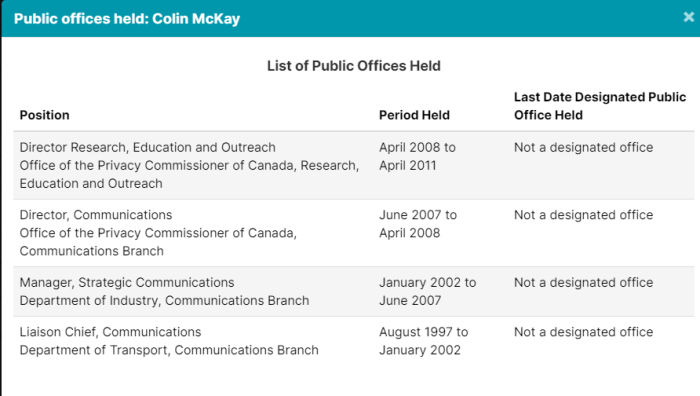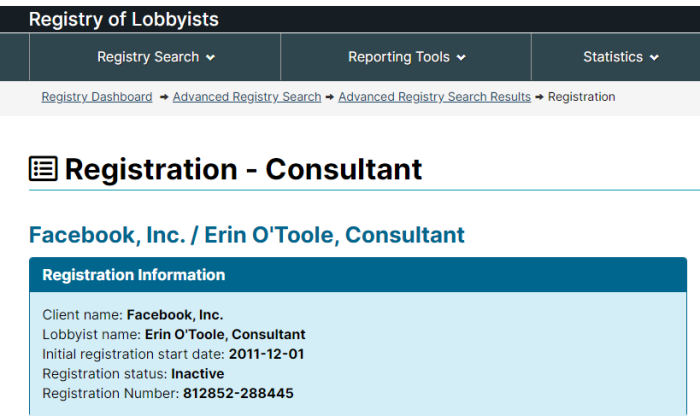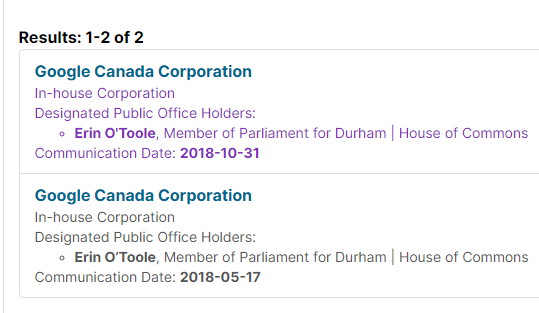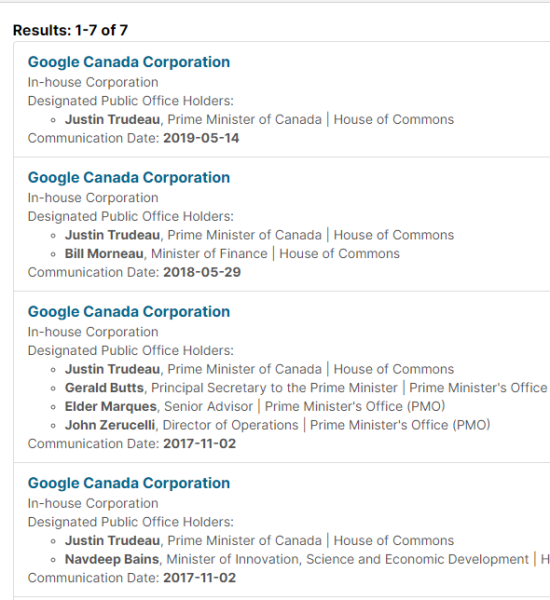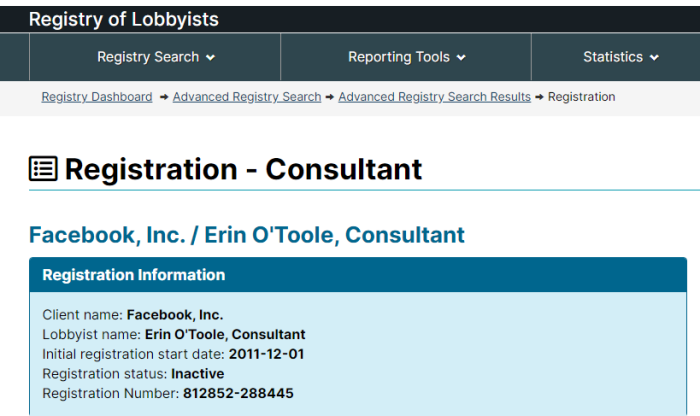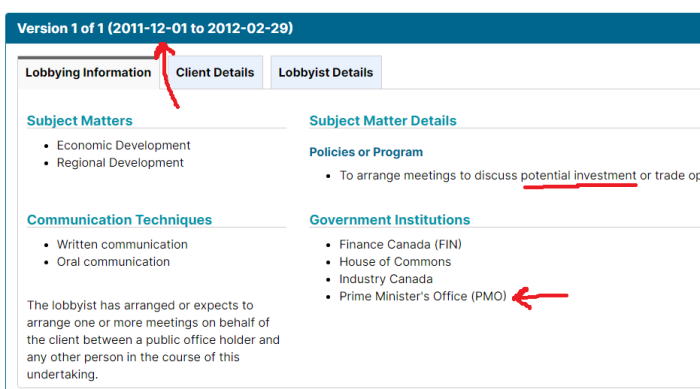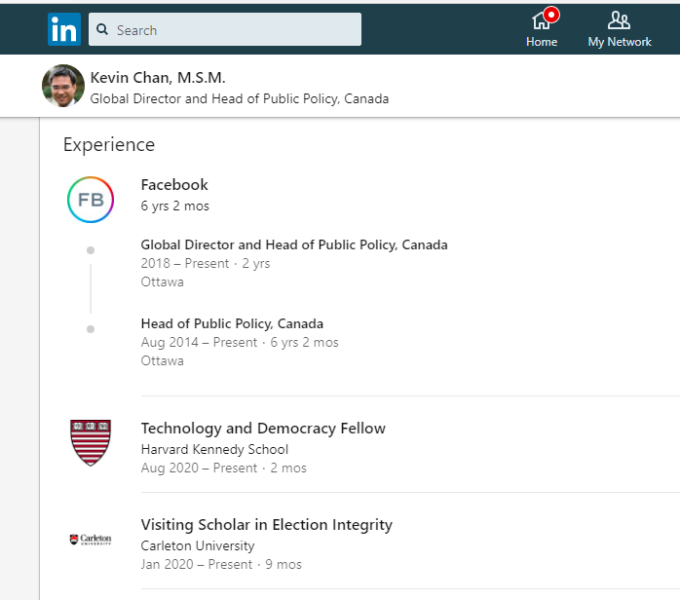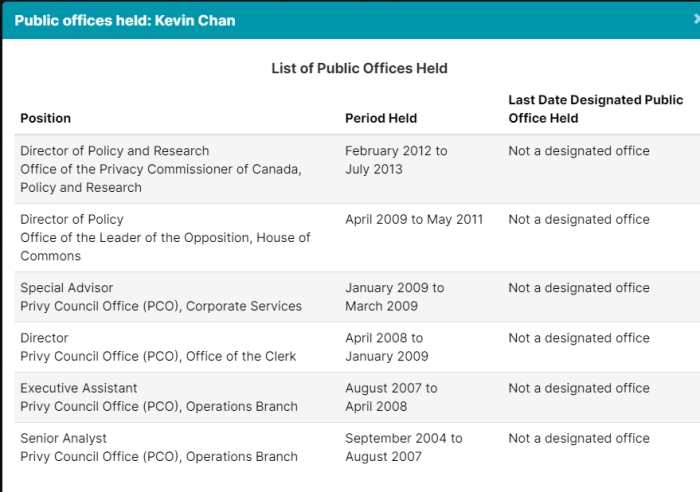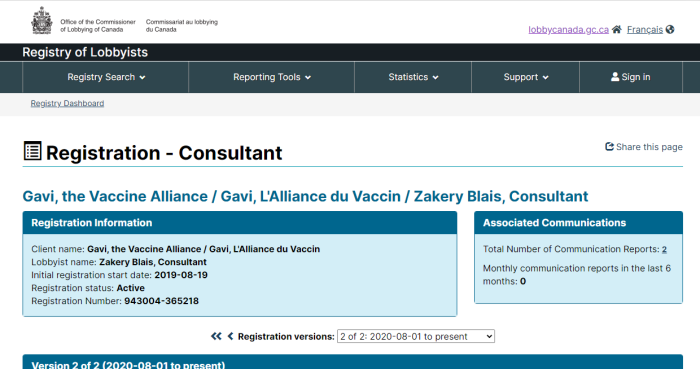