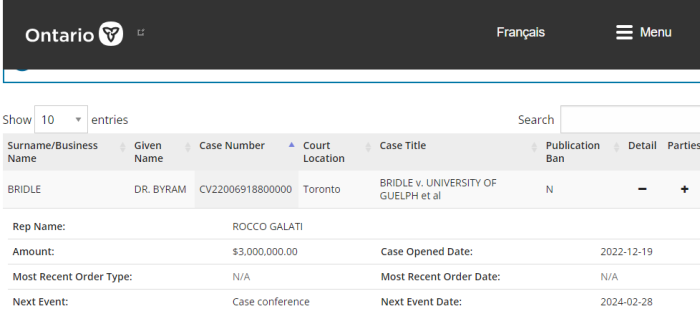
Wednesday, February 28th, 2024, Byram Bridle, the high profile professor from the University of Guelph, was back in Court. This was a short hearing to set down another anti-SLAPP Motion to dismiss his December 2022 lawsuit.
Guelph has previously filed a Statement of Defence, on behalf of all their Defendants. But now, their lawyer, Lynn Turnbell, is asking that the case be thrown out altogether. Their stated reason is that the contents of the Claim are covered under Section 137.1 of the Courts of Justice Act, which is the anti-SLAPP provision.
Guelph further states that the subject matter should be tossed for a lack of jurisdiction. Bridle is a university employee, as are most Defendants. It’s argued that the matter should have gone to arbitration instead of litigation. And they’re not wrong.
The initial anti-SLAPP Motion was filed by Kate Costin, the lawyer for David Fisman. Yes, it’s that David Fisman. It’s unclear why his content (Twitter related) is being connected to this. That will be heard on November 19th, 2024.
Counsel for Bridle requested that everything be moved back to 2025. He stated that he will be taking his annual 2 month vacation to Turkey — for medical reasons.
However, Justice Dow refused that request. The Fisman anti-SLAPP Motion will still be heard in November 2024, and the Guelph Motion is now booked for October 16th, 2025.
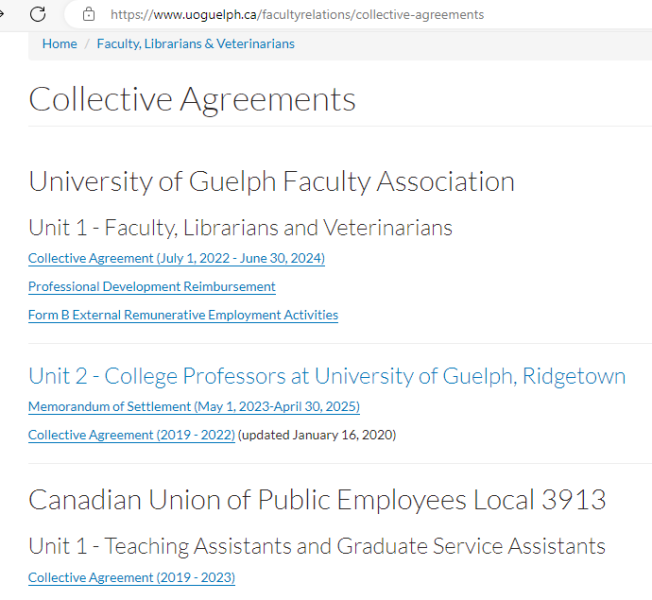


The University of Guelph publicly posts their collective bargaining agreements, which include ones with faculty members. This particular one took only seconds to find.
Article 40 of the agreement, beginning on page 131, makes it clear the steps that are to be taken in the event of a serious problem within the university.
- Informal resolution
- Formal grievance
- Arbitration
This wasn’t difficult to find. Not only does Bridle presumably have a copy of this document, but it’s publicly available on the school’s website.
True, there may be the power of a Court to review the findings of an Arbitrator, depending on the rules that are set out. This would be analogous to filing an Appeal. However, what happened here was suing in Court instead of going to arbitration. These are not the same thing.
40.1 The Parties agree to attempt to resolve disputes arising from this Agreement amicably and promptly.
40.2 In order to ensure that Grievances of Members are remedied in a reasonable, just, and equitable manner, the University and the Association mutually agree that the procedure for submitting and dealing with Grievances shall be as indicated in the remainder of this Article.
Informal Resolution
40.9 The University and the Association mutually agree that it is the desire of the Parties that differences in the interpretation, application, administration, and alleged violations of this Agreement shall be dealt with as quickly as is reasonably possible. If a Member has a complaint or dispute that may give rise to a Grievance, they and/or an Association designate shall first discuss the matter at a meeting arranged for this purpose with the Dean, University Librarian, or, in the case of Veterinarians, Director, or designate, within twenty (20) days after the Member would reasonably be expected to have become aware of the circumstances giving rise to the complaint or dispute.
40.11 Failing informal resolution of the complaint or dispute and within ten (10) days following receipt of notification of the proposed resolution under the informal process, the Association has the right to present the written Formal Grievance to the Provost, or designate, pursuant to this Article.
Formal Grievance Procedure
40.14 Following receipt of a Formal Grievance, the Provost, or designate shall convene a meeting within ten (10) days with the Member and/or the Association designate. With reasonable notice to the other Party prior to the meeting, either Party may have others attend who have information relevant to the specific Grievance. The Provost (or designate) shall reply in writing within fifteen (15) days of that meeting.
40.19 Failing resolution of a Grievance, the University or the Association will provide notification that a matter shall be submitted to Arbitration. Such notification must be made in writing and addressed to the other party within fifteen (15) days of the date of receipt of the Formal Grievance decision.
40.22 The decision of the Arbitrator shall be final and binding upon the Parties.
40.23 All arbitration expenses, including the remuneration of the Arbitrator, shall be shared equally by both Parties, subject to the award of costs by the Arbitrator as part of the remedy.
