(Topic Previously Covered by Canuck Law)
CLICK HERE, for a very interesting page on free speech in Canada (links included).
Here is a portion of what is going to the Federal Court of Canada:
REMEDY SOUGHT
(a) To issue a permanent, binding injunction against the Federal Government ever participating in such a United Nations Parliament or other ”World Government” scheme on the grounds it violates the laws cited above
(b) To find that any such actions in furtherance of this scheme are unconstitutional.
Alternatively an order that:
(c) To rule that any such measure would require the following forms of consent:
I/ Vote from the Federal House of Commons
II/ Vote from the Senate
III/ Signature of the Prime Minister
IV/ Royal Assent from the Governor General
V/ A nationwide referendum on this issue with 75% majority
VI/ 7 of 10 Provinces (with 50%+ population) affirming
Note, should that alternative be ordered, it is asked that the court also rule for (c), that any Province or Municipality that wishes to opt out may do so.
Written submissions For challenge to UN Parliament
Part I: Jurisdiction
Part II: Issues
Part III: Facts
Part IV: Law
Part V: Authorities
Part VI: Order Sought
Part I: Jurisdiction
Part I: Jurisdiction
- Under Section 18 of the Federal Courts Act, and Section 300/301 of Federal Court Rules, the Federal Court of Canada has jurisdiction to hear such an application.
-
Federal Court also has jurisdiction to issue an injunction under Rule 18(1)(a) and 18(3) of Federal Courts Act ”
18 (1) Subject to section 28, the Federal Court has exclusive original jurisdiction (a) to issue an injunction, writ of certiorari, writ of prohibition, writ of mandamus or writ of quo warranto, or grant declaratory relief, against any federal board, commission or other tribunal;
-
Remedies to be obtained on application
(3) The remedies provided for in subsections (1) and (2) may be obtained only on an application for judicial review made under section 18.1.
-
Rule 303(2) in Federal Court Rules states that in an application for judicial review (which an extension of time is sought here), where no person can be named, the Attorney General of Canada shall be named as a Respondent. Since there is no ”single person” who is responsible for this mess, the Attorney General of Canada shall be named as a Defendant
Part II: Issues
- Seven questions to consider
-
First: Does the proposed UN Parliamentary Assembly (World Government), violate the 1867-1982 Constitution Act, which requires the Government of Canada to provide, “Peace, Order and Good Government” and makes no provision for abdication of that duty to supra-national bodies?
-
Second: Does the proposed UN Parliamentary Assembly (World Government) violate the 1982 Constitution Act, which states that it is the supreme law of Canada, and that any laws that any law that is inconsistent with the provisions of the Constitution is, to the extent of the inconsistency, of no force or effect.”
-
Third: Considering that this would add a new layer of Government to Canada, would this violate Sections 91 and 92 of the Consitution, which separate Federal and Provincial Jurisdictions?
-
Fourth: Does the proposed UN Parliamentary Assembly (World Government), require a constitutional amendment (Part V, Section 38 of the Constitution) that would require consent of:
(a) The House of Commons
(b) The Senate
(c) 7 of 10 Provinces, consisting of 50%+ of the population
-
Fifth: Does the proposed UN Parliamentary Assembly (World Government) violate Section 3 of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, which ensure all Canadians the right to participate in their democracy?
-
Sixth: Given some of the initiatives the UN proposes, such as internet regulation and free speech restrictions, would these violate Canadians’ fundamental freedoms, enshrined in Section 2 of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, and explicitly affirmed in Section 32?
-
Seventh: Would the proposed UN Parliamentary Assembly (World Government), violate Part II, Section 35 of the Constitution of Canada, which enshrines Aboriginal Rights?
