(Global News tells “part” of the story on inadmissibles)

1. Previous Solutions Offered
A response that frequently comes up is for people to ask what to do about it. Instead of just constantly pointing out what is wrong, some constructive suggestions should be offered. This section contains a list of proposals that, if implemented, would benefit society. While the details may be difficult to implement, at least they are a starting point.
2. Important Links
(A) “https://canucklaw.ca/students-and-temporary-workers-how-many-actually-stay/
(B) https://canucklaw.ca/full-scale-of-inadmissibles-getting-residency-permits-what-global-news-leaves-out/
(C) https://canucklaw.ca/statscan-research-fake-students-using-visas-to-immigrate/
(D) https://canucklaw.ca/canadian-parliament-discusses-work-permits-that-are-issued-for-illegals/
(E) https://canucklaw.ca/canada-pathway-to-permanent-residence-for-illegals-their-families/
(F) https://canucklaw.ca/sanctuary-cities-an-end-run-around-having-borders/
(1) https://www.ctvnews.ca/canada/canada-to-begin-collecting-exit-passport-data-1.2947418
(2) http://archive.is/feDOA
(3) https://www.cbsa-asfc.gc.ca/btb-pdf/ebsiip-asfipi-eng.html
(4) http://archive.is/krWR3
(5) https://globalnews.ca/news/6040749/canada-border-services-agency-arrest-warrants-cancelled/
(6) http://archive.is/4jQA9
(7) https://www.canada.ca/en/immigration-refugees-citizenship/news/notices/permanent-residence-construction-workers-gta.html
(8) http://archive.is/e6OYZ
(9) https://canadianlabour.ca/permanentresidence/
(10) http://archive.is/s3pq6
(11) https://www.thestar.com/news/canada/2008/05/07/41000_illegal_immigrants_gone_missing.html
(12) http://archive.is/bayYs
(13) https://torontosun.com/2017/03/14/the-high-cost-of-illegal-migrants/wcm/a2cdce17-4808-48df-9569-1247cba8bcf0
(14) http://archive.is/Xk9l4
Annual Immigration Reports To Parliament
(1) 2004 Annual Report to Parliament
(2) 2005 Annual Report to Parliament
(3) 2006 Annual Report to Parliament
(4) 2007 Annual Report to Parliament
(5) 2008 Annual Report to Parliament
(6) 2009 Annual Report to Parliament
(7) 2010 Annual Report to Parliament
(8) 2011 Annual Report to Parliament
(9) 2012 Annual Report to Parliament
(10) 2013 Annual Report to Parliament
(11) 2014 Annual Report to Parliament
(12) 2015 Annual Report to Parliament
(13) 2016 Annual Report to Parliament
(14) 2017 Annual Report to Parliament
(15) 2018 Annual Report to Parliament
(16) 2019 Annual Report to Parliament
(0) Archived listings of Reports
3. Context For This Article
For a nation to have meaningful borders, it must keep track of who is entering and exiting the country. It must do both, as merely recording the entrances is not enough.
Why is this? Because the nation will have no idea how many people actually remain in the country. A person entering on a tourist visa may leave Canada in a week, or may still be there a decade later.
Unfortunately for Canadians, all of the major parties at the Federal level (and many at the Provincial level) are not at all interested in providing meaningful border security to their people. It isn’t for a lack of knowledge of the subject, but instead it’s not on their agendas.
4. Trudeau: 4+ Years To Implement

In 2016, the Federal Government announced plans to start collecting exit information from people leaving the country. This really is common sense. While we (theoretically) know how many people, who, and when, are ENTERING Canada, until now they Government doesn’t track who is LEAVING. Perhaps we just take it on face that everyone leaves when they should.
And one of the major benefits stated is to help reduce immigration fraud. If a person is “counting time” towards living in Canada, but doesn’t actually live here, then the Immigration Ministry should know about it.
When this does get implemented, then a gaping hole in Canadian border security should be fixed, right? Maybe not.
