(Ways to raise money)
(Details of proposed global tax scheme)
These are not the only examples, but should serve as an illustration for the “taxation” efforts the UN is undertaking in order to finance its various agendas. Of course its ultimate goal is world domination. It’s quite the rabbit hole, and this is just surface level.
(Shiva Ayyadurai, Republican and former Senate Candidate explains how the Carbon tax really works.)
1. Paris Accord Is All About Taxation

(This is the Paris Accord, and “Conservative” Garnett Genuis’ dishonest spin in supporting it in Parliament.)
This is not an exaggeration, or hyperbole. The entire point of the agreement is to generate an enormous slush fund. The UN IPCC and select partners can then put that money into the commodities market and make trillions from it.
If you have any doubts about that, read Article 9 from the Paris Agreement. It spells out the “financial flow” in no uncertain terms.
1. Developed country Parties shall provide financial resources to assist developing country Parties with respect to both mitigation and adaptation in continuation of their existing obligations under the Convention.
2. Other Parties are encouraged to provide or continue to provide such support voluntarily.
3. As part of a global effort, developed country Parties should continue to take the lead in mobilizing climate finance from a wide variety of sources, instruments and channels, noting the significant role of public funds, through a variety of actions, including supporting country-driven strategies, and taking into account the needs and priorities of developing country Parties. Such mobilization of climate finance should represent a progression beyond previous efforts.
4. The provision of scaled-up financial resources should aim to achieve a balance between adaptation and mitigation, taking into account country-driven strategies, and the priorities and needs of developing country Parties, especially those that are particularly vulnerable to the adverse effects of climate change and have significant capacity constraints, such as the least developed countries and small island developing States, considering the need for public and grant-based resources for adaptation.
5. Developed country Parties shall biennially communicate indicative quantitative and qualitative information related to paragraphs 1 and 3 of this Article, as applicable, including, as available, projected levels of public financial resources to be provided to developing country Parties. Other Parties providing resources are encouraged to communicate biennially such information on a voluntary basis.
6. The global stock take referred to in Article 14 shall take into account the relevant information provided by developed country Parties and/or Agreement bodies on efforts related to climate finance.
7. Developed country Parties shall provide transparent and consistent information on support for developing country Parties provided and mobilized through public interventions biennially in accordance with the modalities, procedures and guidelines to be adopted by the Conference of the Parties serving as the meeting of the Parties to this Agreement, at its first session, as stipulated in Article 13, paragraph 13. Other Parties are encouraged to do so.
8. The Financial Mechanism of the Convention, including its operating entities, shall serve as the financial mechanism of this Agreement.
9. The institutions serving this Agreement, including the operating entities of the Financial Mechanism of the Convention, shall aim to ensure efficient access to financial resources through simplified approval procedures and enhanced readiness support for developing country Parties, in particular for the least developed countries and small island developing States, in the context of their national climate strategies and plans.
These are quotes directly from the Paris Accord. In particular, Article 9 makes it abundantly clear that this is all about “financial flow” and a transfer of wealth from the developed world to the developing world.
Actual environmental changes seem almost to be an afterthought. This is a giant wealth transfer scheme.
2. New Development Finance, Bait-and-Switch

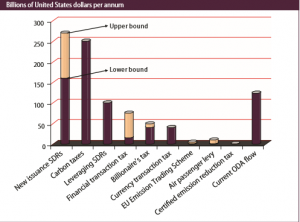
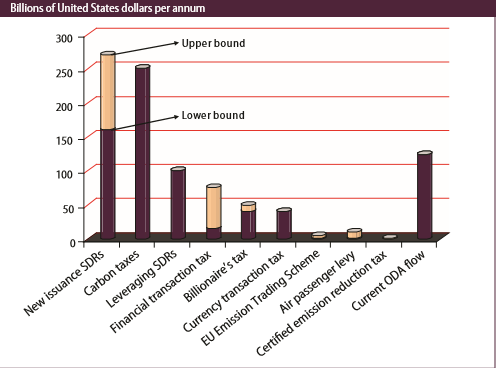
Okay, what are these “revenue sources”?