Part III: Facts
- The United Nations (UN) is a globalist body which more and more is taking rights and sovereignty away from individual nation states
-
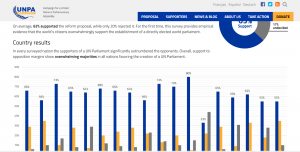
Since 2007, there has been an initiative by high ranking politicians and former politicians of ”UN Countries” to form a United Nations Parliamentary Assembly (UNPA). Dozens of current Canadian MPs, including Liberal, NDP, PM Justin Trudeau, and Green Party Leader Elizabeth May have all endorsed such a World Gov’t (Exhibit B)
-
As shown by screenshots (Exhibit A) from the website, the goal is explicitly to form LEGALLY BINDING decisions. This would in effect reduce nations to mere ”States” or ”Provinces” of the UN.
-
Other initiatives by the UN include
A/ Internet governance (digital cooperation)
B/ Global ban on blasphemy (criticism of Islam)
C/ Gender language agenda
D/ Global MIgration Compact (258M economic migrants)
E/ Paris Accord (carbon taxes)
F/ UN Global Citizenship Education
G/ Encouraging repatriation of Islamic terrorists
H/ Right to abortion (even for children)
I/ Agenda 21 (June 1992)
J/ Agenda 2030 (September 2015)
K/ Urban Development Agenda
-
This is only a partial list. But if this proposed UN Parliamentary Assembly (World Government) were ever to take place, all of these ”non-legally binding” initiatives will become ”legally-binding”.
-
Canadians have never been asked to vote on such a matter, either at the Municipal, Provincial or Federal level. The Government of Canada (nor any Gov’t) has no legal or moral mandate to enact such a proposal.
-
Canadians have never participated in any sort of national referendum to guage interest and approval of such an idea.
-
Canadians have never had the sort of public debate necessary to give an informed and intelligent response to such a proposed World Government.
Part IV: Relevant Laws
- The proposed United Nations Parliamentary Assembly (World Government) should be rejected because it violates a number of Constitutional provisions. Here are some of them:
(a) Section 2 of Charter: Fundamental Freedoms
(b) Section 3 of Charter: Right to participate in democracy
(c) Section 32 of Charter: Applicability
(d) Part II, Section 35 of Constitution, Aboriginal rights
(e) Part V, Section 38 of Constitution, amending Constitution
(f) Part VII, Section 52 of Constitution, primacy of Constitution
(g) Part VI: Section 91 & 92 of Constitution, distribution of powers
FUNDAMENTAL FREEDOMS (S2)
- (a) Fundamental Freedoms
Marginal note:
Fundamental freedoms
- Everyone has the following fundamental freedoms:
(a) freedom of conscience and religion;
(b) freedom of thought, belief, opinion and expression, including freedom of the press and other media of communication;
(c) freedom of peaceful assembly; and
(d) freedom of association.
DEMOCRATIC RIGHTS (S3)
- Democratic Rights
Marginal note:
Democratic rights of citizens
- Every citizen of Canada has the right to vote in an election of members of the House of Commons or of a legislative assembly and to be qualified for membership therein.
APPLICATION OF THE CHARTER (S32)
- Application of Charter
Marginal note:
Application of Charter
- (1) This Charter applies
(a) to the Parliament and government of Canada in respect of all matters within the authority of Parliament including all matters relating to the Yukon Territory and Northwest Territories; and
(b) to the legislature and government of each province in respect of all matters within the authority of the legislature of each province.
ABORIGINAL RIGHTS (S35)
- RIGHTS OF THE ABORIGINAL PEOPLES OF CANADA
Marginal note:
Recognition of existing aboriginal and treaty rights
- (1) The existing aboriginal and treaty rights of the aboriginal peoples of Canada are hereby recognized and affirmed.
Definition of “aboriginal peoples of Canada”
(2) In this Act, “aboriginal peoples of Canada” includes the Indian, Inuit and Métis peoples of Canada.
Marginal note:
Land claims agreements
(3) For greater certainty, in subsection (1) “treaty rights” includes rights that now exist by way of land claims agreements or may be so acquired.