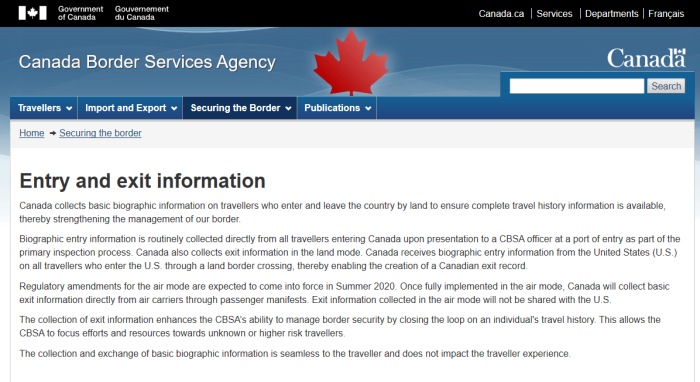
Canada collects basic biographic information on travellers who enter and leave the country by land to ensure complete travel history information is available, thereby strengthening the management of our border.
Biographic entry information is routinely collected directly from all travellers entering Canada upon presentation to a CBSA officer at a port of entry as part of the primary inspection process. Canada also collects exit information in the land mode. Canada receives biographic entry information from the United States (U.S.) on all travellers who enter the U.S. through a land border crossing, thereby enabling the creation of a Canadian exit record.
Regulatory amendments for the air mode are expected to come into force in Summer 2020. Once fully implemented in the air mode, Canada will collect basic exit information directly from air carriers through passenger manifests. Exit information collected in the air mode will not be shared with the U.S.
The collection of exit information enhances the CBSA’s ability to manage border security by closing the loop on an individual’s travel history. This allows the CBSA to focus efforts and resources towards unknown or higher risk travellers.
This still isn’t fully implemented, and won’t be until at least 2020. That’s right, these changes were announced in 2016, and over three years later, are not fully implemented. Guess the potential fraud and security risks aren’t that great.
Right now, departures by air are not recorded by CBSA. Unless someone is travelling to the United States, (and even then not always) he/she is flying in a plane. Boating isn’t really a practical solution for international travel to and from Canada.
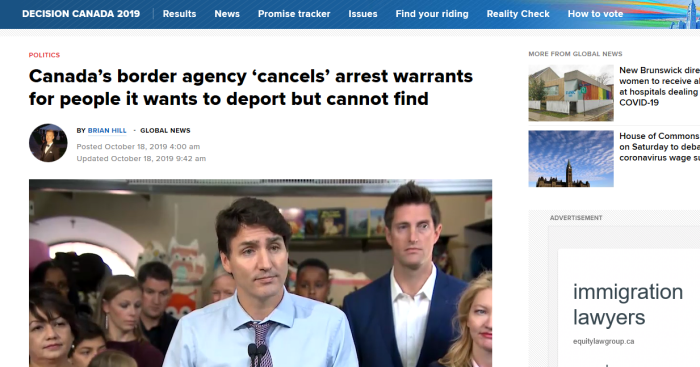
As for people wanted for criminal or other reasons, the CBSA (Canada Border Services Agency) has revealed that it deletes old arrest warrants.
Currently, there are more than 48,000 active arrest warrants in Canada for people wanted on immigration violations. According to the Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA), the “vast majority” of these cases involve people wanted for deportation.
But these figures may not tell the whole story.
Global News has learned the CBSA cancels arrest warrants for failed refugee claimants and other people wanted for removal who it cannot find, even in cases where it is not clear whether a person has left Canada.
What’s more, the CBSA does not track how many warrants it cancels in cases where a person’s whereabouts are unknown.
.
Because the CBSA only recently started tracking people when they exit the country by land — and still doesn’t track people who leave by air — there’s no way for the government or CBSA to say for sure how many people have overstayed their welcome.
Back in the early 2000s, when he worked at the agency that would later become the CBSA, Sundberg says he was assigned to a team in Lethbridge, Alta., tasked with “culling” old warrants for people facing deportation whose cases had been in the system for at least five years.
The protocol for cancelling a warrant, Sundberg said, involved calling known associates of the wanted person, doing internet searches and checking criminal and entry records in other countries to see if someone wanted for arrest had left Canada voluntarily.
