


It’s been a while, but nice to be back!
Back in February, Federal Court Justice Simon Fothergill struck a lawsuit brought by over 600 Plaintiffs. This was over a 2021 requirement to take the experimental injection (a.k.a. get the vaccine passport) in order to keep their jobs.
Now, the ruling (see official version) was interesting, to be blunt.
Part of the ruling differed because of who the Plaintiffs worked for. Approximately 2/3 of them were employed by the Federal Government, while the other 1/3 were part of Federally regulated industries. This caused a split in the ruling, and they were listed as Schedules “A” and “B”.
- Schedule “A” Plaintiffs were ones who were part of the core public administration, or members of some branch of the Government
- Schedule “B” Plaintiffs weren’t with the Government, but instead were parts of industries — like banking, the railways, or aviation — that were regulated by Ottawa
The Claim for all Plaintiffs was struck in its entirety because it was so poorly written. The pleading failed to follow even the basics of civil procedure, and failed to lay out a basis for the suit.
From the Federal Court Rules:
173 (1) Pleadings shall be divided into consecutively numbered paragraphs.
Allegations set out separately
(2) Every allegation in a pleading shall, as far as is practicable, be set out in a separate paragraph.
Material facts
174 Every pleading shall contain a concise statement of the material facts on which the party relies, but shall not include evidence by which those facts are to be proved.
Particulars
181 (1) A pleading shall contain particulars of every allegation contained therein, including
(a) particulars of any alleged misrepresentation, fraud, breach of trust, willful default or undue influence; and
(b) particulars of any alleged state of mind of a person, including any alleged mental disorder or disability, malice or fraudulent intention.
By “particulars”, this really means “specifics”. When pleading a document, the person must give enough specific and detailed information so that the other side is able to address the allegations.
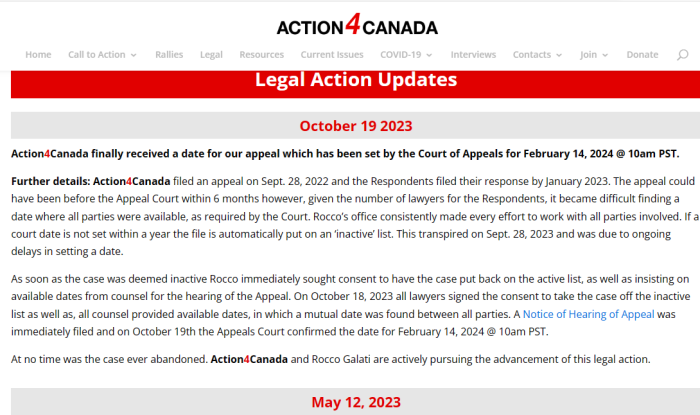
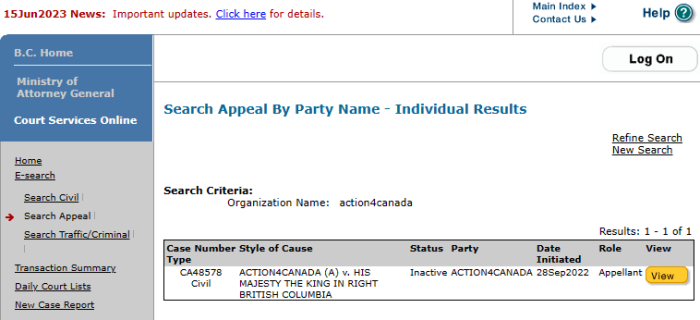
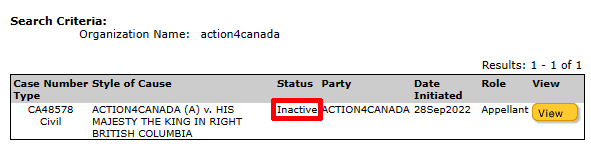
Justice Fothergill found that the Statement of Claim was so poorly crafted that it was impossible for the Defendants to file any meaningful defence. It wasn’t thrown out on its merits. He even referenced the ruling against Action4Canada, which was also found to be “bad beyond argument”.
To clarify: neither the Federal case, nor the Action4Canada case in B.C. were struck on their merits. They were struck because they were confusing, convoluted, and impossible to decipher.
While the Federally regulated employees (Schedule “B”) at least had the chance to refile, former Government workers (Schedule “A”) were not so lucky. The Judge ruled that their claims were barred by a legislative requirement that they go through arbitration. Specifically, this is Section 236 of the FPSLRA, or Federal Public Service Labour Relations Act.
Now we get to the appeal.
