Universal Ostrich Farms (UOF), in British Columbia, has been in the alternative media a lot lately. Specifically, the Canada Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) ordered about 400 birds to be killed after some supposedly tested positive for the H5N1 virus.
UOF filed an Application in Federal Court to challenge the order. A second Application was filed challenging the refusal to grant any sort of exemption. To date, both cases have been dismissed. Barring a successful Appeal, the culling is expected to go ahead.
See Parts 1 and 2 in the Universal Ostrich Farms series for more information.
The first two pieces have interestingly caused quite the backlash. The bulk of it is simply reading from various Court documents, including Affidavits. What people don’t seem to grasp is that when someone asks for money, it becomes public interest litigation. The have GiveSendGo and GoFundMe pages up, among other avenues, soliciting donations.
As such, their case is open to scrutiny, or at least it should be.
Now, let’s see what David Bilinski has to say.
From The Affidavit Of David Bilinski
13. One of the problems we encountered though was there was no good breeding records for ostriches. To starts a recording program, I initiated a DNA fingerprinting program for ostriches in Canada. I worked wit Dr. Kim Cheung, a director of the Avian Research Centre at the University of British Columbia, to develop this program.
14. Unfortunately, shortly after starting the program, the market for breeding ostrich collapsed, and the program was suspended.
19. The antibodies ostriches produce in response to an infection can last several years, and are found in extremely high concentrations in the yolks of their eggs. These antibodies can be used to develop neutralization anitbodies against, among other things, the H5N1 virus. I have attached as Exhibit “B” a true copy of the study published by Dr. Yasuhiro Tsukamoto, Laboratory of Veterinary Anatomy, Graduate School of Biology and Environmental Sciences, Osaka Prefecture University.
34. When the COVID-19 pandemic hit in March 2020, it essentially shut down our business. Processing plants closed, breeder sales plummeted, and farms downsized.
35. We then became familiar with the work of Dr. Tsukamoto, who was studing the IgY Immune Globin Yolk) antibodies in ostrich eggs.
36. Based on Dr. Tsukamoto’s and others’ research, we learned that ostrich eggs are uniquely situated for developing antibodies because of the size of the yolk, and the concentration of the antibodies produced.
39. As a result, we began working with [Immune] Biosolutions Inc. (“Biosolutions”) in Quebec, which was working on protocols to produce antibodies for Covid-19, due to a $13,000,000 grant from the Government of Canada.
40. In or around 2021, Biosolutions provided antigens to the UOF, which then allowed us to produce antibodies using the ostrich eggs.
42. Then, in about 2022, UOF began a venture with Struthio BioScience Inc. (“Struthio”) and entered into a contract wherein UOF must provide Struthio with ostrich eggs, failing which UOF would be in breach of contract.
43. In summary, since 2020 UOF has been entirely dedicated to the production of antibody IgY.
44. To be clear, UOF is not a commercial poultry facility, and it does not produce any ostrich meat or eggs for human consumption.
It would be nice to know more about this DNA fingerprinting program, even if it was ultimately cancelled. Perhaps a later piece can cover that.
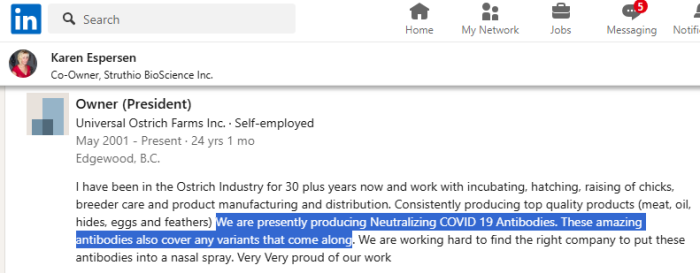
Bilinski tries to portray to the Court there being a “contract” between Universal Ostrich Farms and Struthio BioScience Inc. This is apparently to fulfill business obligations. However, Karen Espersen is both the owner (and president) of UOF, and a co-owner of Struthio. This connection is obvious when looking at her LinkedIn page, but isn’t clear in the Court documents.
Defenders of the farm have pointed to the fact that Immune Biosolutions is the one that got the contract from the ISED, not the farm. While true, it misses the point. Espersen and Bilinski are working with them, and using their antigens, giving it to the ostriches, and creating antibodies in return.
In turn, it then raises all kinds of questions as to what exactly these birds are infected with, and what the risks are to humans. This apparently isn’t explained in any Affidavit.
Despite howls about “protecting the food supply”, Bilinski’s Affidavit makes it clear that these animals aren’t intended for any sort of human consumption. This ostrich farm really is an open-air biolab.
