Have you ever been asked to donate to a public interest lawsuit? Well, if you have any connection to the “freedom movement” in Canada, odds are that the answer is yes.
This piece is designed to offer a constructive suggestion: before donating to any case, it’s best to do some due diligence on what’s going on. Yes, that will involve some work, but life is like that.
To add the disclaimer: poorly written and handled litigation doesn’t always mean corruption. There are other explanations like carelessness and incompetence. But at some point, questions have to be asked.
The following is a list of interrelated ways a person can tell if a lawsuit is designed to fail, or at least is extremely likely to fail. While it’s written with “pandemic” measures in mind, there is cross-over with other issues. A single indicator doesn’t necessarily prove malintent, but these are definitely red flags.
1. The Lawsuit Is Filed In The Wrong Court
This should be obvious: Courts only have jurisdiction to hand out certain remedies. If a relief being sought is outside that jurisdiction, Judges have no power to grant it, regardless of how strong the evidence and/or witness testimony might be.
Action4Canada was called out for doing this. At paragraph 52:
[52] The defendants submit that the NOCC pleads to a number of claims that are improper in a civil action. In part, the defendants point to the following elements of the NOCC as inappropriate:
a) alleging criminal conduct;
b) seeking a declaration that the preponderance of the scientific community is of the view that masks are ineffective in preventing transmission;
c) seeking a declaration that the motive and execution of the COVID-19 prevention measures by the World Health Organization are not related to a bona fide “pandemic”;
d) seeking a declaration that administering medical treatment without informed consent constitutes experimental medical treatment which is contrary to the Nuremberg Code, the Helsinki Declaration and is a crime against humanity under the Criminal Code of Canada;
e) seeking a declaration that the unjustified, irrational, and arbitrary decisions of which businesses would remain open, and which would close, as being “essential”, or not, was designed and implemented to favour mega-corporations and to de facto put most small businesses out of business; and
f) seeking a declaration that the measures of masking, social distancing, PCR testing, and lockdowns are not scientifically based, and are based on a false and fraudulent use of the PCR test.
[53] I agree with the defendants that these are improper claims.
The case was struck (in part) because it demanded many remedies that a Civil Court in British Columbia had no jurisdiction to grant. Action4Canada is appealing, but that will go nowhere.
Earlier this year, a Federal case was thrown out (in part) for the same reason. It too has been appealed.
Another instance where jurisdiction is an issue concerns cases involving Government employees and/or employees of unionized organizations. In those cases, there’s typically a grievance process that leads to arbitration, and a restriction on litigation. There are limited ways around it, but that requires competent attorneys to argue.
It the lawyers managing cases don’t even know what areas the Court has jurisdiction over, then they probably shouldn’t be practicing.
2. The Wrong Paperwork Is Submitted
This is related to jurisdiction, but is a somewhat separate issue. If a person asks a Judge to do something, then the correct forms have to be filed.
A Statement of Claim, (or Notice of Civil Claim in B.C.), is what’s usually filed to start a lawsuit. However, other, more specific or limited remedies must use an Application or Petition.
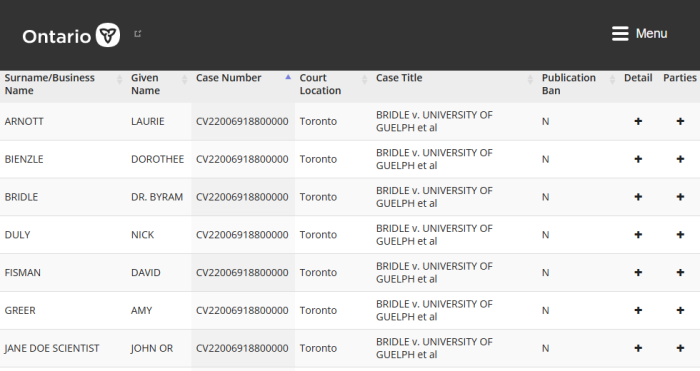
In Ontario, a request for a: Prohibition (ban), Mandamus (order to compel); or Certiorari (review of lower decision) must be done by Application. If put in an Action, the case would probably be thrown out.
