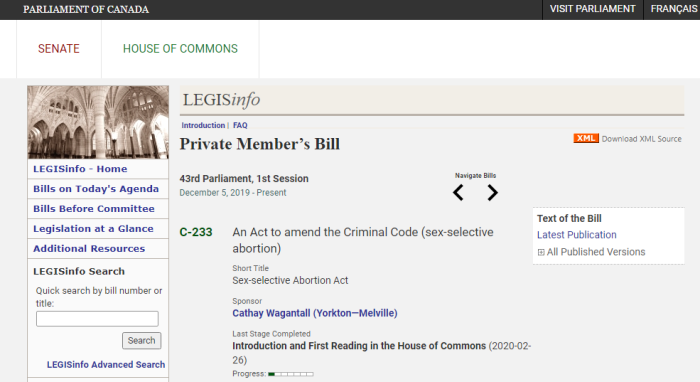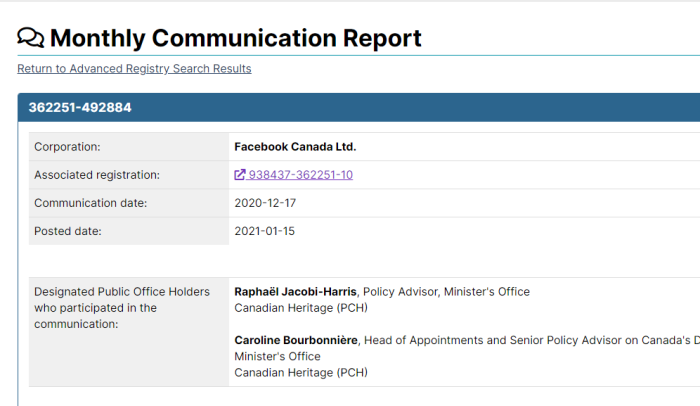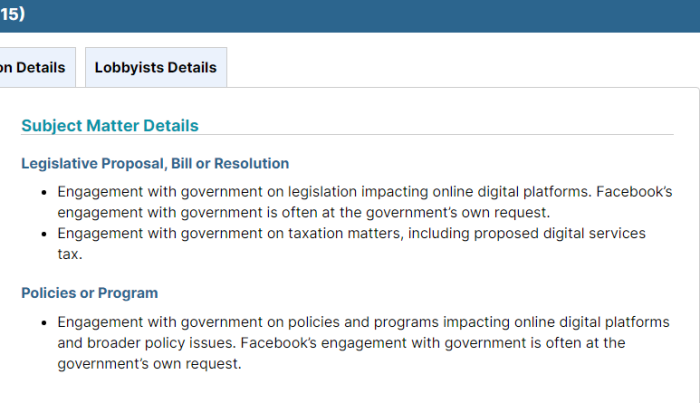
Bill C-7, the expanded version of the assisted suicide bill (or “euthanasia 2.0), is currently being discussed in the Canadian Parliament. It broadens the scope laid out in Bill C-14, from the previous Parliament. A Quebec Court ruled that Bill C-14’s requirement that a death be “reaso
1. Assisted Suicide (MAiD), Euthanasia
CLICK HERE, for #1: Court says referral or service must be provided.
CLICK HERE, for #2: Bill C-14, Medical Assistance in Dying (euthanasia).
2. Important Links
Bill C-14 Introduced In Parliament (2016)
Bill C-14 Committee Hearings
Truchon V AG Of Canada, 2019 QCCS 3792 (CanLII)
Truchon V. AG, Quebec Superior Court Ruling
Bill C-7 Introduced Into Parliament (Feb 2020)
Bill C-7 Re-Introduced Into Parliament (Oct 2020)
Bill C-7 Committee Hearings
C-7 Canadian Bar Association
C-7 Canadian Conference Of Catholic Bishops
C-7 Coelho Ramona
C-7 Commission On End Of Life Care
C-7 DawsTanja
C-7 Jointly1
C-7 Living With Dignity
C-7 Physicians Alliance Against Euthanasia
C-7 Protection Of Conscience Project
C-7 Wickenhesier Alizee
Bill C-7 Evidence November 3
Bill C-7 Evidence November 5
3. Quebec Court Says Changes Needed In MAiD
MEDICAL AID IN DYING
26. Only a patient who meets all of the following criteria may obtain medical aid in dying:
(1) be an insured person within the meaning of the Health Insurance Act (chapter A-29);
(2) be of full age and capable of giving consent to care;
(3) be at the end of life;
(4) suffer from a serious and incurable illness;
(5) be in an advanced state of irreversible decline in capability; and;
(6) experience constant and unbearable physical or psychological suffering which cannot be relieved in a manner the patient deems tolerable.