- SDR (or special drawing rights), from IMF $150B-$270B
- Carbon taxes, $240B
- Leveraging SDR, $90B
- Financial transaction tax, $10B-70B
- Billionaire tax, $90B
- Currency trading tax, $30B
- EU emissions trading scheme, $5B
- Air passenger levy, $10B
- Certified emission reduction tax, $2B
- Current ODA Flow, $120B
If these numbers are accurate, then the US is viewed as a cash cow somewhere to the tune of $627 billion to $807 billion. Yes, this only refers to revenue potential from the United States. I believe this is annually.
What does the report say about SDAs?
These include taxes on financial and currency transactions and on greenhouse gas emissions, as well as the creation of new international liquidity through issuance of special drawing rights (SDRs) by the International Monetary Fund IMF), to be allocated with a bias favouring developing countries or leveraged as development financing. Though their potential may be high, these proposals are subject to political controversy. For instance, many countries are not willing to support international forms of taxation, as these are said to undermine national sovereignty.
No kidding. There is a lot of political opposition to taxes which are deemed to undermine national sovereignty. Could that be because these taxes AREN’T being used to support the well being of the citizenry? Instead the money is being funnelled out of the country in the name of some global good project.
This is how bait-and-switch works:
(1) Raise money using cause A.
(2) Actually spend the money on cause B.
An array of other options with large fundraising potential have been proposed (see figure O.1 and table O.1), but have not been agreed upon internationally thus far. These include taxes on financial and currency transactions and on greenhouse gas emissions, as well as the creation of new international liquidity through issuance of special drawing rights (SDRs) by the International Monetary Fund IMF), to be allocated with a bias favouring developing countries or leveraged as development financing. Though their potential may be high, these proposals are subject to political controversy. For instance, many countries are not willing to support international forms of taxation, as these are said to undermine national sovereignty.
(Page 86) Debt-conversion mechanisms
Debt conversion entails the cancellation by one or more creditors of part of a country’s debt in order to enable the release of funds which would otherwise have been used for debt-servicing, for use instead in social or environmental projects. Where debt is converted at a discount with respect to its face value, only part of the proceeds fund the projects, the remainder reducing the external debt burden, typically as part of a broader debt restructuring.
Debt to developing nations can be “forgiven”, at least partly, if certain conditions are met. However, the obvious question must be asked:
Can nations be loaned money they could never realistically pay back, in order to ensure their compliance in UN or other global agenda, by agreeing to “forgive” part of it?
(Page 86) Debt conversion first emerged, in the guise of debt-for-nature swaps, during the 1980s debt crisis, following an opinion article by Thomas Lovejoy, then Executive Vice-President of the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), in the New York Times in 1984. Lovejoy argued that a developing country’s external debt could be reduced (also providing tax relief to participating creditor banks) in exchange for the country’s taking measures to address environmental challenges. Estimates based on Sheikh (2010) and Buckley, ed. (2011) suggest that between $1.1 billion and $1.5 billion of debt has been exchanged through debt-for-nature swaps since the mid–1980s, although it is not possible to assess how much of this constitutes IDF, for the reasons discussed in box III.1.
If debt can be forgiven in return for environmental measures, then why not simply fund these environmental measures from the beginning? Is it to pressure or coerce otherwise unwilling nations into agreeing with such measures?