The Canada Border Services Agency apparently cancels warrants for people wanted for immigration violations, if the warrants are old.
Moreover, there appears to be no tracking of how many warrants get cancelled either. Just a hunch, but it probably looks bad in the CBSA’s eyes if they have a lot of outstanding warrants. Makes them look slow and unproductive. Alternatively, this could be a deliberate attempt to make sure that people in the country illegally and/or committing other crimes won’t be deported.
5. Previous Efforts At Entry/Exit

Phase I Joint Canada-United States Report
.
Executive Summary
.
As part of the Beyond the Border Declaration and Action Plan agreed to by President Obama and Prime Minister Harper in 2011, the United States and Canada are developing a coordinated Entry/Exit Information System at their shared land border. The Entry/Exit Information System will facilitate exchanges of entry information such that an entry into one country is considered an exit from the other. This exchange will help better manage immigration program and border management practices, as it is important for Canada and the United States to determine when individuals both enter and depart our respective countries. For example, an Entry/Exit Information System will help determine whether third country nationals and permanent residents are complying with domestic immigration laws. This project can help move us closer to meeting this need through mutual collaboration and without expensive new infrastructure or unnecessary processing that would slow down trade and travel between the two countries.
The Entry/Exit Information System will be implemented in three phases. During the first phase, which began in September 2012 and concluded in January 2013, the countries exchanged biographic entry data only on third country nationals and permanent residents (but not U.S. or Canadian citizens) who crossed the common land border at four locations. This report covers the activities of Phase I.
In 2011, Canada and the U.S. reached an agreement to start an entry/exit system between the two countries. Not much progress has been made since.
6. Tourists Coming Into Canada Annually
TRV = Temporary Resident Visa
eTA = Electronic Travel Authorization
| YEAR | TRV Issued | eTA Issued | Totals | Cumulative |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 1,347,898 | 2,605,077 | 3,952,975 | – |
| 2017 | 1,617,222 | 4,109,918 | 5,570,197 | – |
| 2018 | 1,898,324 | 4,125,909 | 6,024,233 | – |
Certainly, the overwhelming majority of these people are simply tourists who will leave. However, without an exit tracking system, we don’t really know how many. That is just the official data for the last few years.
7. “Inadmissibles” Let Into Canada Anyway
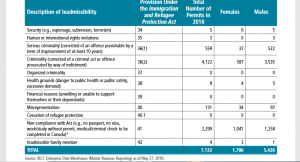
(Source: 2019 Annual Report to Parliament on Immigration)
Broadly speaking, there are two provisions within IRPA, the Immigrant and Refugee Protection Act, that allow people who were previously deemed inadmissible to Canada to be given Temporary Resident Permits anyway. Here are the totals from the Annual Reports to Parliament on Immigration. Note: the first one listed only started in 2010.
| YEAR | TRP Issued |
|---|---|
| 2010 | 17 |
| 2011 | 53 |
| 2012 | 53 |
| 2013 | 280 |
| 2014 | 385 |
| 2015 | 1,063 |
| 2016 | 596 |
| 2017 | 555 |
| 2018 | 669 |
From 2010 to 2018, a total of 3671 people who were otherwise inadmissible to Canada were allowed in anyway under Rule 25.2(1) of IRPA. This is the category that Global News previously reported on. As for the other one, under Rule 24(1) of IRPA, Global News leaves that out:
| Year | Permits | Cumulative |
|---|---|---|
| 2002 | 12,630 | 12,630 |
| 2003 | 12,069 | 24,699 |
| 2004 | 13,598 | 38,297 |
| 2005 | 13,970 | 52,267 |
| 2006 | 13,412 | 65,679 |
| 2007 | 13,244 | 78,923 |
| 2008 | 12,821 | 91,744 |
| 2009 | 15,640 | 107,384 |
| 2010 | 12,452 | 107,384 |
| 2011 | 11,526 | 118,910 |
| 2012 | 13,564 | 132,474 |
| 2013 | 13,115 | 145,589 |
| 2014 | 10,624 | 156,213 |
| 2015 | 10,333 | 166,546 |
| 2016 | 10,568 | 177,114 |
| 2017 | 9,221 | 186,335 |
| 2018 | 7,132 | 193,467 |
From 2002 to 2018 (inclusive), a total of 193,467 people previously deemed inadmissible to Canada were given Temporary Resident Permits anyway. This has almost certainly been going on for a lot longer, but is as far back as the reports go. Now let’s consider the reasons these people are initially refused entry.
