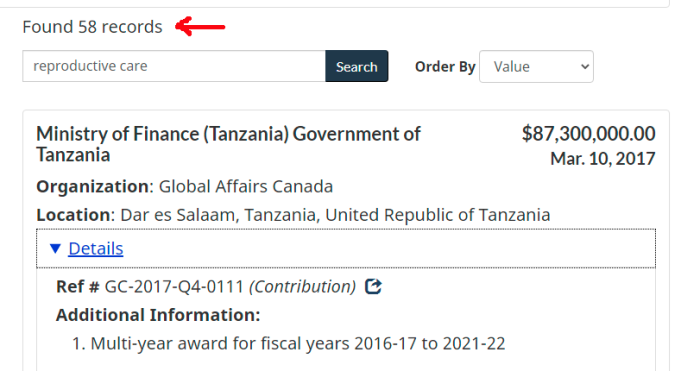
Bill C-12 is the 2005 Quarantine Act, passed by Canada’s Parliament. It was heavily based on presumed changes to the International Health Regulations that the World Health Organization imposed. However, the problem has filtered down to the Provinces as well.
Strangely, it was only the Bloc Quebecois who voted against this. All other parties supported this Bill.
1. Other Articles On CV “Planned-emic”
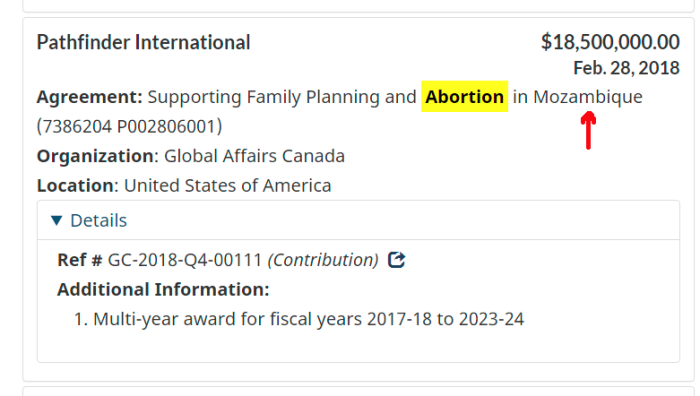
The rest of the series is here. Many lies, lobbying, conflicts of interest, and various globalist agendas operating behind the scenes, obscuring the vile agenda called the GREAT RESET. The Gates Foundation finances: the WHO, the US CDC, GAVI, ID2020, John Hopkins University, Imperial College London, the Pirbright Institute, the BBC, and individual pharmaceutical companies. The International Health Regulations are legally binding. The Postmedia empire and the “independent” media are paid off, as are the fact-checkers. The virus was never isolated, PCR tests are a fraud, as are forced masks, social bubbles, and 2m distancing.
2. Important Links
https://www.ourcommons.ca/Committees/en/HESA/StudyActivity?studyActivityId=981075
https://www.ourcommons.ca/DocumentViewer/en/38-1/HESA/report-2/
(AB) https://www.qp.alberta.ca/documents/Acts/P37.pdf
(SK) https://www.canlii.org/en/sk/laws/stat/ss-1994-c-p-37.1/11022/ss-1994-c-p-37.1.html
(MB) https://web2.gov.mb.ca/laws/statutes/ccsm/p210e.php
(ON) https://healthunit.org/wp-content/uploads/Health_Protection_and_Promotion_Act.pdf
3. Canada’s Quarantine Act Written By WHO
As mentioned earlier, the International Health Regulations (IHR), that the WHO issues are legally binding on all Member States. Countries are expected to follow the directives that are sent, even if they are very much against national self interest.
In declaring this “pandemic”, Trudeau activated the 2005 Quarantine Act, a piece of legislation that violates many basic rights in the name of “public health”. However, Bill C-12 was actually written by the World Health Organization. What this means is that the Bill was drafted in anticipation of changes to the 3rd Edition of the IHR, which remain legally binding today.
But what about the Provinces? What is the situation with their Public Health Acts? Turns out that many of the clauses from the Quarantine Act are included, almost word for word?