(Page 88)
There have been two basic forms of debt-for-nature exchanges (Buckley and Freeland, 2011). In the first, part of a country’s external debt is purchased by an environmental non-governmental organization and offered to the debtor for cancellation in exchange for a commitment to protect a particular area of land. Such transactions occurred mainly in the late 1980s and 1990s and were generally relatively small-scale. An early example was a 1987 deal under which Conservation International, a Washington, D.C.-based environmental non-governmental organization, bought $650,000 of the commercial bank debt of Bolivia (now Plurinational State of Bolivia) in the secondary market for $100,000, and exchanged this for shares in a company established to preserve 3.7 million acres of forest and grassland surrounding the Beni Biosphere Reserve in the north-east part of the country. In the second form, debt is exchanged for local currency (often at a discount), which is then used by local conservation groups or government agencies to fund projects in the debtor country. Swaps of this kind are generally much larger, and have predominated since the 1990s. The largest such swap came in 1991, when a group of bilateral creditors agreed to channel principal and interest payments of $473 million (in local currency) into Poland’s Ecofund set up to finance projects designed to counter environmental deterioration. The EcoFund financed 1,500 programmes between 1992 and 2007, providing grants for conservation projects relating to cross-border air pollution, climate change, biological diversity and the clean-up of the Baltic Sea (Buckley and Freeland, 2011).
We will “forgive” your debt if:
(1) A portion of your land is off limits; or
(2) Debt converted to currency to fund “projects”
The entire document is 178 pages. While a tedious read, it’s worthwhile.
3. UN Wants $400B In Global Taxation

(UN supports global tax to raise $400B)
New York, 5 July 2012 –The United Nations is proposing an international tax, combined with other innovative financing mechanisms, to raise more than $400 billion annually for development and global challenges such as fighting climate change. In its annual report on global development, World Economic and Social Survey 2012: In Search of New Development Finance, (WESS 2012) launched today, the UN says, in the midst of difficult financial times, many donor countries have cut back on development assistance. In 2011, for the first time in many years, aid flows declined in real terms
The survey finds that the financial needs of developing countries have long outstripped the willingness and ability of donors to provide aid. And finding the necessary resources to achieve the Millennium Development Goals and meet other global challenges, such as addressing climate change, will be tough, especially for least developed countries.
The need for additional and more predictable financing has led to a search for new sources not as a substitute for aid, but as a complement to it . A number of innovative initiatives have been launched during the past decade, mainly to fund global health programmes aimed at providing immunizations, AIDS and tuberculosis treatments to millions of people in the developing world. The UN survey finds that while these initiatives have successfully used new methods to channel development financing to combat diseases, they have hardly yielded any additional funding on top of traditional development assistance.
This source explains it straight from the horse’s mouth. The UN is not taking in enough money for its various schemes. In fact, real contributions are shrinking. Therefore it is necessary to come up with new and innovative ways to tax developed nations.
Of course one of the most common ways is with the “climate change” scam. But it is hardly the only one. The UN views many forms of wealth simply as money to tap into.
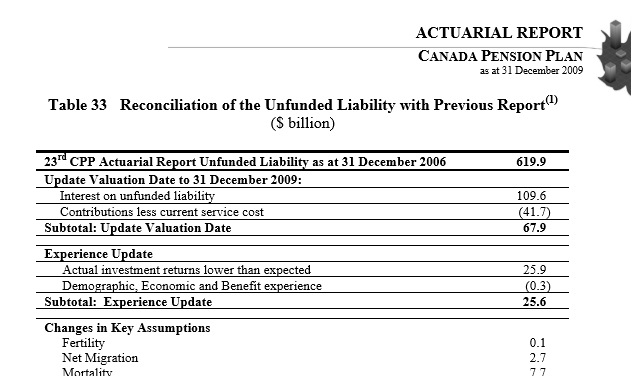
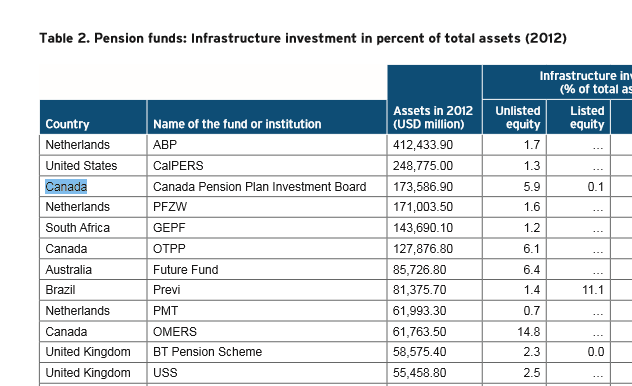
4. UN Eyeing Up African Pensions

(Pensions are also being eyed as a funding source)
(Page 10) III. PENSION FUNDS DIRECT INVESTMENT IN INFRASTRUCTURE
International experience At 36.6 percent of GDP, assets of the pension funds in OECD countries are relatively large. As of end-2013, pension-fund assets were even in excess of 100 percent in countries such as the Netherlands, Iceland, Switzerland, Australia, and the United Kingdom (Figure 1). In absolute terms, pension funds in OECD countries held $10.4 trillion of assets. While large pension funds (LPFs) held about $3.9 trillion of assets, assets in public and private sector and public pension reserves (PPRFs) stood at $6.5 trillion.