.
The patient must request medical aid in dying themselves, in a free and informed manner, by means of the form prescribed by the Minister. The form must be dated and signed by the patient.
.
The form must be signed in the presence of and countersigned by a health or social services professional; if the professional is not the attending physician, the signed form is to be given by the professional to the attending physician.
28. A patient may, at any time and by any means, withdraw their request for
medical aid in dying.
.
A patient may also, at any time and by any means, request that the
administration of medical aid in dying be put off.
31. A physician practising in a centre operated by an institution who refuses are quest for medical aid in dying for a reason not based on section 29 must, as soon as possible, notify the executive director of the institution or any other person designated by the executive director and forward the request form given to the physician, if that is the case, to the executive director or designated person. The executive director of the institution or designated person must then take the necessary steps to find, as soon as possible, another physician willing to deal with the request in accordance with section 29.
.
If the physician who receives the request practises in a private health facility and does not provide medical aid in dying, the physician must, as soon as possible, notify the executive director of the local authority referred to in section 99.4 of the Act respecting health services and social services (chapter S-4.2) that serves the territory in which the patient making the request resides, or notify the person designated by the executive director. The physician forwards the request form received, if that is the case, to the executive director or designated person and the steps mentioned in the first paragraph must be taken.
.
If no local authority serves the territory in which the patient resides, the notice referred to in the second paragraph is forwarded to the executive director of the institution operating a local community service centre in the territory or the person designated by the executive director.
In this case, the Applicant, Jean Truchon, had suffered from spastic cerebral palsy with triparesis since birth. In March 2012, he was diagnosed with severe spinal stenosis (narrowing of the spinal canal) as well as myelomalacia (spinal cord necrosis). This is a degenerative condition for which no surgical or pharmacological treatment exists that caused the gradual paralysis of his only working limb. As a result, in 2012, Mr. Truchon permanently lost the use of his left arm and became fully paralyzed, with no hope of improvement. This new condition was accompanied by significant physical pain in the arms and neck, with intense burning sensations and painful spasms.
While clearly not about to die soon, he seems fully aware of his condition, which has no reasonable prospect of improving. So can he request medically assisted suicide on this basis?
The Quebec Court said there is no reason to deny it.
[375] First, the Court is astounded by the fact that the experts for the Attorney General of Canada had not even a basic knowledge of the practice of medical assistance in dying in Canada, which has nonetheless been legal throughout the country since 2016. None of them has participated in the request process for medical assistance in dying, either by assessing a patient or by providing such medical assistance. None of them has done any research on the subject or even tried to consult the data available in Canada.
[376] Therefore, when they all state that there is no difference between suicide and medical assistance in dying, they are considering and presenting only one side of the story, one part of the equation. They compare the two issues without ever having analyzed, learned, or addressed the specifics of medical assistance in dying, its parameters, its eligibility criteria, or how it is practised in Canada.
As an aside, the Government presented “experts” who had no experience of knowledge whatsoever in medical assistance in dying. Either they couldn’t find better experts, or didn’t even try.
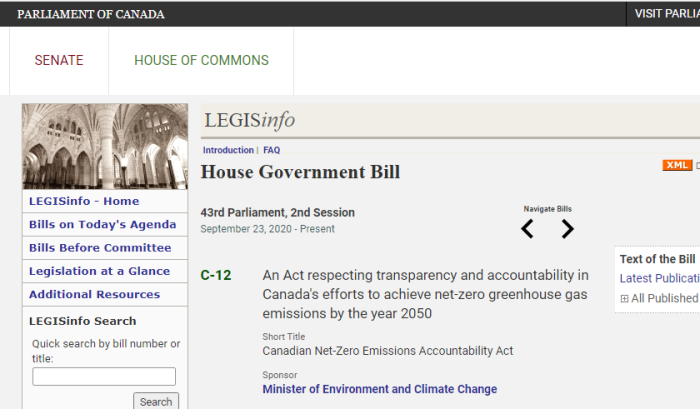
4. Bill C-7 Re-Introduced In Parliament
A point of clarification: Bill C-7 was actually introduced in February 2020, and only got as far as first reading. It died when Parliament was prorogued. It has been re-introduced (again, as Bill C-7), in the latest session.
