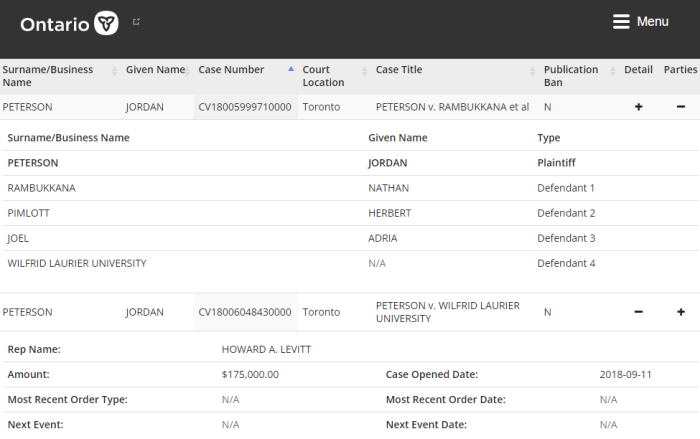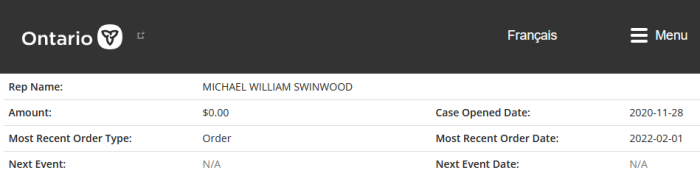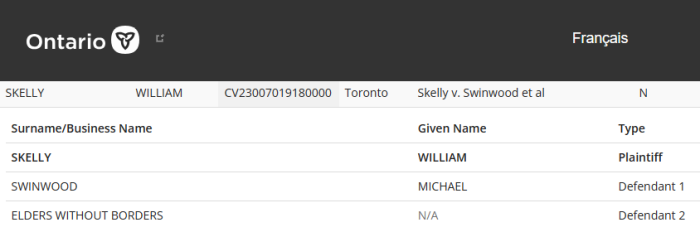
The Federal Court of Appeal partially overturned a 2023 ruling on injection mandates for over 600 Plaintiffs who had sued back in May 2022. This suit covered a broad range of employers, both part of the Government, and others regulated by Ottawa.
There were additional claims pleaded related to loss of mobility rights and freedom of travel. However, these seemed to be almost an afterthought. Primarily, this was a lawsuit over workers refusing to take the injections in the Fall of 2021.
Back in February 2023, Justice Fothergill struck the Claim for most (about 400) of the Plaintiffs without leave to amend. This meant that they wouldn’t be allowed to submit a new version. The other 200 or so saw their claims struck with permission to refile. A lump sum of $5,000 in costs was also awarded.
To explain this a little better: the Court created Schedules “A” and “B”, and lumped various employers into each. The “A” employers were part of the Federal Government. By contrast, The “B” employers weren’t part of the Government, but part of Federally regulated industries. The reason for this is that there’s a distinction in how their respective claims were to be handled.
Employees who fell into Group “A” were prohibited from going to Court at all over employment. The reason is that sections 208 and 236 of the Federal Public Sector Labour Relations Act allow the right to grieve, but not to sue.
Employees who fell into Group “B” were not necessarily restricted from going to going to Court. However, the pleadings were so horribly written that a new version would need to be created. The Court referred to it as “bad beyond argument”, and for “substantially the same reasons” as the Action4Canada case, it had to be struck. As with the Vaccine Choice Canada case, this one failed to follow the basics of civil procedure — once again.
That said, with this Appellate ruling, all Plaintiffs will be allowed to file something.
What this means is that everyone will be able to make claims for restrictions on their movements. That can still go ahead. However, the employment claims for all Schedule “A” litigants are still barred, with the possible exception of those employed by the RCMP. They’re governed by different provisions in the FPSLRA.
One of the problems with having so many Plaintiffs is that there’s no information pleaded about any of them specifically. Instead, generalizations are made, without reference to who it applies to. As for the travel restrictions, it’s unclear which litigants are alleging it.