4. British Columbia Public Health Act

Preventive measure
16 (1) Preventive measures include the following:
(a) being treated or vaccinated;
(b) taking preventive medication;
(c) washing with, applying or ingesting a substance, or having a substance injected or inserted;
(d) undergoing disinfection and decontamination measures;
(e) wearing a type of clothing or other personal protective equipment, or changing, removing or altering clothing or personal protective equipment;
(f) using a type of equipment or implementing a process, or removing or altering equipment or processes.
.
(2) A person subject to a regulation requiring preventive measures must not be in a place or do a thing that is prohibited by the regulation until the person has
(a)taken preventive measures as set out in the regulation, or
(b)if permitted by the regulation, made an objection under subsection (4).
General emergency powers
Division 2 — Order of the Minister
Minister may order temporary quarantine facility
.
26 (1)The minister may by order designate a place as a quarantine facility if the minister reasonably believes that the temporary use of the place for the purposes of isolating or detaining infected persons is necessary to protect public health.
.
(2) A person who has control of a place designated as a quarantine facility must provide the place to the minister or a medical health officer.
Division 3 — Orders Respecting Infectious Agents and Hazardous Agents
When orders respecting infectious agents and hazardous agents may be made
27 (1) A medical health officer may issue an order under this Division only if the medical health officer reasonably believes that
(a) a person
(i) is an infected person, or
(ii) has custody or control of an infected person or an infected thing, and
(b) the order is necessary to protect public health.
.
(2) An order may be issued based on clinical findings or a person’s or thing’s circumstances or medical history, even if the person or thing has been examined and the examination did not reveal the presence of an infectious agent or a hazardous agent.
General powers respecting infectious agents and hazardous agents
.
28 (1) If the circumstances described in section 27 [when orders respecting infectious agents and hazardous agents may be made] apply, a medical health officer may order a person to do anything that the medical health officer reasonably believes is necessary for either or both of the following purposes:
(a) to determine whether an infectious agent or a hazardous agent exists, or likely exists;
(b) to prevent the transmission of an infectious agent or a hazardous agent.
(2 ) A medical health officer may, in respect of an infected thing,
(a) make any order, with any necessary modifications, that can be made under this Division as if the infected thing were an infected person, and
(b) direct the order to any person having custody or control of the infected thing.
Specific powers respecting infectious agents and hazardous agents
.
29 (1) An order may be made under this section only
(a) if the circumstances described in section 27 [when orders respecting infectious agents and hazardous agents may be made] apply, and
(b) for the purposes set out in section 28 (1) [general powers respecting infectious agents and hazardous agents].
.
(2) Without limiting section 28, a medical health officer may order a person to do one or more of the following:
.
(a) remain in a specified place, or not enter a place;
(b) avoid physical contact with, or being near, a person or thing;
(c) be under the supervision or care of a specified person;
(d) provide to the medical health officer or a specified person information, records, samples or other matters relevant to the person’s possible infection with an infectious agent or contamination with a hazardous agent, including information respecting persons who may have been exposed to an infectious agent or a hazardous agent by the person;
(e) be examined by a specified person, including
(i) going to a specified facility for examination, and
(ii) being examined before a particular date or according to a schedule;
(f) submit to diagnostic examination, including going to a specified facility or providing the results to a specified person;
(g) take preventive measures, including
(i) going to a specified facility for preventive measures,
(ii) complying with preventive measures set out in the order, specified by a medical practitioner or nurse practitioner, or both, and
(iii) beginning preventive measures before a particular date, and continuing until a particular date or event;
(h) provide evidence of complying with the order, including
(i) getting a certificate of compliance from a medical practitioner, nurse practitioner or specified person, and
(ii) providing to a medical health officer any relevant record;
(I ) take a prescribed action.
.
(3) For greater certainty, this section applies even if the person subject to the order is complying with all terms and conditions of a licence, a permit, an approval or another authorization issued under this or any other enactment.