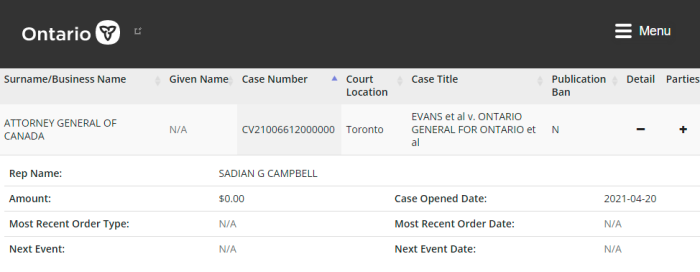
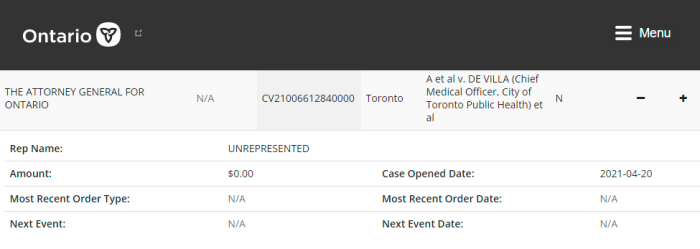
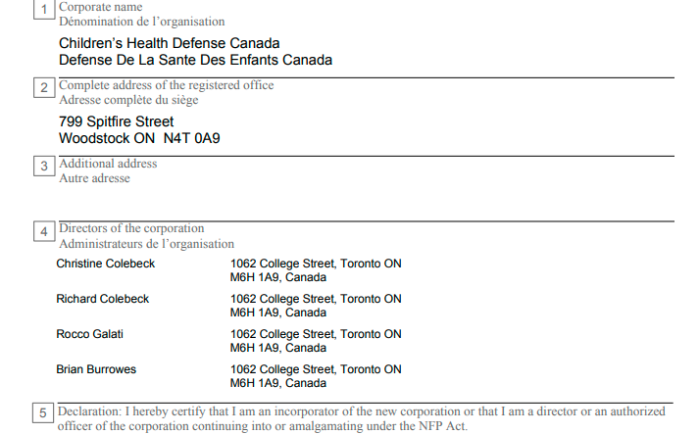
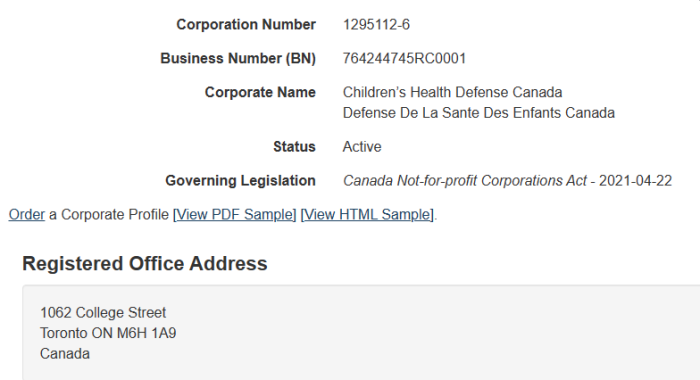
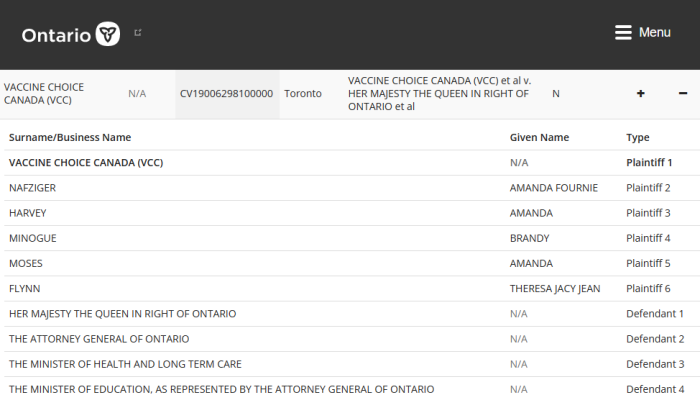
Also, in Ontario, a request for a Prohibition, Mandamus, or Certiorari must be filed in Divisional Court (not Superior), unless permission is granted otherwise. Vaccine Choice (2019 case), Police On Guard, and Children’s Health Defense would likely have their suits tossed just for this.
While it’s true that this can — often — be fixed later, it’s still a huge waste of time and money. At a minimum, it shows great incompetence.
3. There Are Never Any Status Updates Or Announcements
It seems logical that any legitimate person or organization would keep everyone posted as to what’s going on, good or bad. Documents should be posted, along with a “Coles Notes” summary of what has been happening. This not only reassures prospective and returning donors, but shows transparency with money being spent.
Obvious examples where this is not done include: (a) Vaccine Choice Canada (both); (b) Police On Guard; and (c) Children’s Health Defense Canada. The only reason anyone knows about this is because it’s been reported here.
4. Basic Steps Take Unreasonably Long To Accomplish
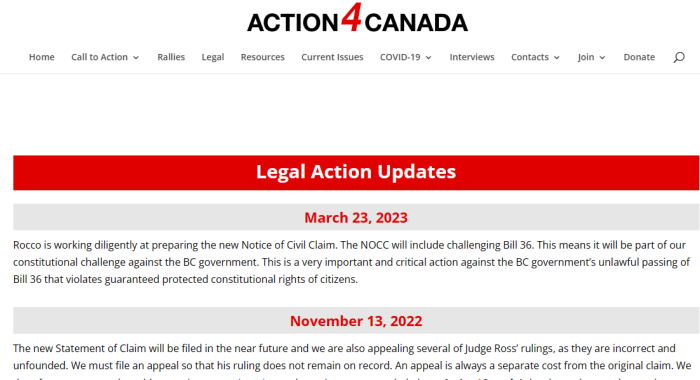
The Notice of Civil Claim took nearly a year for Action4Canada to file. Instead of a short and straightforward pleading, it was a mish-mash of every conspiracy (true and false) crammed together. It didn’t follow the basics for drafting, and more on that later.