(Page 30) C. Policy framework for investment in infrastructure Pension funds—just like other investors, domestic and foreign—need a fair, transparent, clear, and predictable policy framework to invest in infrastructure and other assets. This is important as infrastructure assets have a number of characteristics that increase investors’ perception of risk. First, infrastructure projects typically involve economies of scale and often lead to natural monopolies with high social benefits and, at times, lower private returns. As a result, infrastructure projects may require heavy government involvement. Second, infrastructure projects are often large and long-lived with a significant initial investment but with cash flows that accrue over a long horizon.
In this regard, improving the policy framework for investment can be useful to countries seeking to develop the investor base for infrastructure. For instance, the OECD’s Policy Framework for Investment (PFI) uses self-assessments and/or an external assessment by the OECD to help a country elaborate policies for capacity building and private sector development strategies, and inform the regional dialogue (OECD, 2015b). The PFI’s investment policy refers not only to domestic laws, regulations, and policies relating to investment but also goals and expectations concerning the contribution of investment to sustainable development, such as infrastructure
(Page 31) D. Infrastructure financing instruments available to pension funds Even in well-performing pension systems where the governance, regulation, and supervision of pension funds are conducive to investment in infrastructure and there is a sound policy framework for investment, there is still a need for adequate instruments to channel pension fund assets into the infrastructure sector. Pension funds can use a number of channels to invest in infrastructure. Direct exposure is gained mainly through the unlisted equity instruments (direct investment in projects and infrastructure funds) and project bonds, while indirect exposure is normally associated with listed equity and corporate debt. More specifically, pension funds can rely on a number of options such as
The paper itself is quite long, but here is the gist of it. (See archive). The UN wants to take African pension funds and use them to “invest” it UN type of schemes.
While this seems harmless enough, remember the Paris Accord. The UN thinks nothing of taxing the developed world hundreds of billions of dollars under false pretenses in order to invest in the commodities market. Nor does the UN object to giving “infrastructure loans” to nations that will likely never be able to pay it back.
It should alarm people that an organization with no inherent loyalty to the region would want to use African pension funds to finance its own agenda.
5. UN Environment Programme (UNEP)

(UN Environment Programme)
United Nations Environment Programme – Finance Initiative (UNEP FI) is a partnership between United Nations Environment and the global financial sector created in the wake of the 1992 Earth Summit with a mission to promote sustainable finance. More than 250 financial institutions, including banks, insurers, and investors, work with UN Environment to understand today’s environmental, social and governance challenges, why they matter to finance, and how to actively participate in addressing them.
UNEP FI’s work also includes a strong focus on policy – by facilitating country-level dialogues between finance practitioners, supervisors, regulators and policy-makers, and, at the international level, by promoting financial sector involvement in processes such as the global climate negotiations.
Here are the members of the Global Steering Committee. In short, this is a partnership between the UN and banking sector.
Keep in mind the “New Development Financing” agenda discussed earlier. Money is taken and used to “invest” in 3rd World Development Programs. Countries that are unable to pay back are forced either to give up sovereignty, or comply with other arrangements.