54 (1) A health officer may, in an emergency, do one or more of the following:
(a) act in a shorter or longer time period than is otherwise required;
(b) not provide a notice that is otherwise required;
(c) do orally what must otherwise be done in writing;
(d) in respect of a licence or permit over which the health officer has authority under section 55 [acting outside designated terms during emergencies] or the regulations, suspend or vary the licence or permit without providing an opportunity to dispute the action;
(e) specify in an order a facility, place, person or procedure other than as required under section 63 [power to establish directives and standards], unless an order under that section specifies that the order applies in an emergency;
(f) omit from an order things that are otherwise required;
(g) serve an order in any manner;
(h) not reconsider an order under section 43 [reconsideration of orders], not review an order under section 44 [review of orders] or not reassess an order under section 45 [mandatory reassessment of orders];
(i) exempt an examiner from providing examination results to an examined person;
(j) conduct an inspection at any time, with or without a warrant, including of a private dwelling;
(k) collect, use or disclose information, including personal information,
(i) that could not otherwise be collected, used or disclosed, or
(ii) in a form or manner other than the form or manner required.
Under Section 54 the B.C. Public Health Act, during emergencies (or self-identified emergencies), Health Officers can have any place inspected at any time. A person can be examined, and the results of that exam withheld from him/her. Business can be shut down, without any recourse to challenge it. Health Officers can do things with oral only notice, or with no notice at all, and these privileges can be extended longer than need be.
Under Section 16 of the Act, a person can be ordered to be: vaccinated; medicated; ingest or insert something, and other invasive procedures. Section 26 of the Act allows the Health Minister to take any property and convert it into a quarantine facility. Sections 27 through 29 allows a Medical Health Officer – in this case, Bonnie Henry – virtual dictatorial powers over other people’s lives and livelihoods.
Worth clarifying, these “Health Officers” or “Medical Officers” are not elected by the public in any capacity. They cannot be voted out of their positions, regardless of the sentiments of the general population.
The Act of course is much, much longer than this. However, it is truly stunning just how much power unelected Health Officers are given over other people’s lives. And in B.C., all parties are apparently okay with handing over their duties.
Sure, the B.C. Public Health Act gives bureaucrats that power, but who wrote the Act in the first place? Who was responsible for handing over that power to begin with? This Act was written and voted on by MLAs (Members of Legislative Assembly), who are, in theory, accountable to voters.
A cynic might wonder if MLAs made this law in order to avoid making themselves accountable for decisions they make. Here at least, they can claim it’s not them, and that they are simply following the advice of health professionals.
It’s interesting that the B.C Health Act was assented to (made law) in 2008. The 3rd Edition of WHO’s International Health Regulations came into effect in 2005, and Canada’s 2005 Quarantine Act was heavily based on those IHR. The B.C. Act contains much of the same information and powers as the WHO/Federal documents, and it’s fair to assume that the content was derived from them.
Of course, this is hardly limited to B.C. Other Provinces have their own version of a Provincial Health Act, and they carry many of the same powers. This includes: Alberta , Saskatchewan , Manitoba , among others. What these Acts all have in common is they give broad, sweeping powers to bureaucrats who are not elected by the public, and who cannot be voted out. Looking at Alberta:
5. Alberta Public Health Act

Powers of Chief Medical Officer
.
14(1) The Chief Medical Officer
.
(a) shall, on behalf of the Minister, monitor the health of Albertans and make recommendations to the Minister and regional health authorities on measures to protect and promote the health of the public and to prevent disease and injury,
.
(b) shall act as a liaison between the Government and regional health authorities, medical officers of health and executive officers in the administration of this Act,
.
(c) shall monitor activities of regional health authorities, medical officers of health and executive officers in the administration of this Act, and
.
(d) may give directions to regional health authorities, medical officers of health and executive officers in the exercise of their powers and the carrying out of their responsibilities under this Act.
(2) Where the Chief Medical Officer is of the opinion that a medical officer of health or executive officer is not properly exercising powers or carrying out duties under this Act in respect of a matter, the Chief Medical Officer may assume the powers and duties of the medical officer of health or executive officer in respect of the matter and act in that person’s place.