Hopefully, these people will retain a competent lawyer this time.
Alternatively, maybe counsel will take a remedial refresher course on how to plead documents.
- Canada Opportunities Agency
- Canada Border Services Agency
- Canada Revenue Agency
- Canada School of Public Service
- Canadian Coast Guard (Department of Fisheries and Oceans)
- Canadian Food Inspection Agency*
- Canadian Forestry Service (Department of Natural Resources)
- Canadian Institutes of Health Research*
- Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission*
- Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission
- Canada Revenue Agency*
- Canadian Security Intelligence Service*
- Core Public Service
- Canadian Space Agency
- Correctional Service of Canada
- Courts Administration Service
- Department of Agriculture and Agri-Food
- Department of Canadian Heritage
- Department of Employment and Social Development
- Department of Fisheries and Oceans
- Department of Justice
- Department of National Defence
- Department of Natural Resources
- Department of Transport
- Department of Veterans Affairs
- Elections Canada (“Office of the Chief Electoral Officer” and “The portion of the federal public administration in the Office of the Chief Electoral Officer in which the employees referred to in section 509.3 of the Canada Elections Act occupy their positions”)
- Environment and Climate Change Canada (Department of the Environment)
- Federal Economic Development Agency for Southern Ontario
- Global Affairs Canada (Department of Foreign Affairs, Trade and Development)
- Government of Canada
- Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (Department of Citizenship and Immigration)
- Indigenous and Northern Affairs Canada (Department of Crown-Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs)
- Indigenous Services Canada (Department of Indigenous Services)
- Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada
- National Film Board of Canada (National Film Board)*
- National Research Council Canada*
- National Security and Intelligence Review Agency (National Security and Intelligence Review Agency Secretariat)*
- Office of the Auditor General of Canada*
- Parks Canada*
- Polar Knowledge Canada (Canadian High Arctic Research Station)*
- Public Health Agency of Canada
- Public Safety Canada (Department of Public Safety and Emergency Preparedness)
- Public Services and Procurement Canada
- Royal Canadian Mounted Police**
- Service Canada (Department of Employment and Social Development)
- Shared Services Canada
- Staff of the Supreme Court
- Statistics Canada
- Treasury Board
NOTES:
All organizations are part of the core public administration as defined at s 11(1) of the Financial Administration Act (Schedules I and IV), except as noted.
- Organizations that are portions of the federal public administration listed in Schedule V (Separate Agencies of the Financial Administration Act, whose employees have rights to grieve under the Federal Public Sector Labour Relations Act).
** The RCMP is part of the core public administration and is listed in Schedule IV of the Financial Administration Act; RCMP members have limited rights to grieve under s 238.24 the Federal Public Sector Labour Relations Act, but have other grievance rights under the Royal Canadian Mounted Police Act.
- Air Canada
- Air Canada Jazz
- Air Inuit
- Bank of Canada
- Bank of Montreal
- BC Coast Pilots Ltd
- BC Ferries
- British Columbia Maritime Employers Association
- Brookfield Global Integrated Solutions
- Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation
- Canada Pension Plan
- Canada Post
- Canadian National Railway
- Canadian Pacific Railway
- City of Ottawa Garage Fed Regulated
- DP World
- Export Development Canada
- Farm Credit Canada
- G4S Airport Screening
- Garda Security Screening Inc
- Geotech Aviation
- Global Container Terminals Canada
- Greater Toronto Airports Authority
- House of Commons
- Human Resources Branch, Innovation
- Kelowna Airport Fire Fighters
- National Arts Centre
- NAV Canada
- Ontario Northland Transportation Commission
- Ontario Power Generation
- Pacific Pilotage Authority
- Parliamentary Protection Service
- Public Sector Pension Investment Board
- Purolator Inc
- Questral Helicopters
- RBC Royal Bank
- Rise Air
- Rogers Communications Inc
- Royal Canadian Mint
- Sasktel
- Scotiabank
- Seaspan Victoria Docks
- Shaw
- Skynorth Air Ltd
- Telesat Canada
- Via Rail Canada
- Wasaya Airways
- Waterfront Employers of British Columbia
- Westjet
- Westshore Terminals
- Did the Federal Court err in determining that the plaintiffs employed by the RCMP were subject to the bar in section 236 of the FPSLRA?