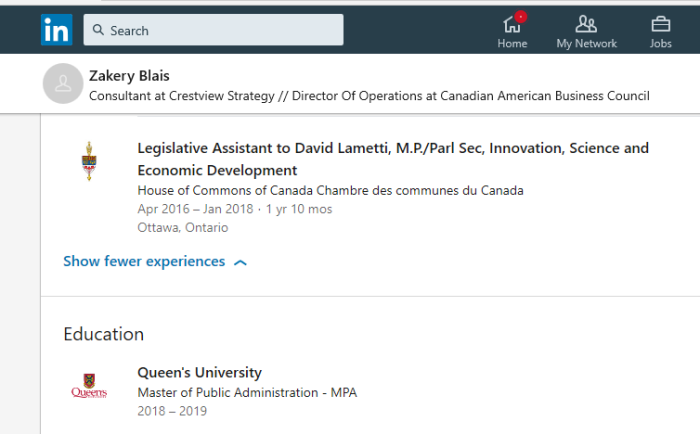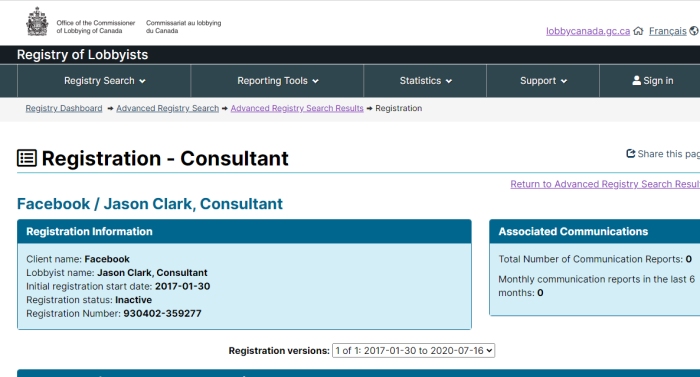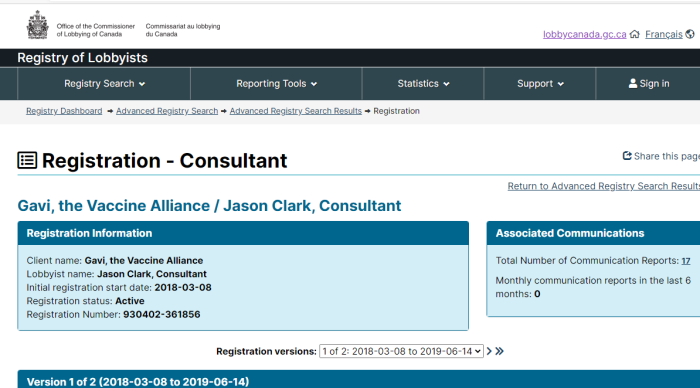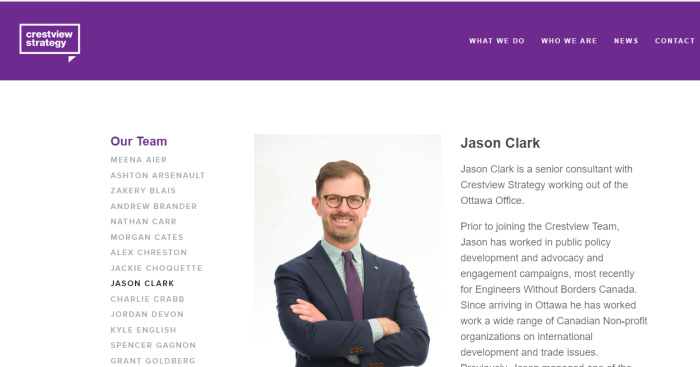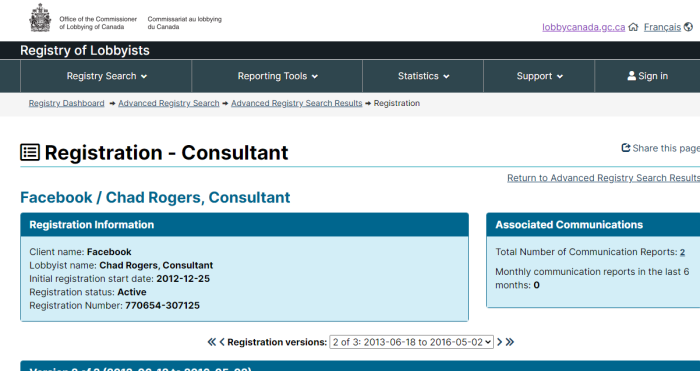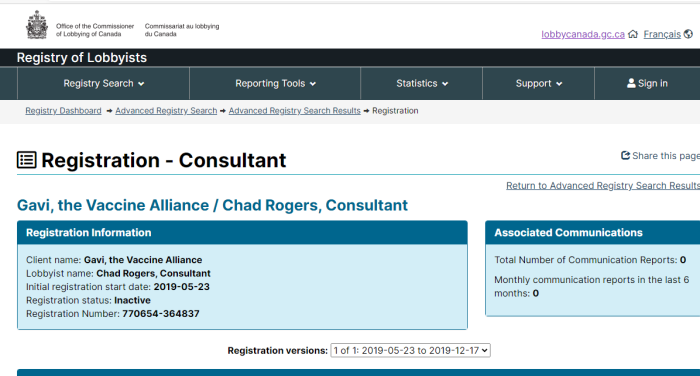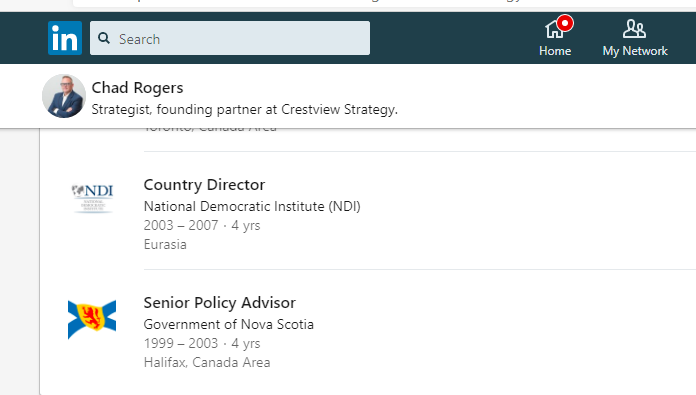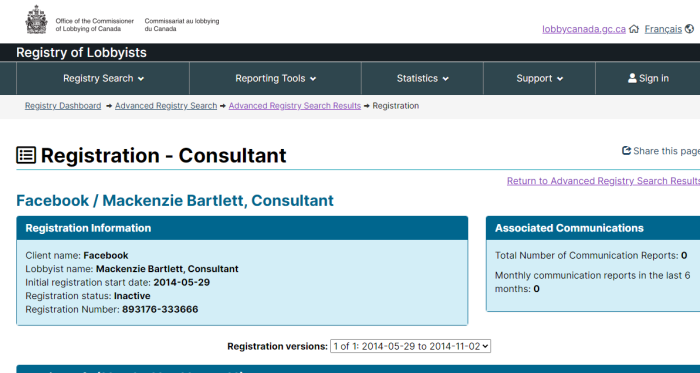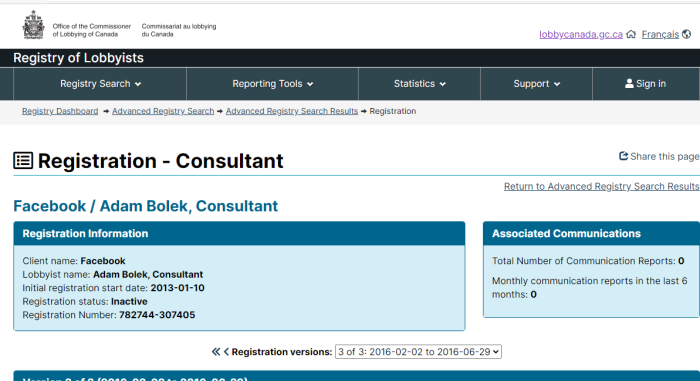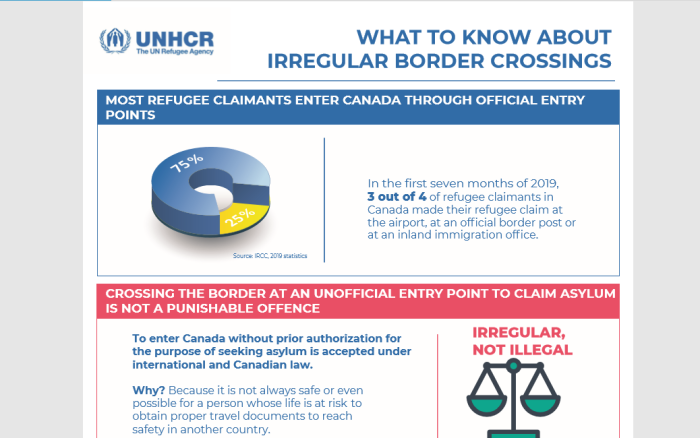
Getting your own politicians to protect free speech is difficult enough. How does it work when the rules are being drafted by unelected officials in other countries?
1. Important Developments On Free Speech
There is already a lot of information on the free speech series on the site. Free speech, while an important topic, doesn’t stand on its own, and is typically intertwined with other categories. For background information for this, please visit: Digital Cooperation; ex-Liberal Candidate Richard Lee; the Digital Charter, big tech collusion in coronavirus, and Dominic LeBlanc’s proposal.
IF you think that Canadian laws don’t do enough to protect free speech in general, or online free speech more specifically, just wait until it is regulated globally.