The irony also seems lost on these litigants. They’re challenging the findings that some of the birds are infected with a virus, claiming that these tests are unreliable. Fair enough. But then, the birds are used to generate antibodies to fight another virus. In fact, they stand to make a fortune if they’re able to sell their work.
Oh well. Live by the shady “science”, die by the shady “science”.
Now, let’s find out a little more about their partner.
Taxpayer Money Funneled Through ISED For Grants

The Government of Canada, or more specifically, Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada, announced a few years ago various projects would be funded. Taxpayers would foot a $2.3 billion bill for 41 different grants, all across the country.
Immune Biosolutions, of Sherbrooke, Quebec, was just one company.
March 16, 2021: Up to $13.44 million to help through the Strategic Innovation Fund (SIF) to develop and advance its therapeutic candidate from pre-clinical studies up to Phase II clinical trials.
Perhaps it would be more accurate to describe groups it partners with as “subcontractors”.
Who Is Immune Biosolutions?
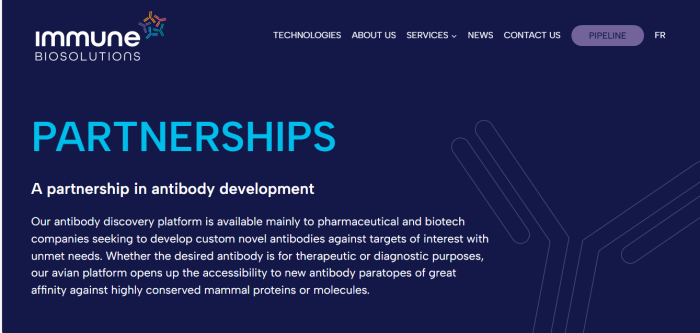
A partnership in antibody development
Our antibody discovery platform is available mainly to pharmaceutical and biotech companies seeking to develop custom novel antibodies against targets of interest with unmet needs. Whether the desired antibody is for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes, our avian platform opens up the accessibility to new antibody paratopes of great affinity against highly conserved mammal proteins or molecules.
Immune Biosolutions is a Quebec company that “partners” with other people or companies in their antibody development. This is the research and development end, while the others are the ones who receive and do the live testing.
Immunization:
- Spatial Peptide design and synthesis for antigen presentation
- Chicken Immunization by vaccination (Peptides, Spatial Peptides, Proteins, Nucleic Acids, Cells, other molecules)
- Chicken Immunization by transcutaneous electroporation (Protein expression DNA plasmid)
Screening:
- Phage-Display Antibody Candidate Screening:
- Chicken Single B Cell Antibody Candidate Screening
- Avian Antibody Sequence Determination
- Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Antibody Library Analysis
Engineering and Production:
- Avian Antibody Optimization & Humanization
- Bi-Specific and Multi-Specific Antibody Engineering
- Antibody Production & Purification
- Stable Cell Line Development
Validation (Antibody Validation):
- Affinity Assays
- Functional Assays
- Flow Cytometry
- Biolayer Interferometry
- Surface Plasmon Resonance
- Static Light Scattering/Dynamic Light Scattering
Immune Biosolutions Has Lobbying Registry Profile
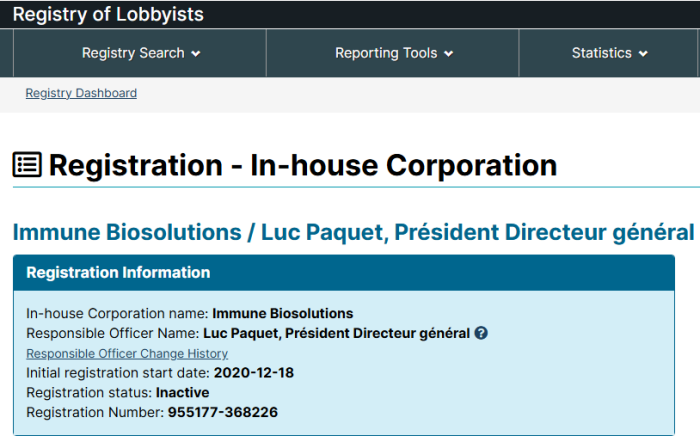
Application Form for COVID-19 Advancement of Vaccines and Therapeutics (SIF Program) Immune Biosolutions and collaborators are developing an immunotherapy based on newly identified antibodies to treat and possibly prevent the SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19). This new accelerated discovery process, aiming at providing Canadians with a treatment for COVID-19 discovered and bio-manufactured in Canada, will be applied to future infections and other diseases, such as cancer.