- Did the Federal Court err in determining that the bar in section 236 of the FPSLRA forecloses the right of action for claims in respect of the Interim Order and other travel related restrictions?
- Did the Federal Court err in striking, without leave to amend, the claims related to the TB Policy made by the plaintiffs who were employed by the organizations listed in Schedule “A” to the Federal Court’s Reasons?
- Did the Federal Court err in finding certain other claims to be non-justiciable?
- Did the Federal Court err in striking the Statement of Claim due its being generally improper and failing to plead necessary material facts?
[42] On the first issue, I conclude that the Federal Court erred in finding that the bar in section 236 of the FPSLRA applies to the plaintiffs who were members of the RCMP.
[43] It will be recalled that subsection 236(1) of the FPSLRA provides that the “right of an employee to seek redress by way of grievance for any dispute relating to his or her terms or conditions of employment is in lieu of any right of action that the employee may have in relation to any act or omission giving rise to the dispute”.
[44] To recall, the relevant definition of what constitutes a grievance is set out in subsection 206(1) of the FPSLRA. That section states that a grievance is one that may be filed under either section 208 or 238.4 of the FPSLRA. Thus, the bar in section 236 applies only to those who could seek redress via a grievance under section 208 or 238.4 of the FPSLRA.
[45] Yet, section 238.4 of the FPSLRA applies only to grievances arising under a collective agreement applicable to RCMP members who meet the statutory definition of “employee” in the FPSLRA. Based on the materials that were before the Federal Court and that are now before this Court, it is impossible to ascertain whether any collective agreement has been negotiated for RCMP members. The National Police Federation was certified as the bargaining agent for RCMP members in 2019 by the FPSLREB in National Police Federation v. Treasury Board, 2019 FPSLREB 74. However, it is unclear if a collective agreement has been achieved and, if so, whether a challenge to the TB Policy could be the subject of a grievance under any such agreement. Given this lack of information, it is not plain and obvious that the plaintiffs who were members of the RCMP possessed rights to grieve the TB Policy under a grievance to which section 238.24 of the FPSLRA pertains.
The RCMP Plaintiffs may still have their employment claims struck at some point. However, with the information available on this Motion, they couldn’t be now.
[53] The Federal Court therefore erred in finding that the plaintiffs’ claims related to the Interim Order and other travel-related measures could have been grieved or were subject to section 236 of the FPSLRA. While these claims suffer from the lack of proper pleadings and a failure to plead the necessary material facts that characterize the Statement of Claim generally, they should not have been struck without leave to amend. If properly pleaded, it may perhaps be possible for the plaintiffs to raise a claim that could come within the jurisdiction of the Federal Court. Without seeing an amended pleading, however, it is impossible to discern whether or not a valid claim might be advanced. The plaintiffs therefore should have been granted leave to amend the claims related to the Interim Order and other travel-related measures on the same basis as the Federal Court allowed other claims to be amended.
All Plaintiffs should be given the right to have their travel-related claims heard.
In fairness to Justice Fothergill, it was unclear who exactly was pleading that their travel related rights were infringed. The Statement of Claim was so lacking in detail that it was impossible to tell.
[54] On the third issue, I conclude that the Federal Court did not err in striking, without leave to amend, the claims related to the TB Policy made by the plaintiffs who were employed by the organizations listed in Schedule “A” to the Federal Court’s Reasons, other than the RCMP. However, the Federal Court erred in striking the claims of RCMP members related to the TB Policy.