2. IGF Meetings Held Since 2006
2006: Athens, Greece, https://archive.is/g2NnZ
2007: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, https://archive.is/uiFsE
2008: Hyderabad, India, https://archive.is/6rV0k
2009: Sharm El Sheikh, Egypt, https://archive.is/dS2SO
2010: Vilnius, Lithuania, https://archive.is/uzC3U
2011: Nairobi, Kenya, https://archive.is/Dl71r
2012: Baku, Azerbaijan, https://archive.is/XUDaX
2013: Bali, Indonesia, https://archive.is/wksxQ
2014: Istanbul, Turkey, https://archive.is/XKnUe
2015: João Pessoa, Brazil, https://archive.is/1CiSE
2016: Jalisco, Mexico, https://archive.is/Rkazl
2017: Geneva, Switzerland, https://archive.is/mtw6w
2018: Paris, France, https://archive.is/zEsjK
2019: Berlin, Germany, https://archive.is/KGwzo
3. Important Issues Global IGF Discusses
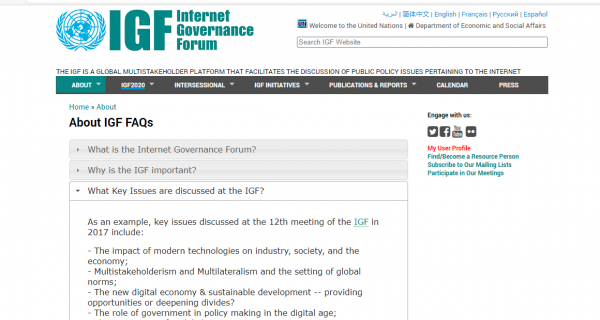
What Key Issues are discussed at the IGF?
As an example, key issues discussed at the 12th meeting of the IGF in 2017 include:
.
– The impact of modern technologies on industry, society, and the economy;
– Multistakeholderism and Multilateralism and the setting of global norms;
– The new digital economy & sustainable development — providing opportunities or deepening divides?
– The role of government in policy making in the digital age;
– The emergence of a global, Internet society;
– Cybersecurity and cyber-threats;
– Artificial intelligence (AI);
– Critical Internet resources;
– Blockchains and bitcoins;
– Fake news;
– Access, inclusion and diversity;
– The pressing need for security in the Internet of Things;
– Digital divides;
https://www.intgovforum.org/multilingual/content/about-igf-faqs
Advocates of strong free speech laws will notice (in particular) the topics of the role of government, and fake news. Makes one wonder if various Heads of State will decide what is real news and what is fake.
4. Who Funds Global IGF?
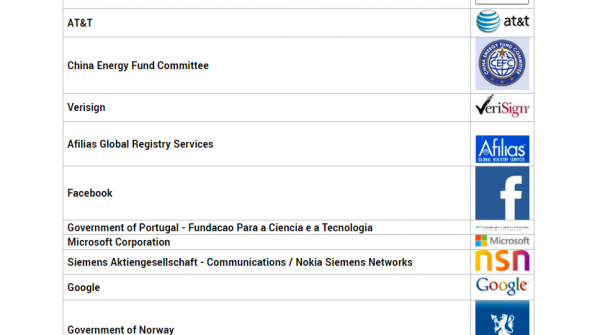
How is the global Internet Governance Forum funded?
.
The Internet Governance Forum (IGF) Secretariat – based in Geneva, is sustained financially through the extra-budgetary Trust Fund Account managed by United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA). The nature of the IGF Trust Fund is such that it is voluntary and multi-donor driven, with varying contributions from Governments and non-governmental organisations from the technical community, the private sector and the civil society. The IGF Trust Fund covers the administrative and operational costs of the IGF Secretariat including personnel, fellowships, and meeting costs (venues, interpretation, logistical costs, etc.); and funds the travel costs of MAG Members from developing countries. More details about the list of donors and funds received are available online. The Trust Fund also provides support to various intersessional activities, inter alia Best Practice Forums, major policy initiatives such as Connecting and Enabling the Next Billion(s), etc.
Each year, the organizational and conference cost of the annual meeting of the Internet Governance Forum is provided for by the Government of the host country, administered through a Host Country Agreement signed between the Government and the UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs.
