 0 | 48 |
| August | 15 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 18 |
| September | 30 | 4 | 7 | 0 | 41 |
| October | 27 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 31 |
| November | 24 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 32 |
| December | 26 | 2 | 8 | 0 | 36 |
| TOTAL | 3,189 | 28 | 84 | 1 | 3,302 |
| YEAR: 2021 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MONTH | QUEBEC | MANITOBA | British Columbia | OTHERS | TOTAL |
| January | 28 | 1 | 10 | 0 | 39 |
| February | 39 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 40 |
| March | 29 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 36 |
| April | 29 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 33 |
| May | 12 | 3 | 13 | 0 | 28 |
| June | 11 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 17 |
| July | 28 | 5 | 6 | 0 | 39 |
| August | 63 | 2 | 11 | 0 | 76 |
| September | 150 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 169 |
| October | 96 | 0 | 17 | 0 | 113 |
| November | 832 | 1 | 12 | 0 | 845 |
| December | 2,778 | 0 | 33 | 0 | 2,811 |
| TOTAL | 4,095 | 19 | 132 | 0 | 4,246 |
Although not listed in the Annual Immigration Report to Parliament, this is worth a mention. Illegal crossings from the U.S. did drop quite drastically in the Spring of 2020. Of course, the Government had to play along and make this “pandemic” seem real. In recent months, however, it seems the numbers are creeping back up again.
Keep in mind, the text of the Safe Third Country Agreement requires both Canada and the U.S. to consult with the UNHCR on refugees, and to get input from NGOs. We haven’t had meaningful borders in a long time.
As a reminder: the Trudeau Government scrapped the DCO, or Designated Country of Origin, back in 2019. This would allow for claims from “safe” countries to be denied much more quickly. However, with things the way they are, it seems nowhere is really safe. While the issue was very mainstream from 2017 to 2019, it seems to have disappeared.
In June 2020, a new policy kicked in to finally track who is leaving the country. Even more strange that a Trudeau would bring it in when he did. Probably to make it harder for people fleeing his regime.
Overall, the replacement agenda slowed down in 2020, but it rebounded significantly in 2021. Expect it to resume in full swing for 2022 and beyond.