PROCEDURE FOR AMENDING CONSTITUTION (S38)
- PROCEDURE FOR AMENDING CONSTITUTION OF CANADA (101)
Marginal note:
General procedure for amending Constitution of Canada
- (1) An amendment to the Constitution of Canada may be made by proclamation issued by the Governor General under the Great Seal of Canada where so authorized by
(a) resolutions of the Senate and House of Commons; and
(b) resolutions of the legislative assemblies of at least two-thirds of the provinces that have, in the aggregate, according to the then latest general census, at least fifty per cent of the population of all the provinces.
Marginal note:
Majority of members
(2) An amendment made under subsection (1) that derogates from the legislative powers, the proprietary rights or any other rights or privileges of the legislature or government of a province shall require a resolution supported by a majority of the members of each of the Senate, the House of Commons and the legislative assemblies required under subsection (1).
Marginal note:
Expression of dissent
(3) An amendment referred to in subsection (2) shall not have effect in a province the legislative assembly of which has expressed its dissent thereto by resolution supported by a majority of its members prior to the issue of the proclamation to which the amendment relates unless that legislative assembly, subsequently, by resolution supported by a majority of its members, revokes its dissent and authorizes the amendment.
PRIMACY OF CONSTITUTION (S52)
- Primacy of Constitution of Canada
- (1) The Constitution of Canada is the supreme law of Canada, and any law that is inconsistent with the provisions of the Constitution is, to the extent of the inconsistency, of no force or effect.
Marginal note:
Constitution of Canada
(2) The Constitution of Canada includes
(a) the Canada Act 1982, including this Act;
(b) the Acts and orders referred to in the schedule; and
(c) any amendment to any Act or order referred to in paragraph (a) or (b).
Marginal note:
Amendments to Constitution of Canada
(3) Amendments to the Constitution of Canada shall be made only in accordance with the authority contained in the Constitution of Canada.
DISTRIBUTION OF POWERS (S91/S92)
- VI. DISTRIBUTION OF LEGISLATIVE POWERS
Powers of the Parliament
Marginal note:
Legislative Authority of Parliament of Canada
- It shall be lawful for the Queen, by and with the Advice and Consent of the Senate and House of Commons, to make Laws for the Peace, Order, and good Government of Canada, in relation to all Matters not coming within the Classes of Subjects by this Act assigned exclusively to the Legislatures of the Provinces; and for greater Certainty, but not so as to restrict the Generality of the foregoing Terms of this Section, it is hereby declared that (notwithstanding anything in this Act) the exclusive Legislative Authority of the Parliament of Canada extends to all Matters coming within the Classes of Subjects next hereinafter enumerated; that is to say,
-
Repealed. (44)
1A.
The Public Debt and Property. (45)
-
The Regulation of Trade and Commerce.
2A.
Unemployment insurance. (46)
-
The raising of Money by any Mode or System of Taxation.
And any Matter coming within any of the Classes of Subjects enumerated in this Section shall not be deemed to come within the Class of Matters of a local or private Nature comprised in the Enumeration of the Classes of Subjects by this Act assigned exclusively to the Legislatures of the Provinces. (47)
Exclusive Powers of Provincial Legislatures
Marginal note:
Subjects of exclusive Provincial Legislation
- In each Province the Legislature may exclusively make Laws in relation to Matters coming within the Classes of Subjects next hereinafter enumerated; that is to say,
-
Repealed. (48)
-
Direct Taxation within the Province in order to the raising of a Revenue for Provincial Purposes.
-
The borrowing of Money on the sole Credit of the Province.
-
The Establishment and Tenure of Provincial Offices and the Appointment and Payment of Provincial Officers.
-
The Management and Sale of the Public Lands belonging to the Province and of the Timber and Wood thereon.
-
The Establishment, Maintenance, and Management of Public and Reformatory Prisons in and for the Province.
-
The Establishment, Maintenance, and Management of Hospitals, Asylums, Charities, and Eleemosynary Institutions in and for the Province, other than Marine Hospitals.
-
Municipal Institutions in the Province.
-
Shop, Saloon, Tavern, Auctioneer, and other Licences in order to the raising of a Revenue for Provincial, Local, or Municipal Purposes.