The NOCC was predictably struck in its entirety. Despite promises of a rewrite — and more requests for donations — an amended version hasn’t materialized in 8 months.
It shouldn’t take months or years to draft a NOCC.
5. The Statute Of Limitations Is Completely Ignored
Jurisdictions all over the world place time limits on how long potential litigants have to launch cases. For civil litigation in Canada and Canadian Provinces, that’s generally 2 years. There are exceptions, but 2 years is the most common.
If a lawyer takes forever to start a case, or just files something — and lets it sit — that places the client at risk. This is because if that person is forced to later get different help, he or she might find their grievances are time barred. Yes, this is a real thing.
Each Province is slightly different, but the Limitation Acts can all be looked up.
6. The Pleadings Are Incoherent And Hard To Follow
This doesn’t really require an explanation. Documents need to be written clearly, and in a way that people who aren’t familiar with the issues can at least understand what’s going on. And that ties in directly with the next point.
7. Basic Rules Of Civil Procedure Are Rarely Followed
Each Court has similar rules for how to draft a lawsuit. These include:
(a) Short, concise set of facts that are being alleged
(b) Don’t plead evidence, or long quotes. That comes later
(c) Clearly state the relief being sought, namely, what you’re asking for
(d) State what laws/regulations will support the suit
(e) Provide enough particulars, or specifics, so the other side can respond
(f) Outline how and why this Court has jurisdiction
(g) Make the pleading organized enough so that it can be understood.
Sounds simple enough, doesn’t it?
See Vaccine Choice Canada, Action4Canada and the Federal case for examples. These were written so poorly that anyone would have considerable difficultly following along.
So far, 2 of those have been struck for essentially the reasons outlined. Vaccine Choice faces a similar hearing in early 2024.
8. The Case Accepts Far Too Much at Face Value
Considering that these martial law measures were based on false pretenses, it’s disheartening to see many lawyers (across Provinces) playing along with this. They rarely, if ever, challenge the fake science. Instead, it’s often just a simple plea for exemptions, or a slight rollback of the measures.
It’s also a source of irritation that few (if any) challenge the notion of a virus itself. If lockdowns, vaccine and mask mandates are all based on fraud, why assume that the virus is real?
9. Lawyers Spend More Time Soliciting Donations Than In Court
Another cause for concern. If there are endless requests for donations, and little progress to show in advancing a lawsuit, it could very well be a scam.
10. Lawyers Are Also Receiving Government Money
Who else are the lawyers getting money from?
CEWS, the Canada Emergency Wage Subsidy, was just one program in operation over the last few years. Yes, it’s been inactive since late 2021, but there were an awful lot of lawyers and firms listed there. This includes some in the “freedom community”. Of course, that was just one program.
11. Gaslighting, Threatening And/Or Suing Of Critics
That has happened here, and will be addressed in much more detail at a later date. Exposing the grifts has certainly come with consequences.
Now for some questions that have come up before.
What should people be looking for?
This is certainly a reasonable thing to ask. Most people have better things to do with their lives than study law, so what should they be alert to?
One idea is to start with points #3 and #6. Check to see what kind of updates are available on the organization’s website. If it’s legitimate, there should be fairly regular postings. Also, are the documents filed straightforward and easy to understand, or do they seem convoluted and incomprehensible?
Ask as a lay person: does this appear legitimate?
Why keep focusing on this topic?
For a few reasons.
First, it’s an issue that few in the movement were willing to touch back in 2020 or 2021. However, the risk has largely gone away since it’s more openly talked about these days. And it’s still happening.
Second, it’s not purity spiraling to have standards. Yes, everyone wants freedom and hates martial law, but it’s predatory to take advantage of people in this manner. No one would tolerate this from Trudeau, Ford, or Horgan, but it’s okay when “freedom fighters” rip others off? They need to be cast out.
Third, see point #11.
Does this mean these cases are so-called “controlled opposition”?
In some sense, it’s irrelevant if a case is shoddy due to greed, incompetence, or corruption. The result is the same. Specifically: litigants who had potentially valid issues will never get their day in Court, due to serious errors made by their lawyer(s).
It’s impossible to know for sure without some inside knowledge. But for a lot of these cases, it seems to be the most plausible explanation.
(1) https://www.canlii.org/en/bc/bcsc/doc/2022/2022bcsc1507/2022bcsc1507.html
(2) https://www.canlii.org/en/ca/fct/doc/2023/2023fc252/2023fc252.html
(3) https://www.canlii.org/en/on/laws/stat/rso-1990-c-j1/latest/rso-1990-c-j1.html
(4) https://apps.cra-arc.gc.ca/ebci/habs/cews/srch/pub/dsplyBscSrch?request_locale=en