https://www.intgovforum.org/multilingual/content/about-igf-faqs
Donors to the Trust Fund (highest to lowest)
- Government of Finland
- Government of Germany
- European Commission
- Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN)
- The Internet Society (ISOC)
- Number Resource Organization (NRO)
- Government of the Netherlands
- Government of Switzerland
- Government of the United States
- Government of the United Kingdom
- Government of Japan
- Nominet UK
- Tides Foundation
- Verizon
- IGFSA
- Brazilian Internet Steering Committee
- AT&T
- China Energy Fund Committee
- Verisign
- Afilias Global Registry Services
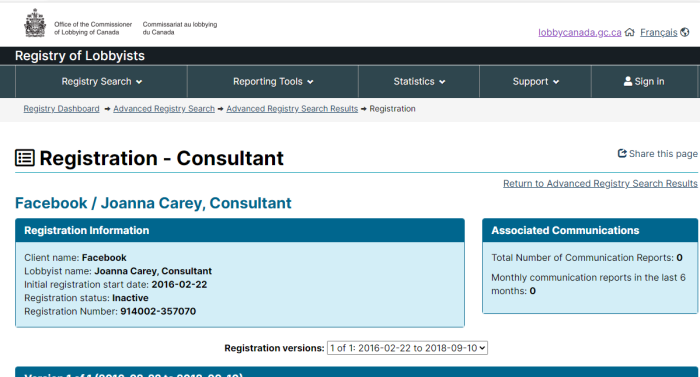
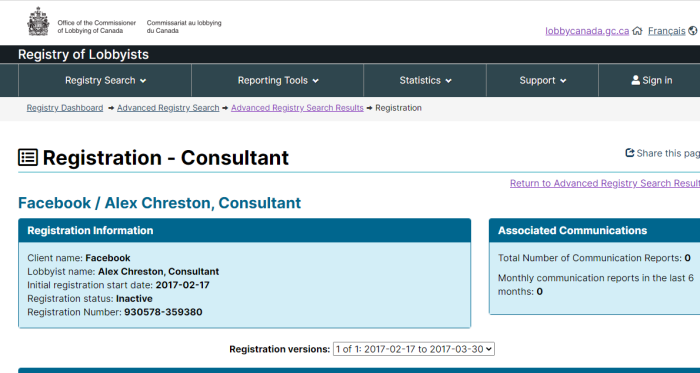
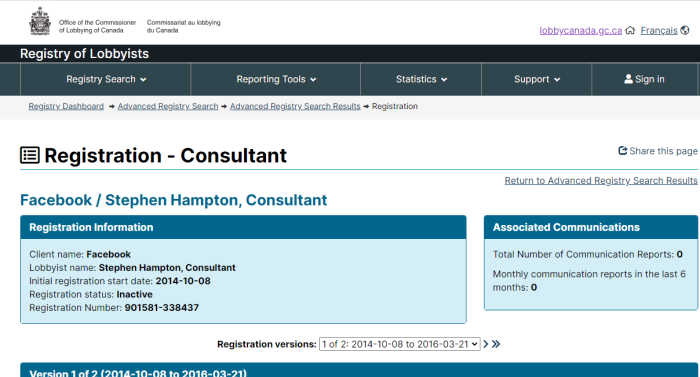
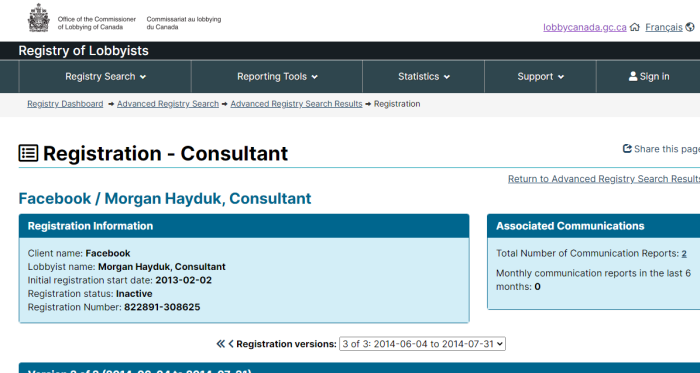
- Facebook
- Government of Portugal – Fundacao Para a Ciencia e a Tecnologia
- Microsoft Corporation
- Siemens Aktiengesellschaft – Communications / Nokia Siemens Networks
- Google
- Government of Norway
- Government of Sweden
- Amazon
- UNINETT Norid
- The Swiss Education & Research Network (SWITCH)
- The Walt Disney Company
- European Registry for Internet domains
- CISCO
- auDA Australia’s Domain Name Administrator
- International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) – Business Action to Support the Information Society (BASIS)
- Coordination Center for TLD
- Danish Internet Forum
- Politecnico di Torino
- Community DNS
- Government of the Republic of Korea
- European Telecommunication Network Operators’ Association
- MCADE, LLC
- NIC-MEXICO
- Nic.at The Austrian Registry
- Summit Strategies International
- NIKKEI DigitalCORE
- Ribose Inc.
In addition to the funding of various governments, the following names should be familiar to almost everyone: Google, Facebook, Microsoft, Disney, Amazon, AT&T, Verizon, and the Soros-funded Tides Foundation.
5. IGF And UNSG Panel On Digital Cooperation
>> FABRIZIO HOCHSCHILD: Excellencies, ladies and gentlemen, dear friends and colleagues. We’re having this conversation under unusual circumstances at a pivotal moment in history.
