(Nebraska Senator Ben Sasse (R), calling out infanticide)

(Washington Senator Patty Murray (D), challenges new bill)
1. Other Articles on Abortion/Infanticide
(1) https://canucklaw.ca/canadian-universities-fighting-against-free-speech-and-free-association-in-court/
(2) https://canucklaw.ca/the-new-lindsay-shepherd-statistics-are-now-violence-infanticide-2/
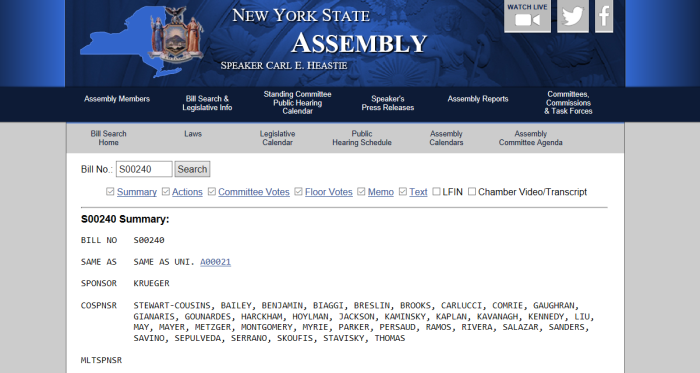
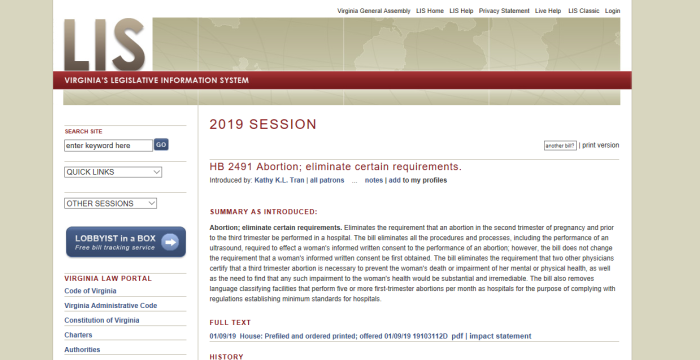
(3) https://canucklaw.ca/infanticide-part-3-ny-virginia-to-legalise-up-to-birth-abortion/
2. Important Links
(1) https://www.congress.gov/bill/116th-congress/senate-bill/130/text (2019 version)
(2) https://www.congress.gov/bill/115th-congress/house-bill/4712/text (2018 version)
(3) https://www.congress.gov/bill/107th-congress/house-bill/2175/text?overview=closed
(4) https://www.plannedparenthoodaction.org/issues/abortion/roe-v-wade
(5) https://caselaw.findlaw.com/us-supreme-court/410/113.html
3. Born Alive Infants Protection Act
SEC. 2. DEFINITION OF BORN-ALIVE INFANT.
(a) In General.–Chapter 1 of title 1, United States Code, is
amended by adding at the end the following:“Sec. 8. `Person’, `human being’, `child’, and `individual’ as
including born-alive infant“(a) In determining the meaning of any Act of Congress, or of any
ruling, regulation, or interpretation of the various administrative
bureaus and agencies of the United States, the words `person’, `human
being’, `child’, and `individual’, shall include every infant member of
the species homo sapiens who is born alive at any stage of development.
“(b) As used in this section, the term `born alive’, with respect
to a member of the species homo sapiens, means the complete expulsion or
extraction from his or her mother of that member, at any stage of
development, who after such expulsion or extraction breathes or has a
beating heart, pulsation of the umbilical cord, or definite movement of
voluntary muscles, regardless of whether the umbilical cord has been
cut, and regardless of whether the expulsion or extraction occurs as a
result of natural or induced labor, cesarean section, or induced
abortion.
“(c) Nothing in this section shall be construed to affirm, deny,
expand, or contract any legal status or legal right applicable to any
member of the species homo sapiens at any point prior to being `born
alive’ as defined in this section.”.
(b) Clerical Amendment.–The table of sections at the beginning of
chapter 1 of title 1, United States Code, is amended by adding at the
end the following new item:“8. `Person’, `human being’, `child’, and `individual’ as including
born-alive infant.”.
Seems harmless enough, right? If it 1/ breathes; 2/ has a heartbeat; and 3/ has muscles that move, it’s alive and needs protecting
Saving the life of infant children “should” be a priority for any civilized society. Unfortunately, as time goes on, we have to legislate further and further to make that point. In fact, pro-death activists have LONG passed the guidelines set out by Roe v. Wade (1973).
Sadly, this common sense legislation is not only needed, but apparently very controversial. This was passed in the House of Representatives last year.
Here is the 2019 Born-Alive Abortion Survivors Protection Act
115th CONGRESS
2d SessionH. R. 4712
IN THE SENATE OF THE UNITED STATES
January 20, 2018
ReceivedAN ACT
To amend title 18, United States Code, to prohibit a health care practitioner from failing to exercise the proper degree of care in the case of a child who survives an abortion or attempted abortion.
Be it enacted by the Senate and House of Representatives of the United States of America in Congress assembled,
SECTION 1. Short title.
This Act may be cited as the “Born-Alive Abortion Survivors Protection Act”.SEC. 2. Findings.
Congress finds as follows:
(1) If an abortion results in the live birth of an infant, the infant is a legal person for all purposes under the laws of the United States, and entitled to all the protections of such laws.
(2) Any infant born alive after an abortion or within a hospital, clinic, or other facility has the same claim to the protection of the law that would arise for any newborn, or for any person who comes to a hospital, clinic, or other facility for screening and treatment or otherwise becomes a patient within its care.