[55] It is not disputed that the plaintiffs who were employed by organizations other than the RCMP could have filed grievances under section 208 of the FPSLRA challenging the TB Policy or its application to them. As noted, the TB Policy was a term and condition of employment and thus subject to grievance under section 208 of the FPSLRA, which allows the employees of the organizations listed in Schedule “A” to the Federal Court’s Reasons other than the RCMP to file grievances relating to their terms and conditions of employment. That said, the FPSLREB recently held in Rehibi v. Deputy Head (Department of Employment and Social Development, 2024 FPSLREB 47, that a grievance challenging the application of the TB Policy could not be referred to adjudication due to the fact that only a subset of matters that may be grieved under the FPSLRA may be referred to adjudication under subsection 209(1) of the FPSLRA.
[64] Since the defendants sought to strike the Statement of Claim based on the fact that a grievance process was available, it was incumbent on the defendants to establish that the TB Policy could have been grieved by RCMP members. However, no evidence was tendered on this issue and the statutory scheme is not sufficiently clear to definitively establish that the TB Policy could have been grieved by RCMP members. I therefore conclude that the Federal Court erred in striking the claims of RCMP members related to the TB Policy without leave to amend. The plaintiffs who were members of the RCMP should have been granted leave to amend their claims related to the TB Policy on the same basis as the plaintiffs who were employed by organizations other than those listed in Schedule “A” to the Federal Court’s Reasons were granted leave to amend.
Since the RCMP are governed by a different part of the FPSLRA, the Federal Court of Appeal concluded that their employment claims shouldn’t have been struck under s.236. That’s not to say that it may not happen anyway. That said, all other Schedule “A” Plaintiffs are out of luck.
This is a pattern that’s become more obvious: lawyers bringing cases to Court that involve Government and/or union workers. There’s almost always some legislation or collective bargaining agreement that gets these thrown out.
See below, under the “precedents” section. Since the 2023 decision, 5 more cases have been thrown out (4 in Federal Court, and 1 in B.C. Supreme Court) citing this Adelberg ruling as precedent.
[65] I see no error in the Federal Court’s determination that allegations of criminal behaviour, broad declarations respecting the current state of medical and scientific knowledge, and a declaration that administering medical treatment without informed consent is a crime against humanity, are not justiciable in a civil action.
[66] As for the validity of the TB Policy and the Interim Order, it would appear that those issues may now well be moot. In addition, while it might have been possible to argue that the policies at issue were invalid in the context of a justiciable claim for relief on some other basis in accordance with the decision of the Supreme Court of Canada in Canada (Attorney General) v. TeleZone Inc., 2010 SCC 62, [2010] 3 S.C.R. 585, the Federal Court did not err in holding that an order setting aside the TB Policy and the Interim Order could only be obtained by way of an application for judicial review.
[67] I accordingly see no basis for setting aside any of the foregoing rulings made by the Federal Court.
This is comical and goofy. Experienced lawyers should know what Courts can and cannot adjudicate over. It reeks of incompetence that this keeps happening over and over again.
Bad beyond argument.
[68] Finally, I see no error in the Federal Court’s finding that the Statement of Claim was improperly pleaded and lacked the necessary material facts. As noted in Mancuso v. Canada (National Health and Welfare) 2015 FCA 227, [2015] F.C.J. No. 1245 at para. 16, a plaintiff must plead, in summary form, but with sufficient detail, the constituent facts to support the relief sought. As the Federal Court rightly noted in this case, for the claims in respect of which leave to amend is granted, the plaintiffs must set out with sufficient particularity the facts they rely on in support of their claim, including details of how they were specifically impacted by the policies they impugn and the bases for and all material facts necessary to ground the claims advanced. The Statement of Claim, as drafted, is entirely devoid of these necessary material facts.
[69] I therefore see no reviewable error in the decision to strike the Statement of Claim in its entirety. However, leave to amend it should be granted to all the plaintiffs in accordance with these reasons.
This is common sense, or at least it should be. If you want to sue someone, you have to spell out the allegations with enough specific detail that they can respond to it.