-
Local Works and Undertakings other than such as are of the following Classes:
(a)
Lines of Steam or other Ships, Railways, Canals, Telegraphs, and other Works and Undertakings connecting the Province with any other or others of the Provinces, or extending beyond the Limits of the Province:
(b)
Lines of Steam Ships between the Province and any British or Foreign Country:
(c)
Such Works as, although wholly situate within the Province, are before or after their Execution declared by the Parliament of Canada to be for the general Advantage of Canada or for the Advantage of Two or more of the Provinces.
-
The Incorporation of Companies with Provincial Objects.
-
The Solemnization of Marriage in the Province.
-
Property and Civil Rights in the Province.
-
The Administration of Justice in the Province, including the Constitution, Maintenance, and Organization of Provincial Courts, both of Civil and of Criminal Jurisdiction, and including Procedure in Civil Matters in those Courts.
-
The Imposition of Punishment by Fine, Penalty, or Imprisonment for enforcing any Law of the Province made in relation to any Matter coming within any of the Classes of Subjects enumerated in this Section.
- Generally all Matters of a merely local or private Nature in the Province.
-
Sections 91 and 92 have no provision for any supra-national body to interfere with this distribution of powers.
-
Note that ”Parliamentary Perogative” does not apply here, since the proposed Gobal Government is not a treaty BETWEEN governments. Rather, it would dissolve nations in favour of a supra-national body,
Part V: Authorities
Reference re Senate Reform, [2014] 1 SCR 704, 2014 SCC 32 (CanLII) (S38)
CLICK HERE, for full text of decision.
Sibbeston v. Canada (Attorney-General), 1988 CanLII 5673 (NWT CA) (S52)
CLICK HERE, for full text of decision.
Irwin Toy Ltd. v. Quebec (Attorney General), [1989] 1 SCR 927, 1989 CanLII 87 (SCC) (S2)
CLICK HERE, for the full text of decision.
Figueroa v. Canada (Attorney General), [2003] 1 S.C.R. 912 (S3)
CLICK HERE, for decision, view para 27, 30, 31.
2 cases on Aboriginal duty to consult:
Haida Nation v. British Columbia (Minister of Forests), [2004] 3 SCR 511, 2004 SCC 73 (CanLII) (S35)
(1) CLICK HERE, for full text of decision.
(2) Taku River Tlingit First Nation v. British Columbia (Project Assessment Director), [2004] 3 SCR 550, 2004 SCC 74 (CanLII) (S35)
CLICK HERE, for full text of decision.
Reference re Senate Reform, [2014] 1 SCR 704, 2014 SCC 32 (CanLII) (S38)
CLICK HERE, for full text of decision.
(a) The General Amending Procedure
[33] Section 38 of the Constitution Act, 1982 provides:
38. (1) An amendment to the Constitution of Canada may be made by proclamation issued by the Governor General under the Great Seal of Canada where so authorized by
(a) resolutions of the Senate and House of Commons; and
(b) resolutions of the legislative assemblies of at least two-thirds of the provinces that have, in the aggregate, according to the then latest general census, at least fifty per cent of the population of all the provinces.
(2) An amendment made under subsection (1) that derogates from the legislative powers, the proprietary rights or any other rights or privileges of the legislature or government of a province shall require a resolution supported by a majority of the members of each of the Senate, the House of Commons and the legislative assemblies required under subsection (1).
(3) An amendment referred to in subsection (2) shall not have effect in a province the legislative assembly of which has expressed its dissent thereto by resolution supported by a majority of its members prior to the issue of the proclamation to which the amendment relates unless that legislative assembly, subsequently, by resolution supported by a majority of its members, revokes its dissent and authorizes the amendment.
(4) A resolution of dissent made for the purposes of subsection (3) may be revoked at any time before or after the issue of the proclamation to which it relates.
[34] The process set out in s. 38 is the general rule for amendments to the Constitution of Canada. It reflects the principle that substantial provincial consent must be obtained for constitutional change that engages provincial interests. Section 38 codifies what is colloquially referred to as the “7/50” procedure — amendments to the Constitution of Canada must be authorized by resolutions of the Senate, the House of Commons, and legislative assemblies of at least seven provinces whose population represents, in the aggregate, at least half of the current population of all the provinces. Additionally, it grants to the provinces the right to “opt out” of constitutional amendments that derogate from “the legislative powers, the proprietary rights or any other rights or privileges of the legislature or government of a province”.