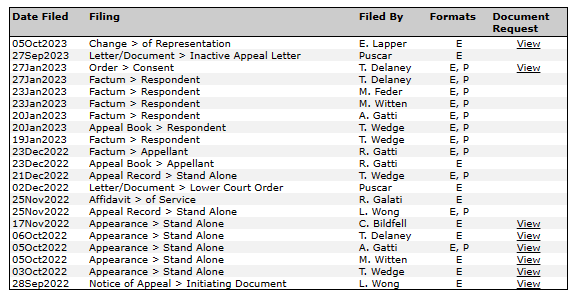
The Notice of Appeal was filed in March. The Appeal Book (collection of documents) came next, followed by the Appellants‘ and Respondents‘ written arguments.
To sum up, there were 2 major areas to cover:
First, the decision to permanently bar the Schedule “A” Plaintiffs was challenged, on the grounds that their claims lay outside what arbitration and the grievance process could offer.
Second, it was claimed that it was inappropriate to rely on the precedent set by the Action4Canada case, and that they had nothing in common.
Anyhow, read the documents for yourselves.
In response, the Government replied that while there were opportunities to get around the grievance process, the Plaintiffs never explained why they had to, or what steps they took. Furthermore, while “malfeasance of public office” was alleged, the details were never laid out.
In other words, yes, this was at least a possibility, but the Claim didn’t address any of this.
As for the Action4Canada case, Justice Alan Ross laid out in great detail how the British Columbia case was a complete mess, incomprehensible, and sought a litany of remedies outside the jurisdiction of a Civil Court. There was also the problem that large sections were included about non-parties. While the Federal Claim was much shorter, the same problems persisted overall.
Justice Fothergill decided not to duplicate the entire ruling, but simply to refer to it.
A competent lawyer might be able to argue around the arbitration requirement. But in any event, the entire Statement of Claim would have to be rewritten anyway. This Appeal will likely go nowhere.
And the requests for money keep coming!
Familiar with the Wayback Machine? It’s a mainstream archiving site that captures websites at certain times, even if the content is no longer available. Some of the recent business ventures include:
There were even donations sought at one point to finance a public inquiry. It’s unclear how much money came in, or whatever became of that.
Also, donations were sought a few years back for a B.C. doctor’s case that doesn’t appear to have materialized. This isn’t the Action4Canada suit.
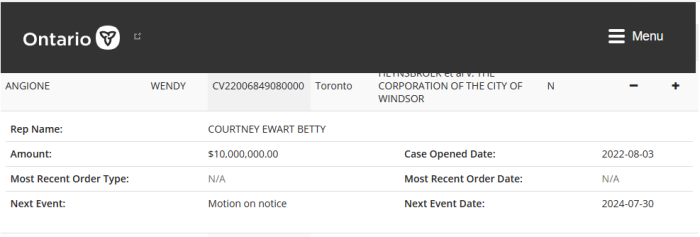
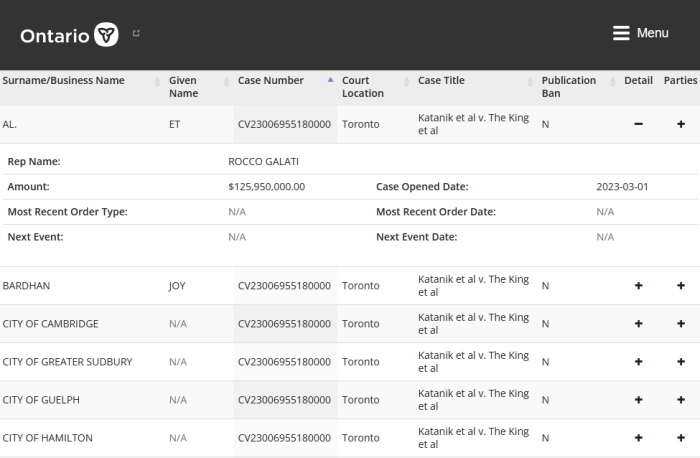
Curiously, both the Federal workers and Ontario first responders Plaintiffs were filling out retainer agreements ($1,000 and $1,500 respectively) while donations to finance the litigation were being sought online. The end results weren’t impressive.
People are being asked to donate to cases which clients are already paying a retainer?! That’s something, to say the least.
Then, we have this from the Federal case:
Hello everyone,
Some of you have already heard but for those who haven’t, the Judge has rendered his decision in the Government’s motion to strike our claim. In a somewhat anticipated move, the claim was struck for 2/3 of the plaintiffs and remains open for 1/3 to amend the claim and resubmit. There is a letter attached from Rocco himself that goes into greater detail about the decision. Needless to say, the decision was an absolute pile of rubbish and the Panel has decided to appeal the decision.
Now, as you will read in Rocco’s attached letter, there are additional fees associated with launching the appeal. The additional fees are minimal in comparison to the initial retainer but an explanation is required.