SUMMARY
This enactment amends the Criminal Code to, among other things,
(a) repeal the provision that requires a person’s natural death be reasonably foreseeable in order for them to be eligible for medical assistance in dying;
(b) specify that persons whose sole underlying medical condition is a mental illness are not eligible for medical assistance in dying;
(c) create two sets of safeguards that must be respected before medical assistance in dying may be provided to a person, the application of which depends on whether the person’s natural death is reasonably foreseeable;
(d) permit medical assistance in dying to be provided to a person who has been found eligible to receive it, whose natural death is reasonably foreseeable and who has lost the capacity to consent before medical assistance in dying is provided, on the basis of a prior agreement they entered into with the medical practitioner or nurse practitioner; and
(e) permit medical assistance in dying to be provided to a person who has lost the capacity to consent to it as a result of the self-administration of a substance that was provided to them under the provisions governing medical assistance in dying in order to cause their own death.
Preamble
Whereas the Government of Canada has committed to responding to the Superior Court of Québec decision in Truchon v. Attorney General of Canada;
.
Whereas Parliament considers that it is appropriate to no longer limit eligibility for medical assistance in dying to persons whose natural death is reasonably foreseeable and to provide additional safeguards for those persons whose natural death is not reasonably foreseeable;
.
Whereas under the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms every individual has the right to life, liberty and security of the person without being deprived of them except in accordance with the principles of fundamental justice and has the right to the equal protection and equal benefit of the law without discrimination;
.
Whereas Canada is a State Party to the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities and recognizes its obligations under it, including in respect of the right to life;
.
Whereas Parliament affirms the inherent and equal value of every person’s life and the importance of taking a human rights-based approach to disability inclusion;
.
Whereas Parliament recognizes the need to balance several interests and societal values, including the autonomy of persons who are eligible to receive medical assistance in dying, the protection of vulnerable persons from being induced to end their lives and the important public health issue that suicide represents;
.
Whereas it is desirable to have a consistent approach to medical assistance in dying across Canada, while recognizing the provinces’ jurisdiction over various matters related to medical assistance in dying, including the delivery of health care services and the regulation of health care professionals, as well as insurance contracts and coroners and medical examiners;
.
Whereas the Government of Canada is committed to having a federal monitoring regime that provides a reliable national dataset and that promotes accountability under the law governing medical assistance in dying and improve the transparency of its implementation;
.
Whereas, while recognizing the inherent risks and complexity of permitting medical assistance in dying for persons who are unable to provide consent at the time of the procedure, Parliament considers it appropriate to permit dying persons who have been found eligible to receive medical assistance in dying and are awaiting its provision to obtain medical assistance in dying even if they lose the capacity to provide final consent, except if they demonstrate signs of resistance to or refusal of the procedure;
.
Whereas further consultation and deliberation are required to determine whether it is appropriate and, if so, how to provide medical assistance in dying to persons whose sole underlying medical condition is a mental illness in light of the inherent risks and complexity of the provision of medical assistance in dying in those circumstances;
.
And whereas the law provides that a committee of Parliament will begin a review of the legislative provisions relating to medical assistance in dying and the state of palliative care in Canada in June 2020, which review may include issues of advance requests and requests where mental illness is the sole underlying medical condition;
Now, therefore, Her Majesty, by and with the advice and consent of the Senate and House of Commons of Canada, enacts as follows:
One of the main takeaways in Bill C-7 is that is removes a requirement from Bill C-14 that a person receiving medical assistance in dying have a death that is “reasonably foreseeable”. Now, a person can get a doctor or nurse to help with euthanasia for a wide array of reasons.
A worthwhile note: it includes language which prevents assisted suicide if the only reason for doing so is a mental illness.
5. Clips From Bill C-7 Parliamentary Hearings
The hearings, of course, last much longer, but those are a few clips of it. An interesting claim (from Roger Foley), about the father of the Judge in the Truchon ruling gave evidence in the case. If true, a huge conflict of interest.
It’s rather strange to see Iqra Khalid, who presented M-103 (the Islamic blasphemy Motion), heading up the hearings on medically assisted suicide. Curious to know what her views are.
6. Roger Foley, Assisted Life Website
My name is Roger Foley. I am the patient who has been in Victoria Hospital for over 4-years being pressured into assisted dying by the hospital and Government while they prevent my access to care options I need to live 1, 2. I have important public interest updates.
The Hospital is currently billing me $1800 dollars per day and continuing to coerce me to Assisted Dying during the Covid-19 pandemic when they threatened me with that and offered me Assisted Dying. Instead of protecting the lives of the elderly, the disabled and the vulnerable, the Hospital and Government are taking advantage, by further exploiting and abusing persons who are vulnerable before and during Covid-19 and not protecting their lives across the Country. So many persons are dying unnecessary deaths, when robust self-directed home care would make all Canadians safer in their own homes.