SEC = Security (espionage, subversion, terrorism)
HRV = Human or International Rights Violations
CRIM = Criminal
S.CRIM = Serious Criminal
NC = Non Compliance
MR = Misrepresentation
| YEAR | Total | SEC | HRV | Crim | S.Crim | NC | MR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2002 | 12,630 | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| 2003 | 12,069 | 17 | 25 | 5,530 | 869 | 4,855 | 39 |
| 2004 | 13,598 | 12 | 12 | 7,096 | 953 | 4,981 | 20 |
| 2005 | 13,970 | 27 | 15 | 7,917 | 981 | 4,635 | 21 |
| 2006 | 13,412 | 29 | 20 | 7,421 | 982 | 4,387 | 18 |
| 2007 | 13,244 | 25 | 8 | 7,539 | 977 | 4,109 | 14 |
| 2008 | 12,821 | 73 | 18 | 7,108 | 898 | 4,170 | 17 |
| 2009 | 15,640 | 32 | 23 | 6,619 | 880 | 7,512 | 10 |
| 2010 | 12,452 | 86 | 24 | 6,451 | 907 | 4,423 | 36 |
| 2011 | 11,526 | 37 | 14 | 6,227 | 899 | 3,932 | 11 |
| 2012 | 13,564 | 20 | 15 | 7,014 | 888 | 5,206 | 18 |
| 2013 | 13,115 | 17 | 10 | 6,816 | 843 | 5,135 | 8 |
| 2014 | 10,624 | 12 | 2 | 5,807 | 716 | 3,895 | 14 |
| 2015 | 10,333 | 3 | 3 | 5,305 | 578 | 4,315 | 28 |
| 2016 | 10,568 | 8 | 4 | 4,509 | 534 | 2,788 | 20 |
| 2017 | 9,221 | 10 | 5 | 5,035 | 591 | 3,412 | 121 |
| 2018 | 7,132 | 5 | 3 | 4,132 | 559 | 2,299 | 131 |
The original work for this section was done back in December 2019, but the findings as just as valid today.
8. Ghost Students Coming On Visas
(StatsCan research on students, including fake student visas)
(Large numbers of student visa holders are not enrolled)
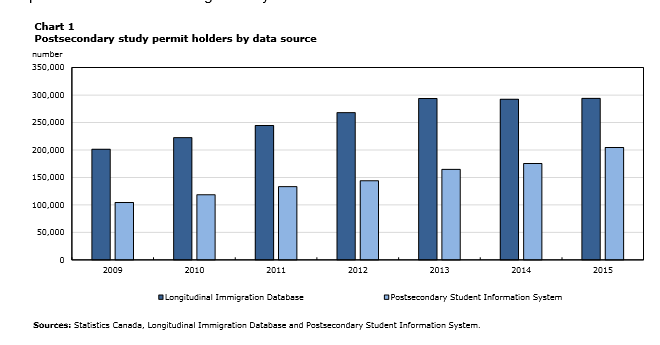
The IMDB contains information on all temporary and permanent residents since 1980. For the purposes of this study, only the information on temporary residents was used. Specifically, the number of valid postsecondary study permit holders was generated to compare it with the actual number of international students enrolled in postsecondary programs based on data from PSIS, which contains program information for all students enrolled in Canadian public postsecondary institutions. Immigration status is listed in PSIS because postsecondary institutions are allowed to charge international students higher tuition fees than Canadian students, and this information is collected annually. Three groups were analyzed separately in this study: Canadian citizens, permanent residents, and student visa or permit holders (international students). The T1FF is a census of all Canadian taxfilers and their spouses and children. It contains detailed income information as well as basic demographics. The information on T4 wages and salaries in the T1FF was of particular interest in this study.