Here’s he TL, DR (too long, didn’t read) version of things:
(1) Members and former members of the RCMP may still be able to bring employment related claims around their refusal to take the injections.
(2) All Plaintiffs — both Schedules “A” and “B” — can make travel related claims
(3) Other than RCMP, all other Schedule “A” Plaintiffs have their employment claims barred
(4) The Statement of Claim is filled with issues a Civil Court can’t preside over
(5) The Statement of Claim fails to comply with the Rules of Civil Procedure, and doesn’t plead the facts necessary to be properly responded to.
(6) The $5,000 cost award is set aside, and no costs were awarded here.
The “bad beyond argument” findings of Justice Fothergill (here), and Justice Ross (Action4Canada) have been upheld. Neither case was pleaded in a coherent manner. And both needed to be redone. It’s still mind boggling that veteran lawyers don’t understand how to draft documents.
While all Plaintiffs can now go ahead with something, a few questions:
(a) Since the Schedule “A” employment claims are still prohibited, will there be an attempt to appeal to the Supreme Court of Canada? That was promised after all.
(b) Since so much time has passed, will any new allegations be barred by the Statute of Limitations? For most things, there’s a 2 year time limit.
(c) Will any more of the litigants discontinue their case? Will others try to proceed, but with more “effective” counsel?
(d) Considering that Action4Canada never bothered to file an amended Notice of Civil Claim, even 4 months after “winning” their Appeal, will this happen here too? Will these Plaintiffs call their critics “paid agitators“?
FEDERAL VAXX PASS CHALLENGE (APPEAL)
(1) FCA Adelberg V. HMTK A-67-23 Notice Of Appeal
(2) FCA Adelberg V. HMTK A-67-23 Appeal Book
(3) FCA Adelberg V. HMTK A-67-23 Appellants MFL
(4) FCA Adelberg V. HMTK A-67-23 Respondents MFL
FEDERAL VAXX PASS CHALLENGE
(1) https://policeonguard.ca/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/Filed-SOC.pdf
(2) Federal Court Vaccine Mandate Challenge
(3) Federal Vaccine Passport Challenge Retainer Agreement
(4) Federal Court Vaccine Mandate Challenge Motion To Strike
(5) Federal Court Vaccine Mandate Challenge Affidavit Of Service
(6) Federal Court Vaccine Mandate Challenge Responding Motion Record
(7) Federal Court Of Canada Rules
(8) Federal Court Decision On Motion To Strike (Archive)
(9) https://decisions.fct-cf.gc.ca/fc-cf/decisions/en/item/522970/index.do
(10) https://www.canlii.org/en/bc/bcsc/doc/2022/2022bcsc1507/2022bcsc1507.html
(11) https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/regulations/sor-98-106/page-9.html#h-1013947
(12) https://www.laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/acts/P-33.3/page-13.html#h-406405
PRECEDENTS CREATED
(1) https://www.canlii.org/en/ca/fct/doc/2023/2023fc280/2023fc280.html#par85
(2) https://www.canlii.org/en/ca/fct/doc/2023/2023fc929/2023fc929.html#par17
(3) https://www.canlii.org/en/bc/bcsc/doc/2023/2023bcsc1701/2023bcsc1701.html#par30
(4) https://www.canlii.org/en/ca/fct/doc/2023/2023fc1752/2023fc1752.html#par24
(5) https://www.canlii.org/en/ca/fct/doc/2024/2024fc137/2024fc137.html#par44
MONEY
(1) Letter to Federal Worker Plaintiffs
(2) Federal Workers Action Donation Link For PayPal
(3) Ontario First Responders Action Donation Link For PayPal
(4) School Action Donation Link For PayPal
(5) Police Officer Action Donation Link For PayPal
(6) https://www.web.archive.org/web/20220526170932/https://www.constitutionalrightscentre.ca/
(7) Federal Workers Retainer Agreement
(8) Ontario First Responders Retainer Agreement
(9) Donate To Public Citizens Inquiry
(10) Donations For Supposed B.C. Doctors Action