Isolation, Quarantine and Special Measures
.
Isolation and quarantine
.
29(1) A medical officer of health who knows of or has reason to suspect the existence of a communicable disease or a public health emergency within the boundaries of the health region in which the medical officer of health has jurisdiction may initiate an investigation to determine whether any action is necessary to protect the public health.
(2) Where the investigation confirms the presence of a communicable disease, the medical officer of health
(a) shall carry out the measures that the medical officer of health is required by this Act and the regulations to carry out, and
(b) may do any or all of the following:
(i) take whatever steps the medical officer of health considers necessary
(A) to suppress the disease in those who may already have been infected with it,
(B) to protect those who have not already been exposed to the disease,
(C) to break the chain of transmission and prevent spread of the disease, and
(D) to remove the source of infection;
(ii) by order
(A) prohibit a person from attending a school,
(B) prohibit a person from engaging in the person’s occupation, or
(C) prohibit a person from having contact with other persons or any class of persons for any period and subject to any conditions that the medical officer of health considers appropriate, where the medical officer of health determines that the person’s engaging in that activity could transmit an infectious agent;
.
(iii) issue written orders for the decontamination or destruction of any bedding, clothing or other articles that
have been contaminated or that the medical officer of health reasonably suspects have been contaminated.
(2.1) Where the investigation confirms the existence of a public health emergency, the medical officer of health
(a) has all the same powers and duties in respect of the public health emergency as he or she has under subsection (2) in the case of a communicable disease, and
(b) may take whatever other steps are, in the medical officer of health’s opinion, necessary in order to lessen the impact of the public health emergency.
Sections 13 to 15 of Alberta’s Public Health Act outline how a Medical Health Officer is appointed, and the vast powers available to that person. In Alberta, that is currently Deena Hinshaw. Like Bonnie Henry, she is not elected, and cannot be held directly liable to the public for anything that she does.
Pages 25 through 31 of the most recent version of that Act relate to quarantine measures, epidemics, and how the average person’s rights can be suspended almost indefinitely under the pretense of “public safety”. It reads like the Provincial counterpart to the Quarantine Act, which of course, was dictated by the WHO.
Pages 39 through 51 cover Section 52 of the Alberta Public Health Act. It gives sweeping powers to unelected bureaucrats in the name of safety. The content of that Section reads almost beat for beat identical to that of the Quarantine Act. Moving on to Saskatchewan, we get this piece of legislation:
6. Saskatchewan Public Health Act
CONTROL OF EPIDEMICS Orders
.
45(1) The minister may make an order described in subsection (2) if the minister believes, on reasonable grounds, that:
.
(a) a serious public health threat exists in Saskatchewan; and (b) the requirements set out in the order are necessary to decrease or eliminate the serious public health threat. (2) An order pursuant to this section may: (a) direct the closing of a public place;
.
(b) restrict travel to or from a specified area of Saskatchewan;
.
(c) prohibit public gatherings in a specified area of Saskatchewan;
.
(d) in the case of a serious public health threat that is a communicable disease, require any person who is not known to be protected against the communicable disease:
(i) to be immunized or given prophylaxis where the disease is one for which immunization or prophylaxis is available; or
(ii) to be excluded from school until the danger of infection is past where the person is a pupil;
.
(e) establish temporary hospitals;
.
(f) require a local authority, a medical health officer or a public health officer to investigate matters relating to the serious public health threat and report to the minister the results of the investigation;
.
(g) require any person who, in the opinion of the minister or medical health officer, is likely to have information that is necessary to decrease or eliminate the serious public health threat to disclose that information to the minister or a medical health officer;
.
(h) authorize public health officers, peace officers or prescribed persons to confiscate substances or other materials found in any place, premises or vehicle, if those substances or materials are suspected by the public health officer, peace officer or prescribed person of causing or contributing to a serious public health threat or packages, containers or devices containing or suspected of containing any of those substances or materials;
.