SEC. 3. Born-alive infants protection.(a) Requirements pertaining to born-Alive abortion survivors.—Chapter 74 of title 18, United States Code, is amended by inserting after section 1531 the following:
Ҥ 1532. Requirements pertaining to born-alive abortion survivors
“(a) Requirements for health care practitioners.—In the case of an abortion or attempted abortion that results in a child born alive (as defined in section 8 of title 1, United States Code (commonly known as the ‘Born-Alive Infants Protection Act’)):“(1) DEGREE OF CARE REQUIRED; IMMEDIATE ADMISSION TO A HOSPITAL.—Any health care practitioner present at the time the child is born alive shall—
“(A) exercise the same degree of professional skill, care, and diligence to preserve the life and health of the child as a reasonably diligent and conscientious health care practitioner would render to any other child born alive at the same gestational age; and
“(B) following the exercise of skill, care, and diligence required under subparagraph (A), ensure that the child born alive is immediately transported and admitted to a hospital.“(2) MANDATORY REPORTING OF VIOLATIONS.—A health care practitioner or any employee of a hospital, a physician’s office, or an abortion clinic who has knowledge of a failure to comply with the requirements of paragraph (1) shall immediately report the failure to an appropriate State or Federal law enforcement agency, or to both.
“(b) Penalties.—
“(1) IN GENERAL.—Whoever violates subsection (a) shall be fined under this title or imprisoned for not more than 5 years, or both.
“(2) INTENTIONAL KILLING OF CHILD BORN ALIVE.—Whoever intentionally performs or attempts to perform an overt act that kills a child born alive described under subsection (a), shall be punished as under section 1111 of this title for intentionally killing or attempting to kill a human being.
“(c) Bar to prosecution.—The mother of a child born alive described under subsection (a) may not be prosecuted under this section, for conspiracy to violate this section, or for an offense under section 3 or 4 of this title based on such a violation.“(d) Civil remedies.—
“(1) CIVIL ACTION BY A WOMAN ON WHOM AN ABORTION IS PERFORMED.—If a child is born alive and there is a violation of subsection (a), the woman upon whom the abortion was performed or attempted may, in a civil action against any person who committed the violation, obtain appropriate relief.
“(2) APPROPRIATE RELIEF.—Appropriate relief in a civil action under this subsection includes—
“(A) objectively verifiable money damage for all injuries, psychological and physical, occasioned by the violation of subsection (a);
“(B) statutory damages equal to 3 times the cost of the abortion or attempted abortion; and“(C) punitive damages.
“(3) ATTORNEY’S FEE FOR PLAINTIFF.—The court shall award a reasonable attorney’s fee to a prevailing plaintiff in a civil action under this subsection.
“(4) ATTORNEY’S FEE FOR DEFENDANT.—If a defendant in a civil action under this subsection prevails and the court finds that the plaintiff’s suit was frivolous, the court shall award a reasonable attorney’s fee in favor of the defendant against the plaintiff.
“(e) Definitions.—In this section the following definitions apply:
“(1) ABORTION.—The term ‘abortion’ means the use or prescription of any instrument, medicine, drug, or any other substance or device—
“(A) to intentionally kill the unborn child of a woman known to be pregnant; or
“(B) to intentionally terminate the pregnancy of a woman known to be pregnant, with an intention other than—
“(i) after viability, to produce a live birth and preserve the life and health of the child born alive; or
“(ii) to remove a dead unborn child.
“(2) ATTEMPT.—The term ‘attempt’, with respect to an abortion, means conduct that, under the circumstances as the actor believes them to be, constitutes a substantial step in a course of conduct planned to culminate in performing an abortion.”.
(b) Clerical amendment.—The table of sections for chapter 74 of title 18, United States Code, is amended by inserting after the item pertaining to section 1531 the following:“1532. Requirements pertaining to born-alive abortion survivors.”.
(c) Chapter heading amendments.—
(1) CHAPTER HEADING IN CHAPTER.—The chapter heading for chapter 74 of title 18, United States Code, is amended by striking “Partial-Birth Abortions” and inserting “Abortions”.
(2) TABLE OF CHAPTERS FOR PART I.—The item relating to chapter 74 in the table of chapters at the beginning of part I of title 18, United States Code, is amended by striking “Partial-Birth Abortions” and inserting “Abortions”.
Passed the House of Representatives January 19, 2018
4. Abortionists Moving The Goalposts
How did we get to this point?
1/ Abortion used to limited to only medical necessity to save the mother’s life, or in such cases as incest.
(0, unless medically necessary)
2/ Roe v. Wade allowed abortions in 1st trimester, but still had some safeguards in place.
(~13 weeks)
3/ Various state movements pushed abortion well into 2nd trimester
(20-24 weeks)
4/ New initiatives like NY Gov. Cuomo, see last article, want abortion up until birth
(0-39 weeks)
5/ Now efforts to keep survivors alive are being fought.
(0-after birth)
5. So, What Happens Now
What’s next? Debating how, many days, weeks or months your child can still be killed?
Will it become like fostering an animal with the SPCA? If it doesn’t work out, you can return the animal within a year. (Disclosure: I did foster an animal, and formally adopt him 2 months later)
Also, how did we get to the point where abortion is “celebrated”? Even if, for the sake of argument, a person decides they can’t become a parent or provide any sort of future, okay. This is a decision that should be taken very carefully, and is nothing to celebrate.
No rational human would celebrate having to put down a sick or dying dog or cat. To them, they are literally losing a family member. However, a flesh and blood child gets nowhere near the same consideration.
My body. My choice. Leave no survivors.
This is truly sick.