
1. Important Links
CLICK HERE, for the Climate Change Scam Part I.
CLICK HERE, for Part II, the Paris Accord.
CLICK HERE, for Part III, Saskatchewan Appeals Court Reference.
CLICK HERE, for Part IV, Controlled Opposition to Carbon Tax.
CLICK HERE, for Part V, UN New Development Funding.
CLICK HERE, for Part VI, Disruptive Innovation Framework.
CLICK HERE, for Part VII, Blaming Arson On Climate Change.
CLICK HERE, for Part VIII, Review Of Green New Deal.
CLICK HERE, for Part VIII(II), Sunrise Movement & Green New Deal.
CLICK HERE, for Part IX, Propaganda Techniques, Max Boykoff.
CLICK HERE, for Part X, GG Pollution Pricing Act & Bill C-97.
CLICK HERE, for part XI, Dr. Shiva Ayyadurai Explains Paris Accord
2. US & Canadian Copyright Laws
Disclaimer #1: The Canadian Copyright Act has a “fair dealing” provision, which allows for copyrighted material to at times be used for specific purposes: research, private study, education, parody, satire, criticism, review and news reporting. Click Here and also Click Here for more information.
Disclaimer #2: The U.S. Copyright Act has a “fair use” provision, which states that the fair use of a copyrighted work, including such use by reproduction in copies or phonorecords or by any other means specified by that section, for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, teaching (including multiple copies for classroom use), scholarship, or research, is not an infringement of copyright. Click Here to read the text.
This should be obvious, but just to clarify, this article is about criticizing, commenting on, teaching and researching purposes.
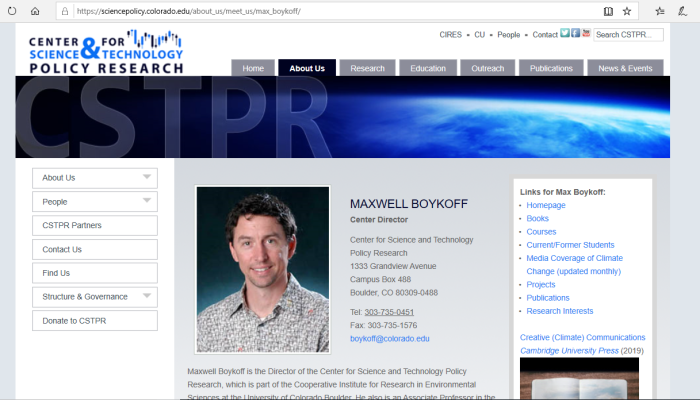
3. About The Author, Maxwell Boykoff
His professional biography is available here.
Max’s research and creative work has developed primarily in two arenas:
(1) cultural politics of science, climate change and environmental issues = this refers to ways that attitudes, intentions, beliefs and behaviors of individuals and groups shape (and are shaped by) the perceived spectrum of possible action in the context of science-policy, climate change and environmental issues.
.
(2) transformations of carbon-based economies and societies (with emphasis on the interface of science and practical action) = this refers to decarbonization politics, policies and decision-making, with particular interest in how these activities find meaning in people’s everyday lives, as well as how they, in turn, feed back into science-policy decision-making.
Feel free to check into his other works.
Now for the book itself.
4. Table Of Contents
(1) Here And Now
(2) How We Know What We Know
(3) Do The Right Thing
(4) Ways Of Learning, Ways Of Knowing
(5) It’s Not You, It’s Me…. Actually It’s Us
(6) Academic Climate Advocacy & Activism
(7) Silver Buckshot
(8) Search For Meaning
5. Quoting Creative Climate Communications
(From back cover) Conversations about climate change at the science-policy interface and in our lives have been stuck for some time. This handbook integrates lessons from the social sciences and humanities to more effectively make connections through issues, people and things that everyday citizens care about. Readers will come away with an enhanced understanding that there is no “silver bullet” to communications about climate change; instead a “silver buckshot” approach is needed where strategies effectively reach different audiences in different contexts.
One thing that will be clear right away: this is not about using scientific methods to PROVE that climate change is a serious threat. Rather, it is about using scientific methods to CONVINCE people that climate change is a serious threat. Very different things.