(i) in the case of a serious public health threat that is a communicable disease, require any person to be isolated from other persons until a medical health officer is satisfied that isolation is no longer necessary to decrease or eliminate the transmission of a communicable disease.
Preventive detention order
45.1(1) If a person fails to comply with an order pursuant to clause 45(2)(i) and a medical health officer believes on reasonable grounds that the person is endangering the lives, safety or health of the public because the person is or probably is infected with, or has been or might have been exposed to, a communicable disease, the medical health officer may detain the person for a period not exceeding the prescribed period of transmissibility of the disease.
(2) A person detained by a medical health officer pursuant to subsection (1) may request a review of his or her detention by application to the Court of Queen’s Bench served on the minister, and the court may make any order with respect to the detention or the release of the person that the court considers appropriate, having regard to the danger to the lives, safety or health of the public.
In similar fashion, Saskatchewan has their own Public Health Act, which has undergone several revisions since the 1990s. It allows for freedoms and liberties to be suspended on even the vaguest suspicion that a person may have an infectious disease. It also allows for property to be seized, and people to be detained.
Things like public gatherings, and freedom of citizens to travel can also be suspended indefinitely under the guise of safety.
Note: as with all of these cases, it’s not the politicians doing the dirty work. It’s the various “experts” who call themselves Chief Medical Officers (or similar titles). This provides cover to elected officials, who want to stamp out civil rights, but don’t want to get their own hands dirty in the process. Now, about Manitoba:
7. Manitoba Public Health Act
PART 6
PUBLIC HEALTH EMERGENCY
Public health emergency
67(1) The chief public health officer may take one or more of the special measures described in subsection (2) if he or she reasonably believes that
(a) a serious and immediate threat to public health exists because of an epidemic or threatened epidemic of a communicable disease; and
(b) the threat to public health cannot be prevented, reduced or eliminated without taking special measures.
Special measures
67(2) The chief public health officer may take the following special measures in the circumstances set out in subsection (1):
(a) issue directions, for the purpose of managing the threat, to a regional health authority, health corporation, health care organization, operator of a laboratory, operator of a licensed emergency medical response system, health professional or health care provider, including directions about
(i) identifying and managing cases,
(ii) controlling infection,
(iii) managing hospitals and other health care facilities and emergency medical response services, and
(iv) managing and distributing equipment and supplies;
(a.1) issue an order prohibiting or restricting persons from travelling to, from or within a specified area, or requiring persons who are doing so to take specified actions;
(b) order the owner, occupant or person who appears to be in charge of any place or premises to deliver up possession of it to the minister for use as a temporary isolation or quarantine facility;
(c) order a public place or premises to be closed;
(d) order persons not to assemble in a public gathering in a specified area;
(d.1) order persons to take specified measures to prevent the spread of a communicable disease, including persons who arrive in Manitoba from another province, territory or country;
(e) order a person who the chief public health officer reasonably believes is not protected against a communicable disease to do one or both of the following:
(i) be immunized, or take any other preventive measures,
(ii) refrain from any activity or employment that poses a significant risk of infection, until the chief public health officer considers the risk of infection no longer exists;
(f) order an employer to exclude from a place of employment any person subject to an order under subclause (e)(ii).
Manitoba’s Public Health Act allows the Chief Medical Officer, and the operatives, to effectively suspend basic civil rights indefinitely. Of course this is “for your safety”, the ever present excuse. Basic liberties such as free association, freedom to peacefully assemble, and freedom to earn a livelihood can be stopped.
Note: the Act was assented to on June 13, 2006, a year after the Federal Quarantine Act, and the 3rd Edition of the International Health Regulations were implemented. The obvious implication is that this Act is just Manitoba enacting its own version.
Section 10 of the Act mandates that a Chief Medical Officer be named. Currently, that is Brent Roussin. In November, he caused a scandal when he openly admitted that public health orders don’t apply to public officials. Not leading by example.
8. Ontario Health Protection & Promotion Act

PART VI.1 PROVINCIAL PUBLIC HEALTH POWERS
.
Chief Medical Officer of Health may act where risk to health
.
