An update on this is coming soon.
It’s time to go through this again.
1. From COMER’s 2011 Press Release
The action also constitutionally challenges the government’s fallacious accounting methods in its tabling of the budget by not calculating nor revealing the true and total revenues of the nation before transferring back “tax credits” to corporations and other taxpayers.
The Plaintiffs state that since 1974 there has been a gradual but sure slide into the reality that the Bank of Canada and Canada’s monetary and financial policy are dictated by private foreign banks and financial interests contrary to the Bank of Canada Act.
The Plaintiffs state that the Bank of International Settlements (BIS), the Financial Stability Forum (FSF) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) were all created with the cognizant intent of keeping poorer nations in their place which has now expanded to all nations in that these financial institutions largely succeed in over-riding governments and constitutional orders in countries such as Canada over which they exert financial control.
The Plaintiffs state that the meetings of the BIS and Financial Stability Board (FSB) (successor of FSF), their minutes, their discussions and deliberations are secret and not available nor accountable to Parliament, the executive, nor the Canadian public notwithstanding that the Bank of Canada policies directly emanate from these meetings. These organizations are essentially private, foreign entities controlling Canada’s banking system and socio-economic policies.
The gist of the press release, and of the Claim overall, is that Canada’s banking system has been hijacked and usurped. As such, it is controlled by foreign entities such as the Bank of International Settlements and the International Monetary Fund.
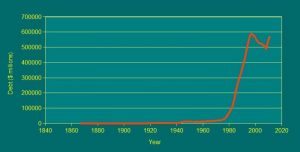
As was outlined in the last article, Canada’s banking “was” effectively turned over. The result is that Canada, instead of loaning money to itself, is now borrowing from private banks. As such, it is being bled dry.
In fact, COMER’s claims can be easily validated by online research. The question for the Court to decide: is this actually legal?
2. Ruling Striking Out Statement of Claim
[5] The core elements of COMER’s Claim can be reduced to three parts:
1. The Bank of Canada (Bank) and Crown refuse to provide interest-free loans for capital expenditures.
2. The Crown uses flawed accounting methods in describing public finances, which provides the rationale for refusing to grant such loans.
3. These and other harms are caused by the Bank being controlled by private foreign interests.
The Pronothary summarizing the main issues the Plaintiffs raise
Discussion
[41] Against these competing positions, it must be remembered that the test for striking an action is a high one. The action must be bereft of any chance of success and as noted above just because it is a novel cause of action it does not automatically fail.[26]
[42] The Supreme Court of Canada has recently summarized the principles to be applied on a motion to strike. In R. v. Imperial Tobacco Canada Ltd.,[27] the Chief Justice, writing for the Court made the following observations regarding a motion to strike:
17. The parties agree on the test applicable on a motion to strike for not disclosing a reasonable cause of action under r. 19(24)(a) of the B.C. Supreme Court Rules. This Court has reiterated the test on many occasions. A claim will only be struck if it is plain and obvious, assuming the facts pleaded to be true, that the pleading discloses no reasonable cause of action: Odhavji Estate v. Woodhouse, 2003 SCC 69 (CanLII), [2003] 3 S.C.R. 263, at para. 15; Hunt v. Carey Canada Inc., 1990 CanLII 90 (SCC), [1990] 2 S.C.R. 959, at p. 980. Another way of putting the test is that the claim has no reasonable prospect of [page 67] success. Where a reasonable prospect of success exists, the matter should be allowed to proceed to trial: see, generally, Syl Apps Secure Treatment Centre v. B.D., 2007 SCC 38 (CanLII), [2007] 3 S.C.R. 83; Odhavji Estate; Hunt; Attorney General of Canada v. Inuit Tapirisat of Canada, 1980 CanLII 21 (SCC), [1980] 2 S.C.R. 735.
. . .
21. Valuable as it is, the motion to strike is a tool that must be used with care. The law is not static and unchanging. Actions that yesterday were deemed hopeless may tomorrow succeed. Before Donoghue v. Stevenson, [1932] A.C. 562 (H.L.) introduced a general duty of care to one’s neighbour premised [page68] on foreseeability, few would have predicted that, absent a contractual relationship, a bottling company could be held liable for physical injury and emotional trauma resulting from a snail in a bottle of ginger beer. Before Hedley Byrne & Co. v. Heller & Partners, Ltd., [1963] 2 All E.R. 575 (H.L.), a tort action for negligent misstatement would have been regarded as incapable of success. The history of our law reveals that often new developments in the law first surface on motions to strike or similar preliminary motions, like the one at issue in Donoghue v. Stevenson. Therefore, on a motion to strike, it is not determinative that the law has not yet recognized the particular claim. The court must rather ask whether, assuming the facts pleaded are true, there is a reasonable prospect that the claim will succeed. The approach must be generous and err on the side of permitting a novel but arguable claim to proceed to trial.
What we can gain from this is that striking out a Statement of Claim is something that must be done cautiously, and only when it is plain and obvious that there is no chance to succeed.
Some of what may be “struck out” now, may in fact later be the basis for new laws, so the Courts should exercise caution and not jump to conclusions.