We live in remarkable times. Amidst high-quality and well-funded research into the causes and consequences of climate change, conversations in our lives — and climate communications — are stuck. Consciously or unconsciously, a feeling of complacency has often weighed on our collective and our individual selves.
Another point made early on, Boykoff expresses no doubt whatsoever in the “scientific findings” of the climate change movement. The entire focus of the book is about using social science and humanities research to persuade people this is a problem.
(Page 2) Responding to these emergent needs, in recent years has been a blossoming of valuable research in the peer-review literature addressing various elements of this larger challenge. More research groups, organizations, institutions and practitioners around the world have increasingly explored creative spaces of climate communication to better understand what works where, with whom (what audiences), when and why.
Boykoff makes an important note here. He is not by any means a revolutionary here. “Climate communications” is a growing field, with people all over the world trying to determine better methods for “selling” the climate change claims. In short, this is research about marketing. Not science.
(Page 2) Creative approaches involve the deployment of multimodal communications. A mode is a system of choices used to communicate meaning. What might count as a mode is an open-ended set, ranging cross a number of systems, including but not limited to language, image, color, typography, music, voice, quality, dress, posture, gestures, special resources, perfume and cuisine.
What superficial points are listed?
- language
- image
- colour
- typography
- music
- voice
- quality
- dress
- posture
- gestures
- special resources
- perfume
- cuisine
We are still just on the second page, and already getting an introduction into the very superficial traits which can subtly be used to convince people of our arguments.
Forget facts, research, data, and logic. This is all about presenting a good sales pitch.
(Page 3) Among many elements seeping into the environments, I consider the dynamics that shape creative and potentially effective messages as well as messengers of those climate change communications. Over time, broad references to communications through media platforms have generally pointed to television, films, books, fliers, magazines, radio and internet for pathways for largescale communications.
Additional modes and manifestations of communications also include (analyses of) documentary films about dystopian futures, stand-up comedy about climate and cultures, podcasts about climate science and policy interactions.
Boykoff notes the traditional forms of media, but laments that they are not enough by themselves to do the job. The job of course, is “pitching” the climate change agenda.
(Page 4) Meeting people where they are takes carefully planned and methodical work. It does not mean “dumbing things down” for different audiences. Through this process of assessment of research and practice in these areas, conversations can more capably seek answers to a provocative question Mike Hulme posted in 2009, “How does the idea of climate change the way we arrive at and achieve our personal aspirations and our collective social goals?”
(Page 5) KNOW THY AUDIENCE
These creative (climate) communication endeavors must start with consideration of the audience. These may be imagined, (un)intended or actual audiences. Researchers and practitioners have increasingly paid attention to differentiated audiences as key components to deliberate development of effective communication.
Knowing who your audience is actually a useful piece of advice, regardless of circumstances. However, in context of this book, it comes across as manipulation.
(Page 6) Audience segmentation and consequent message alteration has been a part of marketing and associated communications strategies since the 1950s (Smith 1956, Slater 1996). Audience segmentation endeavours as they relate to climate change communications, have proliferated over the last decade (Leal Finho 2019).
This book is about marketing strategies of climate change “communications”. Nothing more. It is about manipulative techniques designed to persuade by non-factual means.
6. Where Things Go From Here
The book is 300 pages, the last 60 of which are references. No doubt that an awful lot of work has gone into this. Yes, the intro article is relatively short, but it is setting the stage for later. Sequels will be longer and quote much more.
As alluded to earlier, this is really a book about marketing. It’s not about research done to prove that humans are causing climate change, but rather research to CONVINCE people that they are.
Rather than going into environmental research, the book delves in sociological and social psychological research methods. It looks at work previously done in the fields of persuasion, and applies those principles to “climate communications”.
Boykoff appears to have no doubts about humans causing climate change. Nor does he seem to have any reservations about using these social studies techniques to pursue what is essentially a political goal. He straightforwardly admits that it’s a growing field, and many have contributed to this area of research.
Boykoff admits that this area is “selling” or “pitching” the climate change narrative. While acknowledging it is a start, he has no problems with it. Seems the scientists have given up on the research area of climate science, and are throwing their resources into the marketing aspect.
It’s both nefarious and creepy.