Banks are in the business of making money. Alternatively, they are in the business of acquiring assets which can be converted into money, or otherwise make them money. What if this banking alliance has no altruistic roots, and is meant to be predatory?
Uppity Peasants has an interesting take on the UNEP.
Make no mistake, this is exactly what happens to these people, by the way. One cross-country comparison between microloan recipients in Bangladesh and payday loan recipients in Canada found that both ‘products’ tend to attract the same kinds of people to them from very similar backgrounds, for largely the same reasons — i.e., neither group tends to use these loans for re-investment, such as starting a business; rather, they use them to cover day-to-day expenses at exorbitant interest rates, thus entrapping themselves in a cycle of never ending debt (Islam & Simpson, 2018). If you know how bad the consequences of payday lending can be for people in the first world, imagine how bad it is for someone who’s already living in third world-levels of poverty.
Now, part of the reason why the UNEP, of all possible agencies, is so heavily invested (emotionally and literally) into fintech and other start-up technologies is because many of the “incumbent banks” — the top-players of our current system — don’t think that completely up-ending the global financial system to move the focus away from profits and toward complying with heavy-handed, UN-decided environmental regulations is a particularly attractive road to go down. In the next excerpt, the UNEP openly admit that start-ups in this area are better to invest in for the pursuit of ‘change’, specifically because their owners tend to be new to the world of business and, as such, don’t know enough about what they’re doing to avoid being manipulated — and that’s where the UNEP comes in.
Uppity Peasants argues that the UNEP is driven much more on a business model than on any kind altruistic path. Further, the circumstances which the aid recipients require the resources to cover essential expenses means they are unable to invest anything. This is similar to a payday loan type of system.
6. Green Finance For 3rd World $5-7 Trillion

(Green finance for developing countries)
(Page 13)In 2015, governments adopted three major agreements that set out their vision for the coming decades: a new set of 17 sustainable development goals (SDGs), the Paris Agreement on climate change and the ‘financing for development’ package. Finance is central to realizing all three agreements – and these now need to be translated into practical steps suited to each country’s circumstances.
Sustainable Energy for All estimates that annual global investments in energy will need to scale up from roughly US$400 billion at present to US $1-1.25 trillion. Of that, US$40-100 billion annually is needed to achieve universal access to electricity. Overall, US $5-7 trillion a year is needed to implement the SDGs globally. Developing countries are estimated to face an annual investment gap of US$2.5 trillion in areas such as infrastructure, clean energy, water and sanitation, and agriculture.
(Page 14) The challenge for financial systems is twofold: to mobilize finance for specific sustainable development priorities and to mainstream sustainable development factors across financial decision-making.
Capital needs to be mobilized for inclusion of underserved groups (e.g. small and medium enterprises), raising capital for sustainable infrastructure (e.g. energy, housing, transport, urban design) and financing critical areas of innovation (e.g. agriculture, mobility, power).
Sustainability needs to become mainstream for financial institutions. This starts with ensuring market integrity (e.g. tax, corruption, human rights) and extends to integrating environmental and social (E&S) factors into risk management (e.g. climate disruption, water stress). Sustainability also needs to be incorporated into the responsibilities and reporting of market actors to guide their decision-making. Momentum is building to align financial systems with the financing needs of an inclusive, sustainable economy. This is complementary to ‘real economy’ actions such as environmental regulations, reform of perverse subsidies and changes to resource pricing. However, while these are critical, it is increasingly recognized that changes are also needed in the financial system to ensure that it is both more stable and more connected to the real economy.