The study found that approximately 69.5% of postsecondary study permit holders actually enrolled in a postsecondary program in 2015—up from 51.8% in 2009. Between 2009 and 2015, the number of international postsecondary students nearly doubled. This resulted in a significant increase in the proportion of postsecondary students who were international students (from 6.6% in 2009 to 11.3% in 2015). International students enrolled in university bachelor’s degree programs accounted for about half of this increase. Although a smaller proportion of international students enrolled in college diploma programs, this was the fastest-growing group—accounting for 19.8% of international students in 2015, compared with 12.0% in 2009. In general, international students were more likely to be enrolled in university graduate programs and in higher-paying fields than Canadian students.
The research concludes, that large numbers of people on student visas are not actually enrolled in a Canadian school. While it is true that some people could have stayed home or gone elsewhere, student visas are cancelled if the person changes their mind. So the obvious question: where are these people, and what are they doing?
One of the reasons why international students were less likely to be employed than Canadian students might be because of the rules governing international students’ right to work. Prior to June 1, 2014, international students had to obtain a permit to work off campus and had to study for a period of at least six months before doing so. As of June 1, 2014, these rules are no longer in place, which may result in higher international student employment rates in the future.
Yes, the rules have been relaxed, and that means more and more students are “students” will be working while in school. Sort of a no brainer.
In the future, linking the Longitudinal Immigration Database (IMDB) data with postsecondary and taxation data could open new opportunities for research on international students. First, the IMDB could be used to disaggregate the results of this study by country of citizenship. Second, the relationship between educational experience and the transition to permanent residency could be explored. Third, international students may transition to a post-graduation work permit after completing their studies—future research could examine whether this type of work permit is associated with superior labour market outcomes and an increased propensity to transition to permanent residency.
These last remarks are from the conclusion. It seems to around the obvious, that student visas are a pathway to permanent residence. There is the Provincial Nominee Program, Atlantic Pilot Project, and other such options Even if not right away, the Post Graduate Work Program is one possibility to get PR at a later date.
9. Scale Of Students/Temp Workers
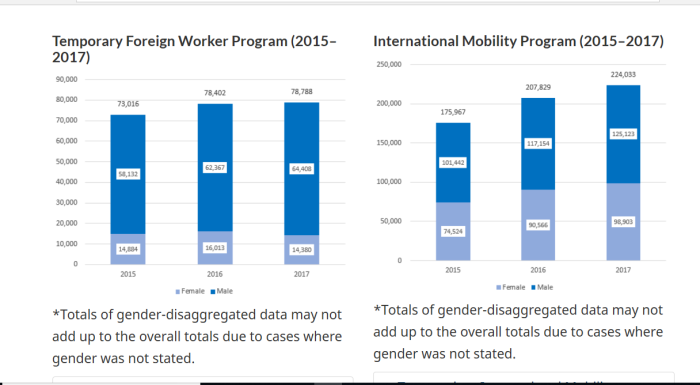
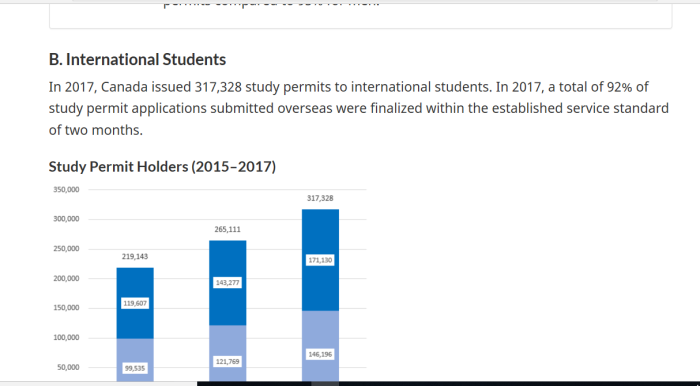
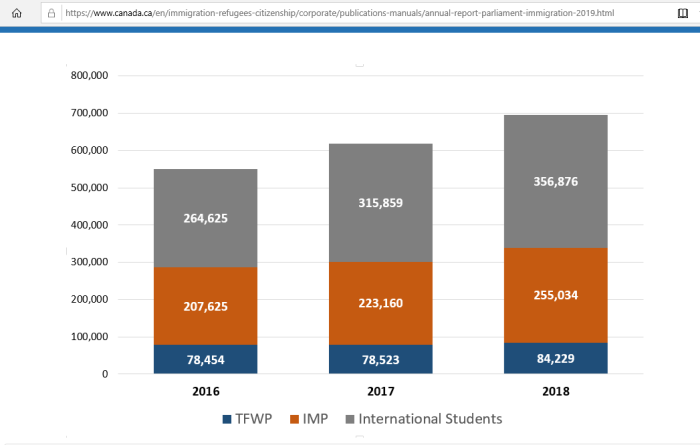
| Year | Stu | TFWP | IMP | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | 61,293 | 82,151 | – | 143,444 | |
| 2004 | 56,536 | 90,668 | – | 147,204 | |
| 2005 | 57,476 | 99,146 | – | 156,622 | |
| 2006 | 61,703 | 112,658 | – | 174,361 | |
| 2007 | 64,636 | 165,198 | – | 229,834 | |
| 2008 | 79,509 | 192,519 | – | 272,028 | |