- Sibbeston v. Canada (Attorney-General), 1988 CanLII 5673 (NWT CA) (S52)
CLICK HERE, for full text of decision.
[6] The respondent’s amended petition cannot be pursued under principles of Canadian constitutional practice that must now be regarded as established. They include the political reality that it is the people of Canada, expressing their political will through the joint constitutional authority of the Parliament of Canada and the elected legislative assemblies of the provinces, who are sovereign in the delineation of federal-provincial power-sharing under the Constitution of Canada. Beyond that no segment of the Constitution of Canada, including the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, is paramount to other segments, or indeed the balance, of the Constitution. The Constitution “as a whole” is Canada’s supreme law.
[7] Section 52 of the Constitution Act, 1982, provides:
52(1) The Constitution of Canada is the supreme law of Canada, and any law that is inconsistent with the provisions of the Constitution is, to the extent of the inconsistency, of no force or effect.
(2) The Constitution of Canada includes
(a) the Canada Act, 1982, including this Act;
(b) the Acts and orders referred to in the schedule; and
(c) any amendment to any Act or order referred to in paragraph (a) or (b).
(3) Amendments to the Constitution of Canada shall be made only in accordance with the authority contained in the Constitution of Canada.
[8] Section 52 espouses the equality of its components including amendments. Charter scrutiny could not have been reserved by its drafters: Reference re an Act to Amend the Education Act (Ontario) (1987), 1987 CanLII 65 (SCC), 40 D.L.R. (4th) 18, [1987] 1 S.C.R. 1148, 77 N.R. 241.
[9] The Constitution Act, 1982, also provides:
Application of Charter
32(1) This Charter applies
(a) to the Parliament and government of Canada in respect of all matters within the authority of Parliament including all matters relating to the Yukon Territory and Northwest Territories; and
(b) to the legislature and government of each province in respect of all matters within the authority of the legislature of each province.
- Irwin Toy Ltd. v. Quebec (Attorney General), [1989] 1 SCR 927, 1989 CanLII 87 (SCC) (S2)
CLICK HERE, for the full text of decision.
C.The Second Step: Was the Purpose or Effect of the Government Action to Restrict Freedom of Expression?
Having found that the plaintiff’s activity does fall within the scope of guaranteed free expression, it must next be determined whether the purpose or effect of the impugned governmental action was to control attempts to convey meaning through that activity. The importance of focussing at this stage on the purpose and effect of the legislation is nowhere more clearly stated than in R. v. Big M Drug Mart Ltd., 1985 CanLII 69 (SCC), [1985] 1 S.C.R. 295, at pp. 331-32 where Dickson J. (as he then was), speaking for the majority, observed:
In my view, both purpose and effect are relevant in determining constitutionality; either an unconstitutional purpose or an unconstitutional effect can invalidate legislation. All legislation is animated by an object the legislature intends to achieve. This object is realized through the impact produced by the operation and application of the legislation. Purpose and effect respectively, in the sense of the legislation’s object and its ultimate impact, are clearly linked, if not indivisible. Intended and actual effects have often been looked to for guidance in assessing the legislation’s object and thus, its validity.
Moreover, consideration of the object of legislation is vital if rights are to be fully protected. The assessment by the courts of legislative purpose focuses scrutiny upon the aims and objectives of the legislature and ensures they are consonant with the guarantees enshrined in the Charter. The declaration that certain objects lie outside the legislature’s power checks governmental action at the first stage of unconstitutional conduct. Further, it will provide more ready and more vigorous protection of constitutional rights by obviating the individual litigant’s need to prove effects violative of Charter rights. It will also allow courts to dispose of cases where the object is clearly improper, without inquiring into the legislation’s actual impact.