Some interesting points here:
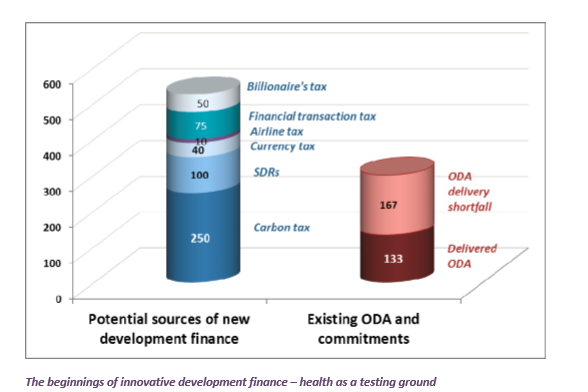
- $5 to $7 trillion (yes trillion) needed annually fulfill these goals. The billions stated before was lowballed.
- The “sustainability” agenda needs mass marketing.
- Finance needed for:
- 17 goals of Agenda 2030
- Paris Climate Accord
- Finance for development
- 3 above items to be integral part of national agendas.
- Most of this has nothing to do with the environment
In fact, it reads like a global version of the US Green New Deal, proposed by Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez. In fact, her Chief of Staff, Saikat Chakrabarti, admitted it was about changing the economy, not the environment.
7. International Chamber Of Commerce

(International Chamber of Commerce)
THE INTERNATIONAL CHAMBER OF COMMERCE ICC is the world’s largest business organization with a network of over 6 million members in more than 130 countries. We work to promote international trade, responsible business conduct and a global approach to regulation through a unique mix of advocacy and standard setting activities—together with market-leading dispute resolution services. Our members include many of the world’s largest companies, SMEs, business associations and local chambers of commerce.
.
We are the world business organization.
That quote came from their policy guide. Pretty straightforward. They want to run business on a global level. Now, let’s get to the meat and potatoes, the tax proposals:
Interplay between tax policy making and economic growth The world’s population is predicted to increase by 2 billion people by 2050, and the population of the world’s least developed countries is projected to double by 2053, in some countries even tripling. By 2025 half of the world’s population will be living in water-stressed areas. Under such circumstances, the need for large-scale investment in economic growth and development becomes evident.
Whilst there is no panacea, it is evident that greater alignment of investment and tax policies would be essential in promoting investment, job creation and economic growth. International commerce remains a powerful mechanism to help lift people out of poverty. Tax is intrinsically linked to development as taxation provides the revenue that states need to mobilize resources and reinforce a country’s infrastructure. Taxation “provides a predictable and stable flow of revenue to finance public spending, and shapes the environment in which investment, employment and trade takes place.”
Further, it is important to have a fair, efficient, and effective revenue collection infrastructure to promote economic and social development. Domestic resource mobilization (DRM) has been proposed as a way to meet the SDGs with the development finance already available. However, DRM can be impeded by unclear and confusing tax systems. It is imperative that companies are able to move products and services into areas where they are most needed without unnecessary administrative impediments.
Having a reliable and consistent taxation policy seems reasonable enough. However, the ICC is not being clear on the reason behind the push. They want better taxation methods in order to INCREASE the amount of revenue available.
Governments often side with these groups, even when it is not in the best interests of the citizens themselves. “Investment” dollars are then shovelled into infrastructure projects.
Tax the people, so that the money can be “properly” spent, as the UN and their partners see fit.
8. Addis Ababa Action Agenda

(Addis Ababa Action Agenda)
(Page 10) DOMESTIC PUBLIC RESOURCE
For all countries, public policies and the mobilization and effective use of domestic resources, underscored by the principle of national ownership, are central to our common pursuit of sustainable development, including achieving the sustainable development goals. Building on the considerable achievements in many countries since Monterrey, we remain committed to further strengthening the mobilization and effective use of domestic resources
(Page 10) 22. We recognize that significant additional domestic public resources, supplemented by international assistance as appropriate, will be critical to realizing sustainable development and achieving the sustainable development goals. We commit to enhancing revenue administration through modernized, progressive tax systems, improved tax policy and more efficient tax collection. We will work to improve the fairness, transparency, efficiency and effectiveness of our tax systems, including by broadening the tax base and continuing efforts to integrate the informal sector into the formal economy in line with country circumstances.