In a world already fundamentally transformed by digital technologies, the onslaught of the COVID-19 pandemic and the need for social distancing have propelled the adoption of information and communications technologies and transformed the bedrock of humanity’s means of survival and prosperity: communication. To cooperate, we must communicate, and to communicate nowadays, we must use digital means. This is an important time for Internet governance.
COVID-19 has raised the stakes for global digital cooperation. Over the last few months, my office, in partnership with the international telecommunications unit, organized a series of webinars on digital cooperation in times of COVID-19 and beyond. These discussions considered challenges when urgent cooperation is required, such as with regard to the ongoing deficit in connectivity, with regard to human rights challenges and trust and security issues.
.
Health systems today don’t just have to treat the sick. They also have to deal with cyber attacks and the spread of dangerous, life-threatening misinformation.
In follow-up to the Secretary-General’s call for a global cease far, I also called for a digital cease fire. Global cooperation is necessary if we wish to overcome the pandemic without drastically compromising values like privacy and freedom of speech.
A few days ago, the Secretary-General presented his roadmap for digital cooperation which sets forth his vision for how the international community should engage on these and other key digital issues outlined in the report of the High-Level Panel on Digital Cooperation. The roadmap describes a range of actions for all stakeholders from the United Nations system to member states, the private sector, civil society organizations, and the technical community. The United Nations, including the IGF, the Internet Governance Forum, can truly serve as a platform for informed discussion and evidence-based decisions and practices.
The High-level Panel had noted, and I quote, “a great deal of dissatisfaction with existing digital cooperation arrangements, a desire for more tangible outcomes, more active and diverse participation by governments and the private sector, and more inclusive processes and better follow-up,” end of quote.
The IGF should be retooled to become more responsive and relevant to current digital issues. We must ensure that the IGF is a forum that governments value and want to attend while preserving the important space it represents for other stakeholder engagement.
The IGF’s coordinating and strategic role needs to be further strengthened. The roadmap includes a series of suggestions to further enhance the IGF, such as by improving fundraising, inclusion, and outcomes. I hope you will all be engaged in the follow-up of the action areas highlighted in the Secretary-General’s roadmap, and I hope you will all share your views specifically on how the IGF can be made even more responsive to the evolving challenges of digital cooperation.
Thank you for your engagement and support of the IGF and digital cooperation. We welcome and we need your ideas, your proposals, and your continued enthusiasm and support.
Thank you.
Don’t worry. It’s not like this will lead to a global body deciding what can or can’t be talked about or shared on the internet. This will absolutely never be abused.
6. Global Digital Cooperation Frameworks
The Global Internet Governance Forum goes on to propose several different ways that “digital cooperation” could be implemented on a world-wide scale. But don’t worry. It’s all just discussion, and nothing that gets suggested will ever become legally binding.
7. Canadian Internet Governance Forum
Save the date: The virtual Canadian IGF will be Nov. 24 and Nov. 25, 2020.
The Canadian Internet Governance Forum (IGF) is Canada’s leading multi-stakeholder forum on digital and internet policy issues.
.
The inaugural event took place last year in Toronto and brought together over 200 representatives from government, civil society, and the private sector to tackle pressing public policy issues facing the internet.
.
The Canadian IGF is a national initiative of the global United-Nations-convened Internet Governance Forum, which holds annual meetings at different locations around the world. The Canadian IGF will produce a report detailing the unique, regional priorities facing Canadian stakeholders in attendance. This report will then be fed into the global IGF.
2019.canadian.internet.governance.forum
This isn’t just some abstract UN group far off. There exists a Canadian branch of the Internet Governance Forum, and its agenda is pretty much what one would expect.

Throughout the discussions, several common themes emerged across subject areas. These
included trends towards increased regulation; the necessity for plain language content; and,
the need for education and digital literacy. For stakeholders engaging in Internet governance
domestically and abroad, priorities going forward include the need for:
• A transnational, multistakeholder approach to internet governance.
• Awareness of/education on the issues, and how users can participate in discussions
related to internet governance.
• Solutions developed by any stakeholder group that are thoughtful, evidence-based, and
proportionate.
• Transparency from both governments and businesses in order to promote public trust
and build the capacity of users.
These priorities are elaborated in the conclusion of this report.
That is from page 5 on the report. They explicitly state that they view internet regulation as a global concept.
Key Issues
• Fake news and misinformation.
• Hateful online speech.
• Global and domestic threats.
• Data security
Discussion Overview
The panel’s discussion surrounded three main topics: 1) While foreign actors are a threat, domestic actors are an equal or higher risk when it comes to the dissemination of fake news and the proliferation of hateful speech online. Social media platforms also have to balance discouraging fake news, while ensuring they are not censoring a legitimate group; 2) Political actors are increasingly using social media platforms as a tool to get messages out; and 3) In the aftermath of Cambridge Analytica, academics have seen social media platforms reduce their access to datasets to study the fake news problem.