77.1 (1) If the Chief Medical Officer of Health is of the opinion that a situation exists anywhere in Ontario that constitutes or may constitute a risk to the health of any persons, he or she may investigate the situation and take such action as he or she considers appropriate to prevent, eliminate or decrease the risk. 2007, c. 10, Sched. F, s. 15.
.
Same (2) For the purpose of subsection
.
(1), the Chief Medical Officer of Health,
.
(a) may exercise anywhere in Ontario,
(i) any of the powers of a board of health, including the power to appoint a medical officer of health or an associate medical officer of health, and (ii) any of the powers of a medical officer of health; and
.
(b) may direct a person whose services are engaged by a board of health to do, anywhere in Ontario, whether within or outside the health unit served by the board of health, any act,
(i) that the person has power to do under this Act, or
(ii) that the medical officer of health for the health unit served by the board of health has authority to direct the person to do within the health unit. 2007, c. 10, Sched. F, s. 15.
.
Authority and duty of person directed to act
(3) If the Chief Medical Officer of Health gives a direction under clause (2) (b) to a person whose services are engaged by a board of health, (a) the person has authority to act, anywhere in Ontario, whether within or outside the health unit served by the board of health, to the same extent as if the direction had been given by the medical officer of health of the board of health and the act had been done in the health unit; and (b) the person shall carry out the direction as soon as practicable. 2007, c. 10, Sched. F, s. 15. Section 22 powers
.
(4) For the purpose of the exercise by the Chief Medical Officer of Health under subsection (2) of the powers of a medical officer of health, a reference in section 22 to a communicable disease shall be deemed to be a reference to an infectious disease. 2007, c. 10, Sched. F, s. 15. Application to judge where risk to health 77.2 (1) If the Chief Medical Officer of Health is of the opinion that a situation exists anywhere in Ontario that constitutes or may constitute a risk to the health of any persons, he or she may apply to a judge of the Superior Court of Justice for an order under subsection (2). 2007, c. 10, Sched. F, s. 15.
Possession of premises for temporary isolation facility
.
77.4 (1) The Minister, in the circumstances mentioned in subsection (3), by order may require the occupier of any premises to deliver possession of all or any specified part of the premises to the Minister to be used as a temporary isolation facility or as part of a temporary isolation facility. 2007, c. 10, Sched. F, s. 15.
.
Extension
(2) An order under subsection (1) shall set out an expiry date for the order that is not more than 12 months after the day of its making and the Minister may extend the order for a further period of not more than 12 months. 2007, c. 10, Sched. F, s. 15.
.
Grounds for order
(3) The Minister may make an order under subsection (1) where the Chief Medical Officer of Health certifies in writing to the Minister that, (a) there exists or there is an immediate risk of an outbreak of a communicable disease anywhere in Ontario; and (b) the premises are needed for use as a temporary isolation facility or as part of a temporary isolation facility in respect of the communicable disease. 2007, c. 10, Sched. F, s. 15.
Ontario has the 2007 Health Protection and Promotion Act. The wording and powers are very similar to other Provinces, and to the Federal Quarantine Act. The timing is also suspicious, given that this was implemented soon after the 2005 International Health Regulations and the Federal legislation.
In Ontario, the Chief Medical Officer is David Williams, and the Deputy Medical Officer is Barbara Yaffe. As with the other so-called experts, these people are not elected, and have no real accountability to the public. Both have made very interesting statements about how dangerous this “pandemic” really is. More on them later.
9. These Acts Strip Away Basic Rights
At no time is there a requirement for there to be PROOF of a public health emergency to act on these powers. These Chief Medical Officers can simply claim that they “reasonably believe”, and that is sufficient.
Provincially and Federally, politicians write laws that allow unelected bureaucrats almost free reign to impose whatever measures they want. Of course, they don’t write content of the laws, but follow the instructions of a supra-national body that is accountable to no one.
This only covers 5 Provinces, however, they all have similar laws. If there is time, a Part II will be published to cover the others.
Like this:
Like Loading...