| 2009 | 85,140 | 178,478 | – | 263,618 | |
| 2010 | 96,157 | 182,276 | – | 278,433 | |
| 2011 | 98,383 | 190,842 | – | 289,225 | |
| 2012 | 104,810 | 213,573 | – | 318,383 | |
| 2013 | 111,865 | 221,310 | – | 333,175 | |
| 2014 | 127,698 | 95,086 | 197,924 | 420,078 | |
| 2015 | 219,143 | 73,016 | 175,967 | 468,126 | |
| 2016 | 265,111 | 78,402 | 207,829 | 551,342 | |
| 2017 | 317,328 | 78,788 | 224,033 | 620,149 | |
| 2018 | 356,876 | 84,229 | 255,034 | 696,139 |
Data compiled from the Annual Immigration Reports to Parliament. True, not everyone will stay illegally, or even stay at all. Still, with these numbers of people entering Canada, wouldn’t it be helpful to have some sort of exit tracking system to see who actually leaves?
Note: there is a small discrepancy between the 2018 and 2019 reports, as the temporary categories are adjusted slightly downwards. Now sure why, but could be a counting error.
10. Visa Overstayers In Canada
It’s a commonly repeated talking point that the overwhelming majority of people in Western nations (particularly Canada and the U.S.) are people who have entered on some sort of visa and overstayed. This means they come legally, and didn’t honour their promise to leave afterwards.
While this claim may be true, it points to an even stronger argument in favour of having a full entry/exit tracking system. Citizens need to know that people who enter (under whatever program) are in fact leaving afterwards.
11. Work Permits For Illegals
Yes, that has seriously discussed in the Federal Parliament: giving people entering the country illegally temporary work permits. The stated rational is that it would help cover the costs. Sure, not letting them into the country in the first place would lower costs, but that’s racist to point out.
(Sept 28, 2017 “Evidence”)
Here are some quotes from the meeting. The topic of open work permits will be mentioned many times in these 5 meetings.
[Translation]
.
Through these measures, we are working to reduce the wait times for eligibility interviews from a few months to a few weeks, after which eligible claims are referred to the IRB.
[English]
This timely scheduling of eligibility interviews is crucial because in order to apply for an open work permit, an asylum seeker must first have their initial eligibility interview, have their claim referred to the IRB, and undergo an immigration medical examination.
.
To also help ease pressures, IRCC has begun to fast-track all work permit applications across Canada from asylum claimants with a commitment to process these within 30 days. In most cases, asylum claimants become eligible for interim federal health program, IFHP, coverage only after an officer has determined that their claim is eligible to be heard before the IRB. IFHP coverage is now available to asylum seekers who enter Canada between ports of entry in Lacolle, and are being processed on or after June 1, for those who have not yet had an eligibility interview.
.
To date, more than 5,600 persons have been issued this interim federal health program coverage under this special provision.
In closing, Chairs, IRCC, with the CBSA and all other partners in the federal family, continue to address irregular migration in accordance with Canadian and international law and in keeping with our values of an open and welcoming country.