Looking at Article 40.22, it seems that the Arbitrator’s ruling is meant to be final. There’s no obvious way to challenge it further, unless the process is demonstrated to be corrupted. Since no arbitration took place, that would be difficult to prove.
The process outlined is pretty straightforward: (a) informal resolution; (b) formal grievance; and (c) arbitration, if needed. There’s no mention whatsoever about having an option to pursue litigation. This is typical in unionized and Government workplaces.
But according to the Statement of Claim, that’s not what happened.
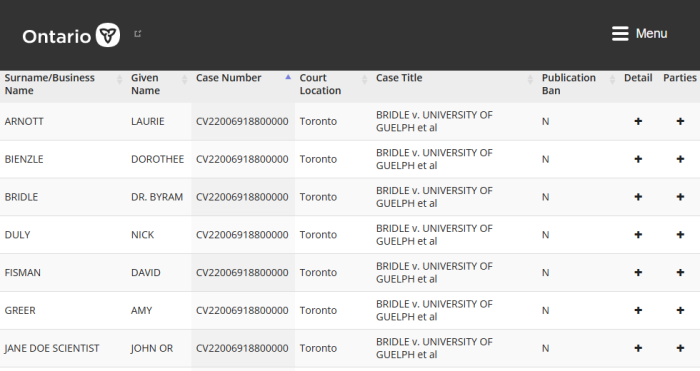
After the grievance process went against Bridle, he didn’t pursue arbitration. Instead, he sued everyone involved. This included Nick Duley, and outside HR consultant, who was hired for an investigation. Also named is Laurie Arnott, Vice President of Faculty Relations. It’s alleged that there’s a grand conspiracy against him.
Paragraph 100, it’s stated that Guelph refused to investigate online harassment that happened outside of school grounds. It fell outside the scope of the collective bargaining agreement, and hence, no ability to do anything. This comes across as reasonable.
Paragraph 136 of the Claim says that Bridle refused to participate in Duley’s investigation, calling it a “kangaroo court”. Duley is referred to as a “hired gun”. That won’t sit well without proof.
The content in the Claim comes across as being so over the top, it’s difficult to determine what’s factual, and what’s overblown.
Now, it’s possible that the Court may find that the grievance process was corrupted and unworkable, but that’s for the Plaintiff to establish. This is sometimes referred to as “residual jurisdiction”. While a major conspiracy is alleged, it seems that it would be very difficult to prove.
Fisman appears to have nothing to do with the University of Guelph, so including him in this case seems unproductive. Even if he did interact with some of the online content, he’s not involved in essentially what is a workplace dispute at Guelph. Considering how hard it is to prove defamation, and to get damages, this will be a tough sell in November.
The Kulvinder Gill/Ashinder Lamba, Boraks and CSASPP cases are also good examples of how much bad lawyering can impact clients.
Gill v. Maciver, 2022 ONSC 1279
Gill v. Maciver, 2022 ONSC 6169
Gill v. Maciver, 2023 ONCA 776
Boraks v. Hussen, 2023 ONSC 4294
Boraks v. Hussen, 2023 ONSC 6420
Galati v. Toews et al, 2023 ONSC 7508
Galati v. Toews et al, 2024 ONSC 935
There’s also this gem from March 2021, with a Motion scheduled for this Fall.
The trend in recent years is to implement mechanisms designed to screen out cases as abusive. For defamation type cases, these are called anti-SLAPP laws. SLAPP is of course an acronym for a strategic lawsuit against public participation.
Again, it’s hard to tell from this Statement of Claim what’s real, and what’s hype and distortion. Hopefully, more will come out in the pending Motions.
To survive an anti-SLAPP Motion, the Plaintiff is required to prove at least some of the damages. This means submitting Affidavit evidence, and being cross examined on it. The Plaintiff must also establish that there are no reasonable defences that could be relied upon. Will this happen?
It’s possible that there will be a negotiated settlement to discontinue the case entirely. Although s.137.1(5) “stays” the case, the parties can always agree to drop it. This sort of thing has happened many times before.
If not, it’s going to be very expensive for Bridle. He’s facing full indemnity (100% of costs) on 2 separate anti-SLAPP Motions. This could set him back $100,000 or more. Courts tend to be very harsh to Plaintiffs who bring lawsuits to silence public speech improperly.
An open question is why this case was even brought. Even a quick read through the collective bargaining agreement would have indicated that this was not the path to take. Should the Guelph Motion not succeed under anti-SLAPP provisions, it will likely still get dismissed due to lack of jurisdiction.
Reading through the Claim, it looks as though large parts of this are simply cut and pasted from earlier lawsuits. The same sorts of allegations come up over and over again. This isn’t original content.
It appears that Bridle was poorly advised both in employment law, and defamation law.
(1) https://www.ontario.ca/page/search-court-cases-online
(2) https://canucklaw.ca/wp-content/uploads/Byram-Bridle-Statement-Of-Claim.pdf
(3) https://canucklaw.ca/wp-content/uploads/Byram-Bridle-Statement-Of-Defence.pdf
(4) https://canucklaw.ca/byram-bridle-lawsuit-unlikely-to-ever-get-anywhere/
(5) https://www.uoguelph.ca/facultyrelations/collective-agreements
(6) https://www.uoguelph.ca/facultyrelations/system/files/UGFA_CA_2022_FinalPrint_Nov20_2023.pdf

I like that word “lawyering”. First time I came across it, was, BC Chief Justice Alan McEachern using it in an article about suing for ‘defamation’. His candid opinion being = such suits are “great entertainment”.
and who would this un-named legal counsel be in these cases of “bad lawyering” ? We can guess,