Figueroa v. Canada (Attorney General), [2003] 1 S.C.R. 912 (S2)
CLICK HERE, for decision, view para 27.
27 An understanding of s. 3 that emphasizes the right of each citizen to play a meaningful role in the electoral process also is sensitive to the full range of reasons that individual participation in the electoral process is of such importance in a free and democratic society. As Dickson C.J. wrote in R. v. Oakes, [1986] 1 S.C.R. 103, at p. 136:
The Court must be guided by the values and principles essential to a free and democratic society which I believe embody, to name but a few, respect for the inherent dignity of the human person, commitment to social justice and equality, accommodation of a wide variety of beliefs, respect for cultural and group identity, and faith in social and political institutions which enhance the participation of individuals and groups in society.
In this passage, Dickson C.J. was addressing s. 1 . Yet since reference to “a free and democratic society” is essential to an enriched understanding of s. 3 , this passage indicates that the best interpretation of s. 3 is one that advances the values and principles that embody a free and democratic state, including respect for a diversity of beliefs and opinions. Defining the purpose of s. 3 with reference to the right of each citizen to meaningful participation in the electoral process, best reflects the capacity of individual participation in the electoral process to enhance the quality of democracy in this country.
30 In the final analysis, I believe that the Court was correct in Haig, supra, to define s. 3 with reference to the right of each citizen to play a meaningful role in the electoral process. Democracy, of course, is a form of government in which sovereign power resides in the people as a whole. In our system of democracy, this means that each citizen must have a genuine opportunity to take part in the governance of the country through participation in the selection of elected representatives. The fundamental purpose of s. 3 , in my view, is to promote and protect the right of each citizen to play a meaningful role in the political life of the country. Absent such a right, ours would not be a true democracy.
31 For this reason, I cannot agree with LeBel J. that it is proper, at this stage of the analysis, to balance the right of each citizen to play a meaningful role in the electoral process against other democratic values, such as the aggregation of political preferences. Legislation that purports to encourage the aggregation of political preferences might advance certain collective interests, but it does not benefit all citizens, namely, those whose interests are not aggregated by the mainstream political parties. As a result, the proportionality analysis endorsed by LeBel J. clearly admits of the possibility that collective or group interests will be balanced against the right of each citizen to play a meaningful role in the electoral process at the infringement stage of the analysis. If the government is to interfere with the right of each citizen to play a meaningful role in the electoral process in order to advance other values, it must justify that infringement under s. 1 .
Also worth noting (need a residency to vote) persons who have recently arrived in a province or territory (Reference Re Yukon Election Residency Requirements (1986), 27 D.L.R. (4th) 146 (Y.T.C.A.); Storey v. Zazelenchuk (1984), 36 Sask.R. 103 (C.A.); Olson v. Ontario (1992), 12 C.R.R. (2d) 120 (Ont.Gen.Div.); Arnold v. Ontario (Attorney General) (1987), 43 D.L.R. 4th 94 (Ont.H.Ct.) — although 6 to 12 month minimum residency requirements were justified under section 1)
Haida Nation v. British Columbia (Minister of Forests), [2004] 3 SCR 511, 2004 SCC 73 (CanLII) (S35)
CLICK HERE, for full text of decision.
26 Honourable negotiation implies a duty to consult with Aboriginal claimants and conclude an honourable agreement reflecting the claimants’ inherent rights. But proving rights may take time, sometimes a very long time. In the meantime, how are the interests under discussion to be treated? Underlying this question is the need to reconcile prior Aboriginal occupation of the land with the reality of Crown sovereignty. Is the Crown, under the aegis of its asserted sovereignty, entitled to use the resources at issue as it chooses, pending proof and resolution of the Aboriginal claim? Or must it adjust its conduct to reflect the as yet unresolved rights claimed by the Aboriginal claimants?