23. We will redouble efforts to substantially reduce illicit financial flows by 2030, with a view to eventually eliminating them, including by combating tax evasion and corruption through strengthened national regulation and increased international cooperation. We will also reduce opportunities for tax avoidance, and consider inserting anti-abuse clauses in all tax treaties. We will enhance disclosure practices and transparency in both source and destination countries, including by seeking to ensure transparency in all financial transactions between Governments and companies to relevant tax authorities. We will make sure that all companies, including multinationals, pay taxes to the Governments of countries where economic activity occurs and value is created, in accordance with national and international laws and policies
(Page 13) 27. We commit to scaling up international tax cooperation. We encourage countries, in accordance with their national capacities and circumstances, to work together to strengthen transparency and adopt appropriate policies, including multinational enterprises reporting country-by-country to tax authorities where they operate; access to beneficial ownership information for competent authorities; and progressively advancing towards automatic exchange of tax information among tax authorities as appropriate, with assistance to developing countries, especially the least developed, as needed. Tax incentives can be an appropriate policy tool. However, to end harmful tax practices, countries can engage in voluntary discussions on tax incentives in regional and international forums.
(Page 45) 98. We affirm the importance of debt restructurings being timely, orderly, effective, fair and negotiated in good faith. We believe that a workout from a sovereign debt crisis should aim to restore public debt sustainability, while preserving access to financing resources under favourable conditions. We further acknowledge that successful debt restructurings enhance the ability of countries to achieve sustainable development and the sustainable development goals. We continue to be concerned with non-cooperative creditors who have demonstrated their ability to disrupt timely completion of the debt restructurings.
In no way does this cover the entire document. However, there are 3 themes which get repeated over and over again.
- Efficient tax collection
- Global tax regulations and data sharing
- “Sustainable” debt and borrowing
There is very little in this document, about actually improving lives, improving infrastructure, or improving the environment. Instead, it is all about implementing a global taxation system, while eliminating “off the books”, or illicit cash.
9. Global Tax Avoidance Measures
(Global tax avoidance measures)
Exchange of information for tax purposes
Exchange of information has long been included as a feature of tax treaty models. By agreeing to exchange information with respect to taxpayers, countries can become more aware of the global activities taxpayers are engaging in and impose tax that should be due.
The upcoming 2017 revision of the United Nations Model Double Taxation Convention between Developed and Developing countries is expected to bring a new revised version of the exchange of information provision, following the approval of the new United Nations Code of Conduct. The Committee agreed in 2016 to a proposal for a United Nations Code of Conduct on Cooperation in Combating International Tax Evasion. This Code supports the automatic exchange of information for tax purposes as the way forward for countries generally, but recognizes that it is vital for developing countries to exchange information, even if they are not ready for automatic exchange. The Code of Conduct has been approved by the Committee of Experts in 2016, and set automatic exchange of information as the new universal standard after ECOSOC adopted the Code of Conduct in a Resolution in 2017, during the ECOSOC Special Meeting on International Cooperation on Tax Matters. .Furthermore, the OECD model convention and commentaries is expected to broaden the scope of the exchange of information article to allow triangular, or multi-party exchange of information requests.
While this certainly sounds like some well meaning way to prevent money laundering and tax fraud, there is another angle to look at.
Having a global (or at least more centralized) database of people and their taxable income will allow for more efficient and effective tax collection. This is especially true whenever a new “development project” needs funding.
Furthermore, if there is such a global system, it will be easier to determine who isn’t paying “their fair share” when it comes to contributions. Those national governments can then act accordingly. Also, who doesn’t view this as becoming a global version of Revenue Canada, or the American IRS?
10. From Billions To Trillions (SF 2.0)

(Why stop at just billions?)
Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) will require an enormous increase in external financing flows to developing countries. Development Finance Institutions (DFIs) have gradually started to shift their business model towards de-risking services to crowd in long-term, low-risk private capital. However, the targeted scaling up of private investment from billions to trillions to realise the SDGs contains massive risks for stability. And good macro-policies are needed, in turn, to address such underlying risks. Countries that need the greatest amount of development finance are often those that have domestic financial resource constraints and underdeveloped markets. Financing their growth and investment opportunities makes the management of exchange rate risks, which are inherent in development finance, a critical challenge.
Merely supplying development finance is not enough. It needs to be done in socially and economically sustainable ways, where risks are allocated to those who can best manage and sustain them. Efficient use of limited public resources, through improved policies and regulatory processes, is required to achieve the SDGs and related efforts. Governments around the world must work together to offer feasible business opportunities to the private sector that are in line with domestic and international development objectives. Only with such coordinated action will we succeed in moving from billions to trillions to realise sustainable progress for all.
This article should serve as a warning to anyone who thinks that this global development system is going to be steady. Wrong. Once considered “fully operational”, the next step is to upscale it, and make it far bigger.
It is not governments who will be paying for these globalist schemes. It is the working class tax-payers who will see more and more of their wealth transferred to these projects.
Of course, once your money leaves Canadian soil, there is little to no accountability or control over what happens to it. But that it routinely downplayed.
11. What To Make From All This?
To state the obvious: these agendas and agreements are bringing nations towards a global taxation model. Countries (presumably under UN control) will be expected to share data on tax paying citizens and other people earning money. While this is touted as an anti-tax avoidance measure, the real goal is making sure the global order accounts for all money and where it goes.
Going towards a “cashless society” also helps in that regard. Hence the push for more and more electronic options, while making cash payments more difficult.
Beyond enforcement, knowing which nations have money and how much will make it easier to determine who shall pay how much as their “fair share” of future projects. We won’t have nations in the traditional sense, just shareholders.
International agreements like the Paris Accord have nothing to do with the environment. That is just the sales pitch. Instead, it an excuse to funnel huge sums of money to the UN to finance their business model. It is taking advantage of an altruistic goal.
This is about having a globalist, centralized economy and taxation. The environmental and humanitarian claims are just talking points.
(1) https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/policy/wess/wess_current/2012wess.pdf
(2) 2012.new.development.finance
(3) https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/policy/wess/wess_current/2012wesspr_en.pdf
(4) 2012, Call To Raise $400 Billion
(5) https://www.fsmgov.org/paris.pdf
(6) https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/2051AAAA_Outcome.pdf
(7) Addis Ababa Action Agenda
(8) https://iccwbo.org/publication/tax-united-nations-sustainable-development-goals/
(9) https://iccwbo.org/content/uploads/sites/3/2018/02/icc-position-paper-on-tax-and-the-un-sdgs.pdf
(10) http://unepinquiry.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/Green_Finance_for_Developing_Countries.pdf
(11) Green_Finance_for_Developing_Countries
(12) https://developmentfinance.un.org/international-efforts-combat-tax-avoidance-and-evasion
(13) https://www.un.org/en/africa/osaa/pdf/pubs/2017pensionfunds.pdf
(14) https://www.un.org/pga/72/wp-content/uploads/sites/51/2018/05/Financing-for-SDGs-29-May.pdf
(15) Financing-for-SDGs-29-May
(16) https://mnetax.com/un-releases-updated-model-tax-treaty-adding-new-technical-service-fees-article-27765
(17) “https://oecd-development-matters.org/2018/07/31/development-finance-2-0-from-billions-to-trillions/
(18) https://developmentfinance.un.org/sites/developmentfinance.un.org/files/FSDR2019_ChptII.pdf
(19) Financing for Sustainable Development 2019
(20) https://www.unepfi.org/about/
(21) https://www.uncdf.org/
(22) https://oim.unjspf.org/
(23) https://www.unfcu.org/home/
(24) https://uppitypeasants.home.blog/2019/08/10/fintech-for-sustainable-development-assessing-the-implications/
(25) https://canucklaw.ca/guest-post-sunrise-movement-and-the-green-new-deal/
Like this:
Like Loading...