[30] The Crown further contends that COMER’s claim is outside this Court’s jurisdiction as it fails to meet the three-part test set out in ITO-International Terminal Operators Ltd v. Miida Electronics Inc.[21] In ITO, the Supreme Court considered the jurisdiction of the Federal Court in the context of an admiralty action. The Supreme Court determined that jurisdiction in the Federal Court depends on three factors:
1. There must be a statutory grant of jurisdiction by the Federal Parliament.
2. There must be an existing of body of federal law which is essential to the disposition of the case and which nourishes the statutory grant of jurisdiction.
3. The law on which the case is based must be a “law of Canada” as the phrase is used in s. 101 of the Constitution Act, 1867 [page 766]
[57] The jurisdictional issue raised by the Crown engages the three part test set out in ITO as discussed above. The Crown argues that this Court has no jurisdiction to entertain tort claims against Federal authorities.
[58] However, pursuant to sections 2, 17 and 18 of the Federal Courts Act, the wording is sufficiently wide to capture these types of claims against federal actors and Crown servants. It is therefore not plain and obvious that this Court is without jurisdiction to entertain claims seeking declaratory relief as here.
One of the major contentions is that the Government alleged that the Federal Court had no jurisdiction to even hear the case. The Pronothary took a different view. However, there were other problems which ended with this.
[71] There is ample authority in this Court and in the jurisprudence generally that where a claim has some kernel of a legitimate claim it should not be tossed aside but permitted to be amended to determine if the clam in law can be cured.[45]
[72] Given that the Claim, in my view, is not justiciable, leave to amend will not cure the defects. Leave to amend is therefore not granted.
The case was thrown out on a motion to strike. However, that will not be the end of it. The Plaintiffs would appeal to a Justice of the Federal Court.
3. COMER Appeals Dismissal
(See here.)
The striking out (without permission to amend) was appealed to a Justice of the Federal Court. This was a partial victory, as the dismissal “was” upheld, but it allowed the Plaintiff’s to file an amended Claim. This would be another “chance” to get it right.
4. COMER Tries To File Again
(See here.)
After the Justice of the Federal Court upheld the dismissal (but giving leave to amend the Statement of Claim), COMER appealed to the Federal Court of Appeal, and the Government cross-appealed.
In short, the Plaintiffs were trying to get the dismissal overturned entirely, while the Government tried to remove the clause to allow COMER to file an amended Statement of Claim.
The Federal Appeals Court panel (3 Justices) threw out both the appeal and cross-appeal.
5. COMER’s Amended Statement Thrown Out
(See here.)
[66] In terms of the general principles that ought to be applied on a motion to strike, the Plaintiffs assert that the facts pleaded by the Plaintiffs must be taken as proven: Canada (Attorney General) v Inuit Tapirasat of Canada, 1980 CanLII 21 (SCC), [1980] 2 SCR 735; Nelles v Ontario (1989), DLR (4th) 609 (SCC) [Nelles]; Operation Dismantle, above; Hunt v Carey Canada Inc 1990 CanLII 90 (SCC), [1990] 2 SCR 959 [Hunt]; Dumont v Canada (Attorney General), 1990 CanLII 131 (SCC), [1990] 1 SCR 279 [Dumont]; Nash v Ontario (1995), 1995 CanLII 2934 (ON CA), 27 OR (3d) 1 (Ont CA) [Nash]; Canada v Arsenault, 2009 FCA 242 (CanLII) [Arsenault].
[67] The Plaintiffs echo the test referenced by the Defendants, asserting that a claim can be struck only in plain and obvious cases where the pleading is bad beyond argument: Nelles, above, at para 3. The Court has provided further guidance in Dumont, above, that an outcome should be “plain and obvious” or “beyond doubt” before striking can be invoked (at para 2). Striking cannot be justified by a claim that raises an “arguable, difficult or important point of law”: Hunt, above, at para 55.
[68] The novelty of the Amended Claim is not reason in and of itself to strike it: Nash, above, at para 11; Hanson v Bank of Nova Scotia (1994), 1994 CanLII 573 (ON CA), 19 OR (3d) 142 (CA); Adams-Smith v Christian Horizons (1997), 3 OR (3d) 640 (Ont Gen Div). Additionally, matters that are not fully settled by the jurisprudence should not be disposed of on a motion to strike: RD Belanger & Associates Ltd v Stadium Corp of Ontario Ltd (1991), 1991 CanLII 2731 (ON CA), 5 OR (3d) 778 (CA). In order for the Defendants to succeed, the Plaintiffs state that a case from the same jurisdiction that squarely deals with, and rejects, the very same issue must be presented: Dalex Co v Schwartz Levitsky Feldman (1994), 19 OR (3d) 215 (CA). The Court should be generous when interpreting the drafting of the pleadings, and allow for amendments prior to striking: Grant v Cormier – Grant et al (2001), 2001 CanLII 3041 (ON CA), 56 OR (3d) 215 (CA).
[69] The Plaintiffs also remind the Court that the line between fact and evidence is not always clear (Liebmann v Canada, 1993 CanLII 3006 (FC), [1994] 2 FC 3 at para 20) and that the Amended Claim must be taken as pleaded by the Plaintiffs, not as reconfigured by the Defendants: Arsenault, above, at para 10.