A/Commr Joanne Crampton:
In terms of someone crossing the border between the ports of entry, the RCMP would intercept the person or persons. We then advise them that they are breaking the law under the Customs Act by crossing the border between ports of entry. The persons are then detained. Their possessions are searched to ensure there is no contraband or other illegal items. Their person is searched, because they are under arrest under the Customs Act. We then verify their identification. We do background checks and local indices checks, as well as international indices checks. If there is no noted criminality or concerns for national security and, once we have interviewed them and had a lengthy discussion as to where they came from and what their intentions are, if nothing negative comes as a result of that, we pass the individual over to Canada Border Services for further processing.
Mr. Jacques Cloutier:
At this point, for the CBSA, we receive the individual from the RCMP, as well as the information collected by the RCMP. We proceed with fingerprinting, taking of biometric information, and a cursory interview to elicit additional information. We verify identity. In those cases where we are satisfied that there are no immigration-related issues from an admissibility perspective, these individuals would be released on the terms and conditions and given an appointment to complete their eligibility interview. In cases where issues are discovered, several actions are taken immediately, including completing the interview for eligibility in its entirety, or proceeding with detention if the person is deemed to pose a risk to the public.
To be clear, the police are not detaining people illegally crossing the border for any length of time. Once identity (or who they allege to be) is determined, then they are released into Canada on a promise to appear.
Ms. Jenny Kwan:
If I may interrupt, I’ll ask if you can share this information with the committee then. Has the federal government provided any additional resources to provinces with these asylum seekers, not just for the housing component but also to support the asylum seekers as they wait for their claims to be processed?
.
Mr. Michael MacDonald:
The federal government does not provide direct support to provinces for asylum seekers awaiting their claims. The support comes at the permanent resident granting determination process, afterwards. That being said, we have taken various measures to help the provinces and to help asylum seekers by expediting across Canada all work permit applications and trying to—
.
Ms. Jenny Kwan:
If I may interrupt then, how many work permit applications have been processed and approved?
.
Mr. Michael MacDonald:
About six or seven weeks ago, we had over 6,000 work permit applications for all asylum seekers across Canada in our inventory. That is now almost eliminated, and we are processing in under 30 days any new asylum seeker’s work permit that is coming in from across Canada. We are doing those in well under 30 days. The idea is to help people get into the work force quicker.
Exactly, Very few if them will ever be forced to leave Canada. This is about putting them to work as cheap labour. Funny how the “conservatives” seem less apprehensive about illegals in this context.
Mr. Michael MacDonald:
The key to this from our perspective is allowing all asylum claimants to get their work permit faster and be able to enter the workforce if they have to.
.
At the same time, we work with community organizations as part of our regular outreach, and we do that across Canada so partnerships and getting that work permit is the key.
The abovhttps://www.ourcommons.ca/DocumentViewer/en/42-1/CIMM/meeting-71/evidencee is quotes from just one meeting held by the committee. Below are links for the others. Also, read the previous article done on the topic.
(1) https://www.ourcommons.ca/Committees/en/CIMM/StudyActivity?studyActivityId=9661587
(2) http://archive.is/elDlW
(3) https://www.ourcommons.ca/DocumentViewer/en/42-1/CIMM/meeting-71/evidence
(4) http://archive.is/uxtIR
(5) https://www.ourcommons.ca/DocumentViewer/en/42-1/CIMM/meeting-72/evidence
(6) http://archive.is/cAsj9
(7) https://www.ourcommons.ca/DocumentViewer/en/42-1/CIMM/meeting-73/evidence
(8) http://archive.is/H7uM7
(9) https://www.ourcommons.ca/DocumentViewer/en/42-1/CIMM/meeting-108/evidence
(10) http://archive.is/GBRrl
(11) https://www.ourcommons.ca/DocumentViewer/en/42-1/CIMM/meeting-112/evidence
(12) http://archive.is/zIFLn
(13) https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/89-611-x/89-611-x2003001-eng.pdf
12. Amnesty For Illegals Started Up
(Program launched in July:, 2019 PR-Path for illegals)
(Canadian Labour Congress)
See this previous piece, for more context on the situation. This is a start up amnesty program for illegals in Canada. It could lead to them (and family members) becoming permanent residents.