A recent report on Canadians’ use of social media shows that 94% of internet users here in this country have at least one social media account. The exposure to potential misinformation and disinformation campaigns is enormous.
Both technological and policy-based solutions are needed to confront the fake news problem. Facebook, for instance, has a three-pronged strategy focusing on people, technology and, increasingly, partnerships. Facebook has gone from 10,000 to 30,000 people dedicated to working on this challenge. In Q2 and Q3 of last year, Facebook removed approximately 1.5 billion fake accounts. The development of digital literacy skills is required to help users discern between real and fake news. The need for civility among users was also stressed. Canada must decide on its approach to fake news and newer technology, generally. Do we want to follow the lead of the United States or Europe?
A void has been created in the news world because traditional journalism is fading quickly. Social media platforms have become a new distribution channel for news. Panelists disagreed on whether the problem can be solved through technology or if it is more deeply rooted in human causes for which technology has no response
2019.canadian.internet.governance.forum
From pages 18/19 in the report: it seems that outlets like Facebook have taken it upon themselves to determine what accounts are fake, and what counts as fake news.

The authors of this report, (and of IGF more broadly), keep referring to “international stakeholders”. It seems to imply that other parties should have some say over free speech on the internet, instead of Canadians themselves.
8. Canada Gov’t Bought Off Media (2018)

It’s interesting that the report talks about the decline of traditional media (which is true), but omits the tax-payer funded bailout that the Canadian Government gave. In effect, old-stock media in Canada is now subsidized even more so. Even without the IGF, the media is already pretty corrupt.
9. UNESCO Campaign Against Mis-Information
This was covered a few months ago, but UNESCO has been embarking on a serious campaign against what it calls “misinformation”. UNESCO reminds people to only trust official sources for information on coronavirus.
10. UN Wants Internet Ruled By International Law

Tremendous progress has been made internationally in accepting that international law and the UN Charter apply in cyberspace. He urged the private sector to be involved in countering the number of malevolent tools being deployed in cyberspace, especially in developing more secure software.
Combating Fake News and Dangerous Content in the Digital Age
.
The consensus from the session on Fake News was that part of the complexity to tackle disinformation was the challenge to define it. From election interference to stoking up hate or increase religious hatred, there are also other multilayered levels such as spam, and misleading types of content like opinion pieces masking as objective journalism.
Irene Poetrant, Senior Researcher for Citizen Lab of University of Toronto agreed, saying definitions matter and in order to maintain an open and democratic system, it is important for government, private sector, civil society and institutions to work together, and that fake news is not just a problem of the west but a global problem.
“Misinformation is the antithesis of Google’s mission”, said Jake Lucchi, Head of Online Safety and Social Impact. Partnering with journalists, governments, and third parties, they try to find product solutions to identify misinformation and find ways to surface authoritative content. “Young people need to have critical thinking and skills to be able to navigate the internet and check our sources.” Improved algorithms and having policies in place to prohibit hate speech are also key – providers have to ensure misinformation are not allowed on their platforms.
That page is from the November 2018 meeting is Paris. While it sounds benevolent on the surface, who exactly will be the arbitrator of what is “fake news”? Remember, UNESCO (as an example), repeatedly says that only official sources can be trusted. This comes in spite of a wealth of information that CONTRADICTS those narratives. This raises the question of can valid media be shut down if factual reporting is tagged as “misinformation”?
11. Digital Charter Long In The Making
Think that the “Digital Charter” was an idea suddenly concocted? It wasn’t. The UN Digital Cooperation Panel was launched in the Summer of 2018. When the New Zealand shooting happened in March 2019, the stage had already been set.
In a similar vein, the mass shooting in Nova Scotia appears to be a pretext for the Federal Government imposing a mass gun grab.
12. Calls To Expand Digital Cooperation

11 June 2020 – New York
United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres presented today a set of recommended actions for the international community to help ensure all people are connected, respected, and protected in the digital age. The Secretary-General’s Roadmap for Digital Cooperation is the result of a multi-year, multi-stakeholder, global effort to address a range of issues related to the Internet, artificial intelligence, and other digital technologies.
The Roadmap for Digital Cooperation comes at a critical inflection point for digital issues, with the COVID-19 pandemic accelerating digitization and magnifying both opportunities and challenges of digital technology.
digital.cooperation.roadmap.expand
But don’t worry. These resolutions and agreements won’t ever become legally binding, or anything like that. These are just ideas being thrown around.
Like this:
Like Loading...