Plaintiffs arguing that the Defendant has not actually met the burden to strike out a Statement of Claim. However, the Justice decides differently.
[137] In the present case, the Plaintiffs have not, in their Amended Claim, pleaded facts to demonstrate a “real” issue concerning the relative interests of each party, and the nexus of that real issue to the Plaintiffs and their claim for relief. Although as I pointed out in my Order of April 24, 2014, the Plaintiffs do distinguish between legal issues and policy issues, the legal issues remain theoretical with no real nexus to some interest of the Plaintiffs, other than an interest in having the Court endorse their opinion on the Bank Act issues raised.
[138] The Plaintiffs have not addressed the jurisdictional problems I referred to in paras 85 to 91 of my Order of April 24, 2014 and/or what might generally be referred to as the jurisdiction of the Court to entertain, or its willingness to grant, free-standing requests for declaration.
The Justice Rules that the original problems are left unfixed. As such, the case is thrown out. This time, there is no leave to amend, so if this is to continue, it must go back to the Federal Court of Appeals.
6. Return to Federal Court of Appeals
(See here.)
[9] The essence of the Federal Court judge’s reasoning for striking the amended statement of claim is summed up at paragraph 144 of his reasons: It seems to me, then, that the latest Amended Claim discloses no reasonable cause of action and has no prospect of success at trial. It also seems to me that the Plaintiffs are still asking the Court for an advisory opinion in the form of declarations that their view of the way the Bank Act and the Constitution should be read is correct. It also seems to me that they have failed to show a statutory grant of jurisdiction by Parliament that this Court can entertain and rule on their claim as presently constituted, or that they have any specific rights under the legislation which they invoke, or a legal framework for any such rights. As the Supreme Court of Canada pointed out in Operation Dismantle, above, the preventive function of a declaratory judgment must be more than hypothetical and requires “a cognizable threat to a legal interest before the Court will entertain the use of its process as a preventative measure” (para 33). The Court is not here to declare the law generally or to give an advisory opinion. The Court is here to decide and declare contested legal rights.
[10] The appellants assert that the opinion so expressed is wrong in law. In support of this proposition, they essentially reiterate the arguments which they urged upon the Federal Court judge and ask that we come to a different conclusion. Counsel for the appellants focused his argument during the hearing on the issue of standing and the right to seek declarations of constitutionality. It remains however that, as the Federal Court judge found, the right to a remedy is conditional on the existence of a justiciable issue.
The Federal Appeals Court believes that COMER is still asking for an advisory opinion. Furthermore, the FCA still believes that no justiciable issue has been raised.
7. Supreme Court of Canada Declines To Hear Case
(See here.)
The Supreme Court refuses to hear the case, which means it is legally over. It would have been nice to have some actual reasons included. However, due to the volume of cases it receives, rejected applications generally don’t receive them.
Despite repeated rejection by the Courts, the questions about the changes in banking policy were never really addressed. Does giving control of our central bank to foreign powers break the law?
This is supposedly a “political” issue, but no politicians are willing to talk about it.
As of now, Canada is still borrowing money from private banks, as opposed to ourselves. We are racking up huge levels of debt that we shouldn’t be.
INITIAL PLEADING STRUCK WITHOUT LEAVE TO AMEND:
(1) COMER Statement Of Claim December 2011
(2) COMER Amended Statement Of Claim January 2012
(3) COMER Defendants Motion Record March 2012
(4) COMER Defendants Notice Of Motion March 2012
(5) COMER Defendants Written Submissions March 2012
(6) https://www.canlii.org/en/ca/fct/doc/2013/2013fc855/2013fc855.html
RULE 51 MOTION FOR REVIEW, LEAVE TO AMEND GRANTED:
(1) COMER Moving Party Motion Record August 2013
(2) COMER Defendants Motion Record November 2013
(3) https://www.canlii.org/en/ca/fct/doc/2014/2014fc380/2014fc380.html
FIRST APPEAL, CROSS-APPEAL BOTH DISMISSED:
(1) COMER Notice Of Appeal April 2014
(2) COMER Appellants Memorandum Of Fact And Law August 2014
(3) https://www.canlii.org/en/ca/fca/doc/2015/2015fca20/2015fca20.html
SECOND MOTION TO STRIKE, NO LEAVE TO AMEND:
(1) COMER Amended Statement Of Claim March 2015
(2) COMER Defendants Motion Record April 2015
(3) COMER Defendants Written Submissions April 2015
(4) COMER Plaintiff Responding Motion Record April 2015
(5) COMER Plaintiff Responding Motion Record April 2015
(6) https://www.canlii.org/en/ca/fct/doc/2016/2016fc147/2016fc147.html
SECOND APPEAL, DISMISSED:
(1) COMER Notice Of Appeal March 2016
(2) https://www.canlii.org/en/ca/fca/doc/2016/2016fca312/2016fca312.html
LEAVE TO APPEAL, SCC, DENIED:
(1) https://www.canlii.org/en/ca/scc-l/doc/2017/2017canlii25790/2017canlii25790.html