Ottawa, July 5, 2019 – Canada has launched a new temporary initiative to create a pathway to permanent residency for up to 500 out-of-status workers in the construction industry in the Greater Toronto Area (GTA). These construction workers have come to Canada and made contributions to its economy and currently have limited means to regularize their status.
And if this “temporary” initiative is deemed to be successful, then how much will it be extended by? Guaranteed it is not 500 people.
Over many years, even decades, some workers who have come to Canada with valid temporary resident status, and who have filled labour shortages in the construction industry, have fallen out of status. Previous changes, such as “four in, four out”, have resulted in some workers losing their status. These workers have continued to address significant labour shortages in the construction industry, while also contributing to the economy and their communities. Without valid immigration status, these workers and their families have lived in fear and been left feeling very vulnerable. The presence of out-of-status workers in a significant industry leads to depressed wages for Canadians and makes workers vulnerable to employer exploitation and abuse.
Over many years and decades? So the government admits that people have been overstaying visas or work permits for decades. Why hasn’t this been addressed long ago.
Illegals living in Canada leads to depressed wages? I would actually agree, but up to a point. Yes, the extra labour available does drive down wages. However, that would still be the case even if they were “legalized”. It would still be an abundance of cheap labour.
So how many illegals are there, particularly in major cities? Who knows, it’s not like we actually track who is leaving Canada.
13. Sanctuary Cities/Provinces
(Andrea Horwath ran to be Ontario Premier in June 2018. She offered the entire Province of Ontario to become a “sanctuary” Province)
NDP Leader Andrea Horwath dodged questions Tuesday about how much her campaign promise to declare Ontario a “sanctuary province” for illegal migrants and refugee claimants will cost taxpayers.
Instead, she said providing public services without asking questions about anyone’s legal status in Ontario, or co-operating with federal authorities to determine it, is the humane thing to do.
During the 2018 Provincial election campaign in Ontario, NDP Leader Andrea Horwath campaigned on (among other things), turning Ontario into a sanctuary province. She claimed providing social services to people with no legal right to be in the country was “humane”. Unsurprisingly, she refused to tell the public how much it would cost, fearing a backlash.
To be fair however, Conservative leader Doug Ford supported Toronto becoming a sanctuary city. So did his brother, Rob Ford. Both men claimed to be “populists” yet supported giving illegal aliens (with no right to be in the country), the right to remain in Toronto and receive taxpayer funded services. It also needs to be said that John Tory, the current mayor of Toronto, supports sanctuary cities as well. He used to be the leader of the Conservative Party of Ontario.
Not tracking the names and numbers of people leaving the country is bad enough. When corrupt politicians enact policies such as sanctuary cities/provinces it makes it a whole lot worse, as government officials are aiding and abetting in circumventing good policies.
While “Sanctuary Ontario” is not yet a reality, several sanctuary cities are, such as Toronto, Montreal, Hamilton and Edmonton. Also noteworthy is that “conservative” Ontario Premier Doug Ford supported Sanctuary Toronto when he was on the city council. Current Toronto Mayor John Tory (formerly the Ontario Conservative Leader) also supports sanctuary status for his city.
14. Impact Of Not Tracking Exits
These are some of the things that Canadians need to think about with regards to their borders. This list is not exhaustive.
- Temporary resident visas
- Electronic travel authorizations
- Inadmissibles let in under 24(1) of IRPA
- Inadmissibles let in under 25.2(1) of IRPA
- Hordes of student and temporary work visas
- Visa overstayers
- Work permits for illegals
- Amnesty for illegals
- Sanctuary cities/provinces
With all of these issues to consider, why would any sane government not want to have a strong and accurate entry/exit system at the borders? The only reason I can think of is that it is intentionally designed to fail.
Any serious leader would have crafted new rules right away, and used their executive power immediately to at least stop the bleeding. But much like Donald Trump and his “wall” Canadian Federal politicians are not serious about border security.