27 The answer, once again, lies in the honour of the Crown. The Crown, acting honourably, cannot cavalierly run roughshod over Aboriginal interests where claims affecting these interests are being seriously pursued in the process of treaty negotiation and proof. It must respect these potential, but yet unproven, interests. The Crown is not rendered impotent. It may continue to manage the resource in question pending claims resolution. But, depending on the circumstances, discussed more fully below, the honour of the Crown may require it to consult with and reasonably accommodate Aboriginal interests pending resolution of the claim. To unilaterally exploit a claimed resource during the process of proving and resolving the Aboriginal claim to that resource, may be to deprive the Aboriginal claimants of some or all of the benefit of the resource. That is not honourable.
Taku River Tlingit First Nation v. British Columbia (Project Assessment Director), [2004] 3 SCR 550, 2004 SCC 74 (CanLII)
CLICK HERE, for full text of decision.
23 The Province argues that, before the determination of rights through litigation or conclusion of a treaty, it owes only a common law “duty of fair dealing” to Aboriginal peoples whose claims may be affected by government decisions. It argues that a duty to consult could arise after rights have been determined, through what it terms a “justificatory fiduciary duty”. Alternatively, it submits, a fiduciary duty may arise where the Crown has undertaken to act only in the best interests of an Aboriginal people. The Province submits that it owes the TRTFN no duty outside of these specific situations.
24 The Province’s submissions present an impoverished vision of the honour of the Crown and all that it implies. As discussed in the companion case of Haida, supra, the principle of the honour of the Crown grounds the Crown’s duty to consult and if indicated accommodate Aboriginal peoples, even prior to proof of asserted Aboriginal rights and title. The duty of honour derives from the Crown’s assertion of sovereignty in the face of prior Aboriginal occupation. It has been enshrined in s. 35(1) of the Constitution Act, 1982, which recognizes and affirms existing Aboriginal rights and titles. Section 35(1) has, as one of its purposes, negotiation of just settlement of Aboriginal claims. In all its dealings with Aboriginal peoples, the Crown must act honourably, in accordance with its historical and future relationship with the Aboriginal peoples in question. The Crown’s honour cannot be interpreted narrowly or technically, but must be given full effect in order to promote the process of reconciliation mandated by s. 35(1).
25 As discussed in Haida, what the honour of the Crown requires varies with the circumstances. It may require the Crown to consult with and accommodate Aboriginal peoples prior to taking decisions: R. v. Sparrow, 1990 CanLII 104 (SCC), [1990] 1 S.C.R. 1075, at p. 1119; R. v. Nikal, 1996 CanLII 245 (SCC), [1996] 1 S.C.R. 1013; R. v. Gladstone, 1996 CanLII 160 (SCC), [1996] 2 S.C.R. 723; Delgamuukw v. British Columbia, 1997 CanLII 302 (SCC), [1997] 3 S.C.R. 1010, at para. 168. The obligation to consult does not arise only upon proof of an Aboriginal claim, in order to justify infringement. That understanding of consultation would deny the significance of the historical roots of the honour of the Crown, and deprive it of its role in the reconciliation process. Although determining the required extent of consultation and accommodation before a final settlement is challenging, it is essential to the process mandated by s. 35(1). The duty to consult arises when a Crown actor has knowledge, real or constructive, of the potential existence of Aboriginal rights or title and contemplates conduct that might adversely affect them. This in turn may lead to a duty to change government plans or policy to accommodate Aboriginal concerns. Responsiveness is a key requirement of both consultation and accommodation.
Part VI: Order Sought
- (a) To issue a permanent, binding injunction against the Federal Government ever participating in such a United Nations Parliament or other ”World Government” scheme on the grounds it violates the laws cited above
(b) To find that any such actions in furtherance of this scheme are unconstitutional.
Alternatively an order that:
(c) To rule that any such measure would require the following forms of consent:
I/ Vote from the Federal House of Commons
II/ Vote from the Senate
III/ Signature of the Prime Minister
IV/ Royal Assent from the Governor General
V/ A nationwide referendum on this issue with 75% majority
VI/ 7 of 10 Provinces (with 50%+ population) affirming
Note, should that alternative be ordered, it is asked that the court also rule for (c), that any Province or Municipality that wishes to opt out may do so.
Sincerely,
Me
Like this:
Like Loading...