It shouldn’t really surprise anyone that this company is set up to lobby members of the Federal Government for funding. Their name wasn’t picked randomly.
| SOURCE OF FUNDING | DATE | AMOUNT |
|---|---|---|
| Canexport | April, 2020 | $22,754.38 |
| Canexport | April, 2021 | $22,754.38 |
| Canexport | April, 2023 | $22,754.38 |
| Canexport | April, 2024 | $27,500.00 |
| Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada | April, 2023 | $5,496,072.00 |
| Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada | April, 2024 | $2,082,706.00 |
| Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada | April, 2024 | $5,496,072.00 |
| National Research Council | April, 2020 | $33,108.69 |
| National Research Council | April, 2021 | $33,108.69 |
| National Research Council | April, 2023 | $33,108.69 |
| National Research Council | April, 2023 | $212,219.00 |
| National Research Council | April, 2024 | $212,219.00 |
| National Research Council | April, 2024 | $222,880.00 |
| SIF – Strategic Innovation Fund | April, 2024 | $5,496,072.00 |
Note: while there appear to be duplicate entries, the notes from the Lobbying Registry suggest that a few agencies made multiple payments in the same fiscal year.
Immune Biosolutions Received Wage Subsidies
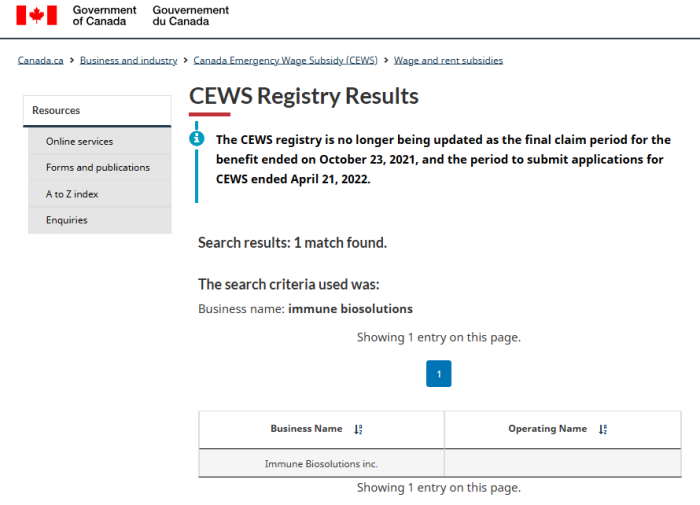
As an aside, Immune Biosolutions received CEWS (the Canada Emergency Wage Subsidy) in 2020/2021. In fairness though, it doesn’t specify the amounts.
Now, there has been a lot of noise about how it was Immune Biosolutions that got the Government grant, not Universal Ostrich Farms itself. This misses the point. While the tech company may have gotten it directly, what was UOF using to pay its bills in the meantime?
2 scenarios are possible. Either: (a) UOF got a cut of the money directly from IBio, or; (b) UOF would make money from selling the research, thus profiting from taxpayer subsidies. While the grant went to the firm, this seems to be a distinction without a difference.
People need to be asking the hard questions.
(1) https://ised-isde.canada.ca/site/biomanufacturing/en/biomanufacturing-projects-underway
(2) https://immunebiosolutions.com/en
(3) https://immunebiosolutions.com/en/partnerships/
(4) https://lobbycanada.gc.ca/app/secure/ocl/lrs/do/vwRg?cno=368226®Id=914362#regStart
(5) https://apps.cra-arc.gc.ca/ebci/habs/cews/srch/pub/bscSrch
(6) https://unlockalberta.substack.com/p/christine-massey-david-dickson-pat
FEDERAL COURT DOCUMENTS:
(1) Ostrich Notice Of Application Certified (January, 2025)
(2) Ostrich Notice Of Application (January, 2025)
(3) Ostrich Notice Of Motion (January, 2025)
(4) Ostrich Bilinski Affidavit (January, 2025)
(5) Ostrich Espersen Affidavit (January, 2025)
(6) Ostrich Pelech Affidavit (January, 2025)
(7) Ostrich Jones Affidavit (January, 2025)
(8) Ostrich Responding Motion Record (January, 2025)
(9) Ostrich Responding Motion Record Expedited (February, 2025)
(10) Ostrich Motion Record Ex-Parte (February, 2025)
(11) Ostrich Exemption Notice Of Application (February, 2025)
(12) Ostrich Exemption Motion Record (February, 2025)
(13) Ostrich Ruling Of Justice Zinn (May, 2025)
MONEY:
(1) https://bcrising.ca/save-our-ostriches/
(2) https://www.gofundme.com/f/help-ostrich-farmers-fight-to-save-herd-from-avian-flu?attribution_id=sl%3A80e09934-7413-429b-acfb-2f7015cc19d3&lang=en_CA
(3) https://www.givesendgo.com/save-our-ostriches
(4) https://www.kinexus.ca/