As Rocco’s letter will clarify, the retainer fee was to cover all that was required to see this matter through a trial in the Federal Court. Now that an appeal is required, it is required to go through the Federal Court of Appeals and that alone will cost in excess of $100,000. Rocco budgeted the retainer fee on doing everything to see a trial through the Federal Court which did not include appeals.
We feel it necessary at this juncture to apologize to each and every one of you. We misinterpreted the finer details of what the retainer fee covered due, no doubt, to our limited knowledge about how the civil court process works and a misunderstanding of the information Rocco provided to us. Some of you asked specifically what all would be covered with the retainer fee and were informed it would cover this entire matter all the way through no matter what action was required and for this, we apologize.
We wish to reinforce with you that this was not done out of an attempt to deceive or act maliciously. We are going to be out the same amount as anyone else who desires to proceed and be a part of the appeal.
To avoid repeating the same confusion, the panel asked Rocco to outline the cost implications for every step and all the way to the Supreme Court which Rocco now outlined in his letter. We hope this will better serve all of us and it is also our hopes that you will see this effort by the panel as a way to remain fully transparent on what transpired but also on what to expect going forward. We too, do not want to see other surprises but more importantly, we do agree with Rocco that we have a strong position for an appeal. We ultimately hope for our day in Court but sadly, we did not have our day in Court here as our lawsuit was wrongly struck down as evidently explained in Rocco’s letter.
We are planning to host another info session with Rocco via Zoom within the next few weeks to answer questions you may have and to provide more information regarding how the appeal process will work. We are not going to attempt to solicit any money from anyone prior to this information session. Our intent is to allow you to consider whether each of you as individuals wish to proceed from this point.
We understand many of you will have questions. We will do our best to answer them or have Rocco address them in the upcoming info session.
We have also attached a link to the decision on the Federal Court website.
Sincerely and most humbly,
The Federal Employee Lawsuit Panel
https://decisions.fct-cf.gc.ca/fc-cf/decisions/en/item/522970/index.do
Shortly after the decision, there was already a request for more money. Even though the Plaintiffs had paid $1,000 each (see agreement), more money was needed to appeal. See letter providing more details about the fees.
The above email was leaked by unhappy client(s), and it eventually made its way here. Unfortunately, it seems to be real.
Apparently, the Schedule “B” Plaintiffs who had their pleadings struck as “bad beyond argument” should consider that a win, because at least they are allowed a rewrite.
For reference: the email and the attachment were both sent here shortly after the February ruling. Fair to say, some are unhappy with the services they’ve received.
It’s worth asking why the this isn’t being done for free, given the shoddy drafting of the Statement of Claim to begin with. And budgeting for a Trial? Does anyone seriously think this will get that far?
The Federal Court of Appeals will throw this case out, just like the B.C. Court of Appeals will throw out Action4Canada’s. And Vaccine Choice’s suit will get tossed in early 2024.
FEDERAL VAXX PASS CHALLENGE (APPEAL)
(1) FCA Adelberg V. HMTK A-67-23 Notice Of Appeal
(2) FCA Adelberg V. HMTK A-67-23 Appeal Book
(3) FCA Adelberg V. HMTK A-67-23 Appellants MFL
(4) FCA Adelberg V. HMTK A-67-23 Respondents MFL
FEDERAL VAXX PASS CHALLENGE
(1) https://policeonguard.ca/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/Filed-SOC.pdf
(2) Federal Court Vaccine Mandate Challenge
(3) Federal Vaccine Passport Challenge Retainer Agreement
(4) Federal Court Vaccine Mandate Challenge Motion To Strike
(5) Federal Court Vaccine Mandate Challenge Affidavit Of Service
(6) Federal Court Vaccine Mandate Challenge Responding Motion Record
(7) Federal Court Of Canada Rules
(8) Federal Court Decision On Motion To Strike (Archive)
(9) https://decisions.fct-cf.gc.ca/fc-cf/decisions/en/item/522970/index.do
(10) https://www.canlii.org/en/bc/bcsc/doc/2022/2022bcsc1507/2022bcsc1507.html
(11) https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/regulations/sor-98-106/page-9.html#h-1013947
(12) https://www.laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/acts/P-33.3/page-13.html#h-406405
MONEY
(1) Letter to Federal Worker Plaintiffs
(2) Federal Workers Action Donation Link For PayPal
(3) Ontario First Responders Action Donation Link For PayPal
(4) School Action Donation Link For PayPal
(5) Police Officer Action Donation Link For PayPal
(6) https://www.web.archive.org/web/20220526170932/https://www.constitutionalrightscentre.ca/
(7) Federal Workers Retainer Agreement
(8) Ontario First Responders Retainer Agreement
(9) Donate To Public Citizens Inquiry
(10) Donations For Supposed B.C. Doctors Action
Like this:
Like Loading...