The Government cannot be trusted and they admitted rather than preparing for the Covid-19 pandemic, they were selling their exploitation and abuse of vulnerable Canadians to Assisted Dying rather than calling China to learn about the threat, ordering ventilators, protecting those in Long-Term Care facilities and Group Homes, and ordering Personal Protecting Equipment for Health Care workers to make sure frontline Health Care workers were safe. They also during the Pandemic in March, when thousands of people were dying, released their bias propaganda assisted dying expansion survey to continue to abuse, exploit and end the lives of vulnerable disabled and elderly Canadians. I am continuing to be attacked through my care, being denied basic necessities of life, and being denied proper and dignified health care. I am very scared, and the Government and the Health Care systems want to end my life rather than help me to live with dignity and compassion.
Assisted Life is documenting and chronicling the problems and conflicts of interests in proceedings. This is too long to cover in a single article, but it’s worth a good read.
7. Protection Of Conscience Project

An Act to amend the Criminal Code (medical assistance in dying)
.
I.1 The Protection of Conscience Project does not take a position on the acceptability of euthanasia or physician assisted suicide. The Project supports legislation that ensures that health care workers who object to providing or participating in homicide and suicide for reasons of conscience or religion are not compelled to do so or punished or disadvantaged for refusal.
One of the valid topics that needs to be discussed is the conscience rights of health care professionals who believe that participating in assisted suicide (or legalized murder) is wrong, and goes against their oath.
8. Physicians Alliance Against Euthanasia

To the Committee,
The danger of universal euthanasia access is similar to the passive, everpresent danger of drowning. A few people will die voluntarily by jumping in the water. But others will simply stumble. And yet others may be pushed.
.
Similarly, while some people will truly die by choice, others may “choose” euthanasia on a whim born of passing despair. But worse still: all people eligible for euthanasia become automatically vulnerable to pressure from others who cannot bear to see them suffer, are exhausted by their care, or will in some way benefit from their death, be they health professionals, caregivers or heirs.
Clearly, the most egregious harm of Bill C-7 lies in the extension of euthanasia to those who are not dying. The Carter decision specified that any legalization of euthanasia must include effective safeguards, of which the reasonably foreseeable death criterion was one.
In addition, Bill C-7 only requires that patients be informed of real alternatives to death in order to relieve suffering. That is clearly insufficient, given the scarcity of medical, psychological, and social resources for the many groups of people who might contemplate death as a solution to their troubles. It is essential that such alternatives be actually available to all patients considering euthanasia.
“Bill C-7 does not just expand MAiD; it fundamentally redefines it. No longer limited to hastening death, Bill C-7 embraces MAiD as a means of terminating an otherwise viable life – but only the life of someone with an illness or disability (italics added).
.
Bill C-7 (therefore) undermines our constitutional commitment to the equal and inherent value of all lives”
Other issues mysteriously bundled in Bill C-7
.
Whereas the end-of-life provision is of greatest importance, certain other elements of Bill C-7 have nothing to do with the requirements of Truchon/Gladu and their effects go far beyond compliance with that judgment. Two of these involve weakening euthanasia safeguards in cases where natural death is reasonably foreseeable: It is proposed that the existing ten-day waiting period be eliminated for all patients; and that the number of witnesses to the request be lowered from two to only one (who may also be a health care professional involved in the patient’s care).
The Physicians Alliance Against Euthanasia raises a number of valid points about Bill C-14, including:
(a) people may choose death in a moment of despair
(b) death may be promoted be interested parties
(c) Bill C-7 redefines MAiD, not just expands it
(d) eliminating the 10 day waiting period
(e) reducing the 2 witness threshold to 1
9. Was Bill C-14 Just A Gateway?
This is a fair question to ask: was Bill C-14 just a stepping stone to more widespread euthanasia. By allowing medically assisted suicide for terminally ill people, Parliament unwittingly, (or perhaps wittingly), set a precedent to broader implementation. How do we determine that the right person — the one whose life would end — is actually making the decision, and in a fully informed way?
While the prospect of relatives hastening death in anticipation of an inheritance seems like a movie script, it is a realistic possibility. Greed makes some people do horrible things.
Standards also have to be set to ensure the person has fully thought out the consequences, and is not just suffering from a bad day (or series or days).
It’s also been mentioned by Roger Foley, and AssistedLife.ca, that these court decisions have been influenced by conflicts of interest. The research done is quite impressive. That will be addressed separately.
Of course, there are a lot of legitimate concerns and questions (such as being used to outright murder) that will likely never be fully addressed.
Like this:
Like Loading...